How does the electrolyzed water treatment system work?
As people's requirements for water quality continue to increase, various water treatment technologies have emerged. Among them, electrolyzed water technology has attracted much attention due to its unique treatment effect and wide application prospects.
So, what is electrolyzed water? How does the electrolyzed water treatment system work? This article will analyze this modern water treatment technology in detail for you.
What is electrolyzed water?
Electrolyzed water, also known as electrolyzed reduced water, is the decomposition of ordinary tap water into two types of water containing different ions, namely acidic water and alkaline water, through electrolysis. Electrolyzed water has many unique properties, such as sterilization, disinfection, degreasing, etc., and has therefore been widely used in the fields of home, medical care, agriculture, food processing, etc.
What are the classifications of electrolyzed water?
According to the use and properties after electrolysis, electrolyzed water is mainly divided into: acidic electrolyzed water, alkaline electrolyzed water and neutral electrolyzed water.
1. Acidic electrolyzed water: Water rich in chloride ions and oxides produced during the electrolysis process is usually acidic and has strong bactericidal and disinfecting effects.
2. Alkaline electrolyzed water: Water rich in hydrogen ions and reduced products produced during the electrolysis process is usually alkaline and has strong degreasing and cleaning effects.
3. Neutral electrolyzed water: Water produced by a specific electrolysis process is neither obviously acidic nor obviously alkaline, and has mild bactericidal and cleaning effects.

What is the working principle of the electrolysis water treatment system?
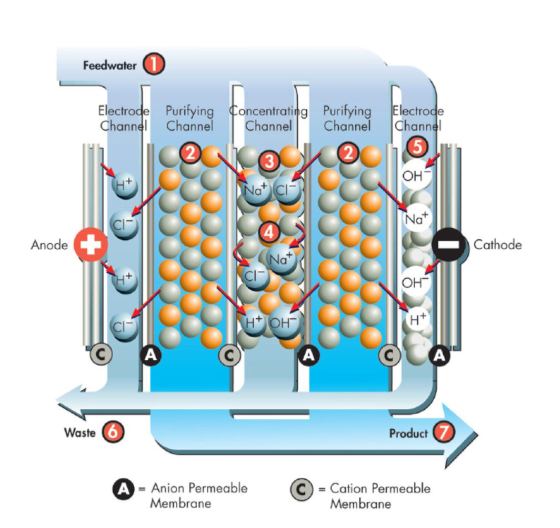
The electrolysis water treatment system is mainly composed of an electrolytic cell, an electrode, a diaphragm, a water supply device, and a control system. Its working principle is based on the electrochemical reaction of an electrolyte solution under the action of an electric field.
1. Electrolyzer:
The electrolytic cell is the core component of the electrolysis water treatment system, which is used to accommodate the water to be electrolyzed and the electrode. The electrolytic cell is usually made of corrosion-resistant materials to ensure that it is not damaged during the electrolysis process.
2. Electrode:
Electrode is a key component in the electrolyzer, usually made of inert metal materials such as platinum and titanium. The electrode is divided into an anode and a cathode, which are connected to the positive and negative poles of a DC power supply respectively. During the electrolysis process, oxidation and reduction reactions occur at the anode and cathode respectively, thereby decomposing water into electrolyzed water of different properties.
3. Diaphragm:
The diaphragm is used to separate the electrolyzer into two areas to prevent the different ions produced by the anode and cathode from mixing with each other. Commonly used diaphragm materials include ion exchange membranes and microporous membranes, which allow specific ions to pass through while preventing the diffusion of other ions.
4. Water supply device:
The water supply device is used to provide source water to the electrolyzer, usually including a water pump, a filter and a regulating valve. The filter is used to remove suspended matter and impurities in the source water to ensure the stability of the electrolysis process and the purity of the electrolyzed water.
5. Control system:
The control system is used to adjust parameters such as current, voltage and water flow in the electrolyzer to achieve automation and precise control of the electrolysis process. Modern electrolytic water treatment systems are usually equipped with microprocessors and sensors, which can monitor and adjust electrolysis conditions in real time to obtain the best treatment effect.

What is the working process of the electrolytic water treatment system?
The working process of the electrolytic water treatment system is mainly divided into 4 steps: water supply and pretreatment → electrolysis reaction → separation and collection → post-treatment and application.
1. Water supply and pretreatment:
Before the source water enters the electrolytic cell through the water supply device, it is first filtered and purified by the pretreatment system. The pretreatment system usually includes mechanical filters, activated carbon filters and softeners to remove suspended matter, organic matter and hardness ions in the water.
2. Electrolysis reaction:
The pretreated water enters the electrolytic cell and undergoes electrolysis reaction under the action of the electric field. The following reactions occur at the anode and cathode respectively:
● Anode reaction (oxidation reaction): 2H2O→O2+4H++4e−
● Cathode reaction (reduction reaction): 4H2O+4e−→2H2+4OH−
Through the electrolysis reaction, water is decomposed into hydrogen, oxygen, hydroxide ions and hydrogen ions to form acidic water and alkaline water.
3. Separation and collection:
The diaphragm in the electrolyzer separates the acidic water and alkaline water, which flow out from different outlets. The acidic water and alkaline water are collected in storage tanks for different purposes.
4. Post-treatment and application:
Electrolyzed water can be post-treated as needed, such as adjusting the pH value, removing gases, etc. The treated electrolyzed water can be used in a variety of applications, such as disinfection, cleaning and decontamination, agricultural irrigation and food processing.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of the electrolysis water treatment system?
Advantages of the electrolysis water treatment system: efficient sterilization, environmental protection and safety, and wide application.
1. High efficiency sterilization: The active oxides and hydroxide ions in electrolyzed water have strong sterilization ability and can effectively remove bacteria, viruses and fungi in water.
2. Environmental protection and safety: The electrolysis water treatment process does not require the addition of chemical agents, does not produce harmful by-products, and is environmentally friendly.
3. Wide application: Electrolyzed water can be used in many fields, such as household drinking water, medical and health care, agricultural irrigation and food processing.
Disadvantages of electrolysis water treatment system: high equipment cost, high energy consumption and high water quality requirements.
1. High equipment cost: The electrolysis water treatment system requires the use of corrosion-resistant materials and high-efficiency electrodes, and the equipment cost is high.
2. High energy consumption: The electrolysis water treatment process consumes a lot of electricity and has high operating costs.
3. High water quality requirements: Impurities and hardness ions in the source water will affect the electrolysis effect and need to be pretreated.
Conclusion on the electrolysis water treatment system
As a new type of water treatment technology, electrolysis water has the advantages of high efficiency sterilization, environmental protection and safety, and wide application. However, its equipment cost and operating energy consumption are high, and strict pretreatment of source water is required. Through the detailed introduction of electrolyzed water and electrolyzed water treatment system, I believe readers have a deeper understanding of this modern water treatment technology. When selecting and using the electrolyzed water treatment system, its advantages and disadvantages should be comprehensively considered according to the specific water quality and usage requirements to achieve the best water treatment effect.