What is a water treatment machine for dialysis? Why is reverse osmosis water used in dialysis?
Dialysis is a key technology in modern medicine to save the lives of patients with renal failure, and the success and safety of dialysis cannot be separated from the strict control of water quality. The water used in the dialysis process must reach an extremely high degree of purity to ensure the safety of patients. To this end, medical institutions generally use special water treatment equipment to prepare dialysis water, and the reverse osmosis system plays a vital role in this.
So, what is a water treatment machine for dialysis? Why must reverse osmosis water be used in dialysis? This article will explore these issues in depth.
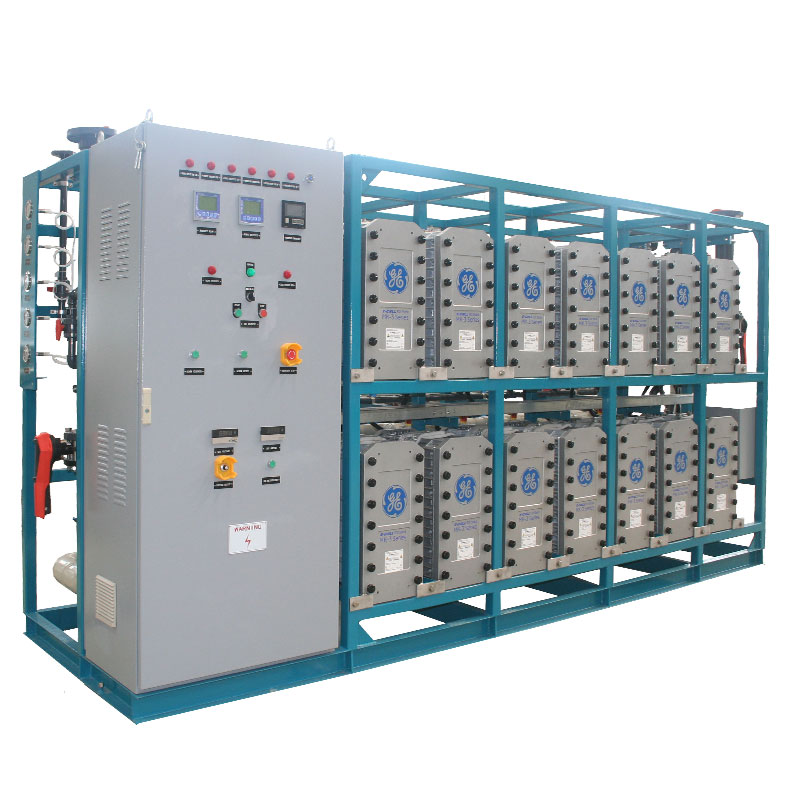

What is a water treatment machine for dialysis?
A water treatment machine for dialysis refers to a high-purity water treatment system used to prepare dialysis fluid. Dialysis fluid is a key medium for removing metabolic waste and excess electrolytes from the patient's body, and the water in the dialysis fluid must be highly pure to avoid infection or other complications. The main function of the water treatment machine is to treat tap water into high-purity water (i.e. dialysis water) that meets dialysis requirements to ensure the safety and effectiveness of dialysis.
The purity standard for dialysis water is extremely strict. According to the medical standards of different countries, such as the United States Pharmacopoeia (USP), the European Pharmacopoeia (EP) and the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (ChP), the bacterial content, conductivity, total organic carbon (TOC) and endotoxin level of dialysis water are strictly limited. For example, the bacterial content in water is usually required to be no more than 100 CFU/mL, and the endotoxin content is no more than 0.25 EU/mL. The strict control of these indicators is to prevent impurities in the water from causing potential harm to patients.
Components of dialysis water treatment machine
The dialysis water treatment machine usually consists of multiple treatment units to gradually remove suspended matter, soluble salts, organic matter and microorganisms in the water. These units include:
● Pretreatment system: including sand filter, activated carbon filter and softener, etc., used to remove large suspended particles, residual chlorine, organic matter and hardness ions in water, and protect subsequent treatment equipment.
● Reverse osmosis system (RO system): core component, used to remove soluble salts, heavy metals, organic matter and microorganisms in water, etc., which is a key step in preparing high-purity water.
● Ultrapure water system: In some cases, ultrafiltration, deionization exchange, etc. are used to further remove ions and microorganisms in the water to ensure that the purity of the water reaches the ultimate level.
● Disinfection system: Ultraviolet disinfection or ozone disinfection system is used to control the level of microorganisms in the water and prevent secondary contamination.
These treatment units work together to ensure that dialysis water meets or even exceeds medical standards and ensures the safety of dialysis treatment.
