How Does Electrodeionization Work?
As the demand for water quality safety and purification technology continues to increase, electrodeionization (EDI) technology has attracted much attention as an efficient water treatment method. So, how does electrodeionization work?
Electrodeionization (EDI) is a technology that uses electric fields to remove ions from water. Its main function is to remove ions from water by applying electric current, thereby purifying water. Specifically, when water enters the EDI system and an electric current is applied, the cations and anions in the water are attracted to the corresponding electrodes and are thereby removed. This process does not require chemical reagents and can effectively purify water sources and provide high-quality water. It is commonly used to purify reverse osmosis (RO) permeate to produce high-purity water.
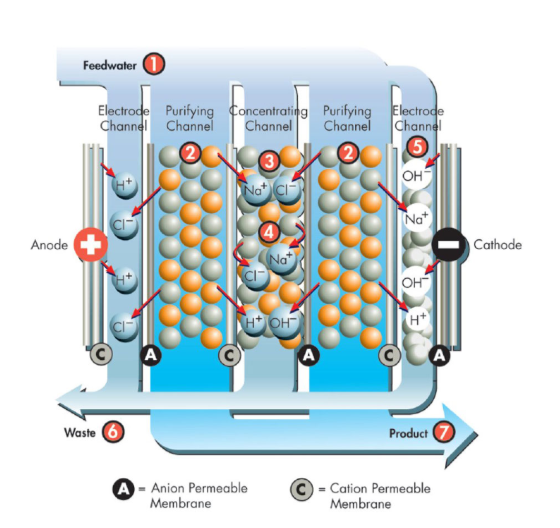
Electrodeionization workflow:
The EDI system consists of a series of anodes and cathodes, with ion exchange membranes between them. When water entering the EDI system passes through these electrodes, an electric current is applied. This current causes ions in the water to be attracted to the corresponding polarity electrodes. In this process, cations are attracted to the cathode and anions are attracted to the anode.
In an EDI system, there are also spaces called dilution chambers. In the dilution chamber, most of the ions are adsorbed and removed, and pure water is delivered to the output of the system. In this way, by continuously applying electric current, the EDI system can continuously remove ions from the water, thereby producing high-purity water.
Then, when an electric current passes through the solid resin particle layer, the ions on these particles are attracted to the opposite electrode, thereby achieving the separation and removal of cations and anions.
In this way, most of the ions in the permeate water will be captured and removed, causing the ion concentration in the outlet water to be significantly reduced.
Key to this process is the application of an electrical current, which imparts an electric charge to the layer of solid resin particles, thereby attracting and removing ions from the permeating water. Compared with traditional ion exchange technology, this method does not require the use of chemical regenerants, is more environmentally friendly, and has lower operating costs.
Therefore, electrodeionization technology provides a continuous and stable purification method for RO systems by efficiently removing ions from permeated water, and provides reliable water treatment solutions for various industrial and commercial applications.

How to optimize the operating efficiency of EDI technology?
Clean and maintain EDI equipment regularly to keep the equipment in normal operation. According to water quality and treatment needs, the operating parameters of EDI equipment are reasonably adjusted to improve treatment efficiency and water quality stability. Regularly monitor the operation of the EDI system, detect problems in time and deal with them to ensure the stable operation of the equipment. Keep abreast of new technologies and equipment, update and upgrade EDI systems, and improve treatment efficiency and water quality.
What are the applications of EDI technology in water treatment?
Electrodeionization technology is widely used in high-tech manufacturing fields such as electronics, semiconductors, and photovoltaics. These industries have extremely high requirements for water quality and need to remove trace ions and impurities in the water to ensure the stability of the production process and the quality of the product.
Secondly, electrodeionization technology is also widely used in pharmaceutical, biotechnology and laboratory fields. These industries require high-purity water sources for pharmaceuticals and experiments, and electrodeionization technology can provide stable high-purity water sources to meet their special water quality requirements.
In addition, electrodeionization technology is also used in industrial fields such as power generation, chemical industry, and automobile manufacturing, as well as in commercial places such as hotels, hospitals, and schools, to provide safe and stable water sources for these fields.

How is EDI technology different from traditional ion exchange technology?
First, traditional ion exchange technology requires the use of chemical regenerants, such as salt solutions or acid-base solutions, to periodically regenerate the exchange resin to restore its ability to remove ions. Electrodeionization technology does not require the use of these chemicals, reducing environmental pollution and safety risks to operators.
Secondly, traditional ion exchange technology produces a large amount of wastewater and chemical waste during the regeneration process, which requires treatment and disposal, increasing operating and treatment costs. Electrodeionization technology does not produce wastewater and chemical waste, has lower operating costs and is more environmentally friendly.
In addition, traditional ion exchange technology requires regular replacement and regeneration of the exchange resin, while the solid resin particle layer of electrodeionization technology can be used continuously under normal operating conditions without frequent replacement, reducing maintenance and downtime.
To sum up, compared with traditional ion exchange technology, electrodeionization technology has higher environmental protection, lower operating costs and less maintenance requirements, so it is increasingly widely used in the field of water treatment.