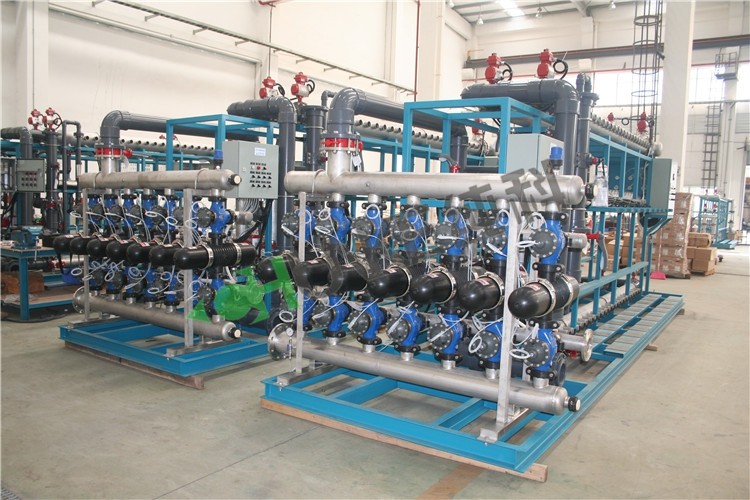

What is the core role of the reverse osmosis system in dialysis water treatment?
The reverse osmosis system (RO) is the core part of the dialysis water treatment machine. Its main function is to remove most of the soluble salts, heavy metals, microorganisms and organic matter in the water through semipermeable membrane technology, so that the purity of the output water is extremely high. Reverse osmosis technology is widely used in the preparation of dialysis water due to its high efficiency and reliability.
Reverse osmosis is a method of purifying water by applying high pressure to make water molecules pass through a semipermeable membrane, while larger molecules such as soluble salts, organic matter and microorganisms are blocked on the other side of the membrane. Specifically, when water flows through the reverse osmosis membrane, water molecules can pass through the membrane freely, while most ions, particles and other contaminants cannot pass through and are concentrated on the wastewater side. This process effectively removes most impurities in the water, making the purity of dialysis water meet medical standards.
Key parameters of reverse osmosis system
In the dialysis water treatment machine, the performance of the reverse osmosis system directly determines the quality of the final effluent. Key parameters include:
● Recovery rate: the ratio of pure water to raw water. Dialysis water usually requires a higher purity, so the recovery rate is lower to ensure sufficient impurity removal.
● Desalination rate: the efficiency of the reverse osmosis membrane in removing soluble salts in water. Dialysis water usually requires a desalination rate of more than 99% to ensure that the conductivity of the effluent meets the standard.
● Water output: the processing capacity of the reverse osmosis system, usually calculated in liters/hour (L/h) or cubic meters/hour (m³/h). Dialysis centers choose the appropriate water output based on the number of patients and the number of dialysis machines to meet treatment needs.
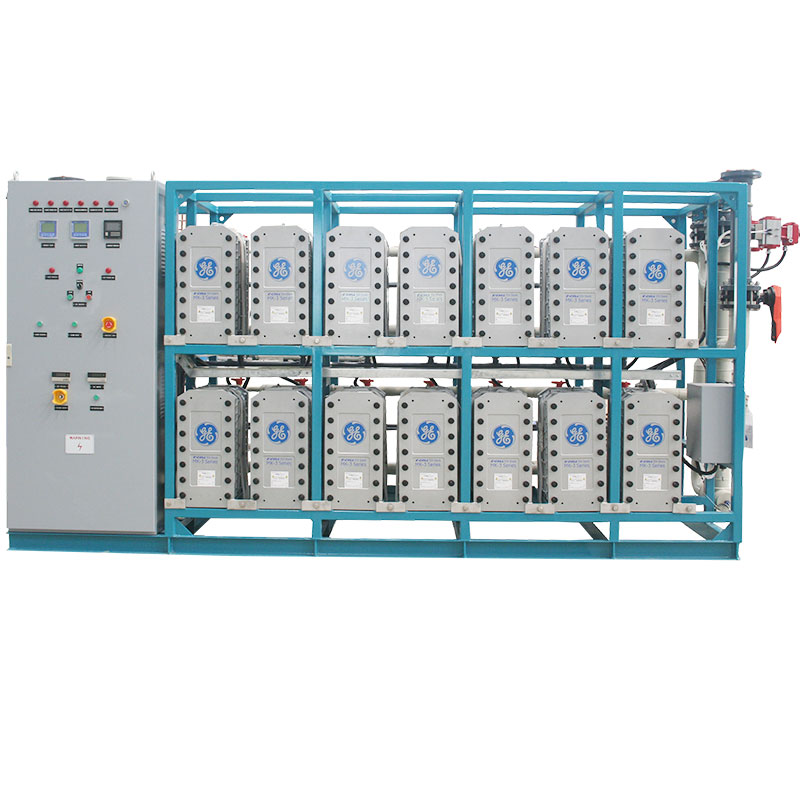

Why is reverse osmosis water used in dialysis?
Dialysis patients usually have renal failure, and their bodies cannot effectively eliminate metabolic waste and excess electrolytes. Therefore, the purity of the dialysate directly affects the treatment effect and the health of the patient. If the dissolved salts, heavy metals, organic matter or microorganisms in the dialysis water exceed the standard, it may lead to a variety of complications, such as dialysis-related hypotension, allergic reactions and even infections. Therefore, the high purity of reverse osmosis water is essential to avoid these risks.
Secondly, the preparation of dialysis fluid usually requires precise control of the electrolyte concentration in it to simulate the normal blood composition of the human body, help patients remove metabolic waste and regulate water and electrolyte balance in the body. The low conductivity and high purity of reverse osmosis water ensure accuracy during the preparation process and avoid formulation errors caused by water quality problems.
Reverse osmosis water is not only critical to patient safety, but also effectively protects dialysis equipment. If the dissolved salts and other impurities in the water are not effectively removed, they may form scale or corrosion in the dialysis equipment, affecting the operating efficiency and life of the equipment. Using reverse osmosis water can significantly reduce the frequency of equipment maintenance, reduce the failure rate, and improve the long-term reliability of the equipment.
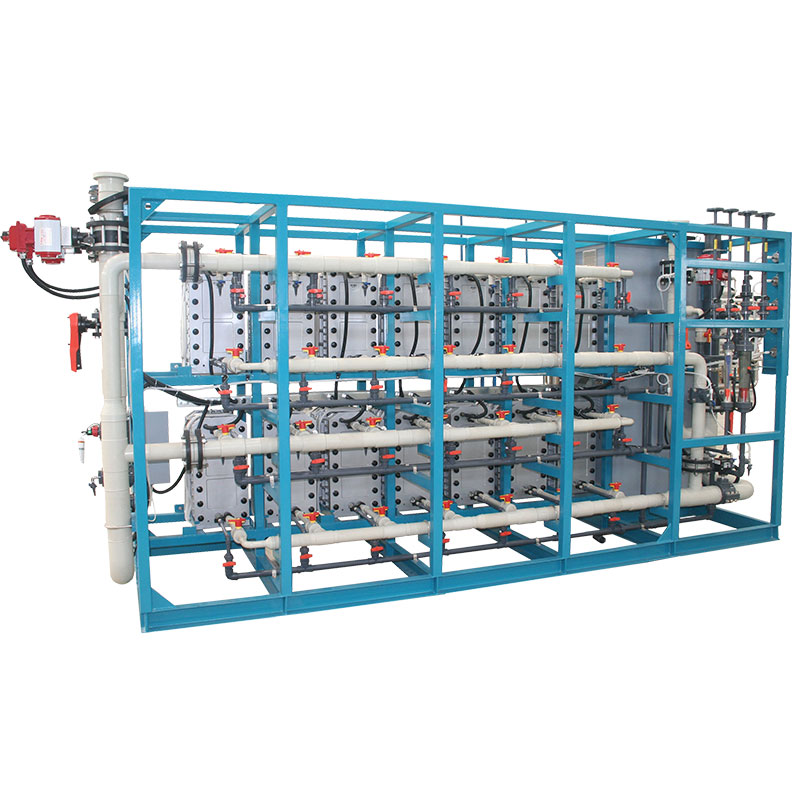

How to maintain and manage reverse osmosis water treatment machines?
Although the reverse osmosis water treatment machine can provide high-purity dialysis water, its performance and water quality depend on regular maintenance and proper management of the equipment. The reverse osmosis membrane is the core component of the system, but as the use time increases, impurities may accumulate or biofilm may form on the membrane surface, resulting in a decrease in desalination rate. Regular chemical cleaning and physical flushing can extend the service life of the membrane. Generally speaking, the life of the reverse osmosis membrane is 2-3 years, but the specific replacement cycle depends on the usage and water quality.
In order to ensure the continuous and efficient operation of the reverse osmosis system, medical institutions usually install online monitoring equipment to monitor water parameters such as conductivity, pressure and flow in real time. Once an abnormality is found, such as an increase in conductivity or a decrease in pressure, the system will automatically alarm to remind the operator to check and deal with the problem in time. In addition, pretreatment systems such as activated carbon filters and softener resins need to be replaced or regenerated regularly to maintain good water quality. The effect of pretreatment directly affects the working state of the reverse osmosis membrane, so the maintenance of the pretreatment unit is crucial.