How does a desalination plant work?
A desalination plant is a facility that converts seawater into drinkable fresh water. In many areas where water resources are scarce, desalination has become a key technology to solve the problem of drinking water shortage. Although desalination is a complex and resource-intensive process, it has become an important source of water supply for many coastal cities.
This article will introduce the working principle, main process flow and technical equipment of the desalination plant in detail to help readers better understand this process.
What is the basic principle of a desalination plant?
The basic principle of desalination is to remove salt and other impurities from seawater through physical or chemical methods to obtain fresh water that meets drinking water standards. The core of this process is to separate the solutes (mainly salts) dissolved in seawater while retaining water molecules. Common desalination methods include reverse osmosis (RO) and multi-stage flash evaporation (MSF), each of which has its own unique advantages and application scenarios.
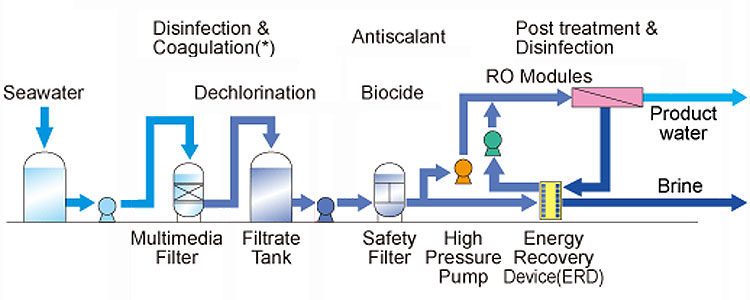
What is the main process flow of a desalination plant?
The process flow of a desalination plant is usually divided into 5 steps:
1. Seawater intake
2. Pretreatment
3. Core desalination process
4. Post-treatment
5. Concentrate discharge
Seawater intake
Seawater intake is the first step in a desalination plant, and seawater is usually pumped from the ocean through coastal intakes. The design of the intake needs to take into account the impact of marine life and suspended matter, so it is usually equipped with a filter to block larger impurities and marine life from entering the intake system. In addition, in order to reduce the impact on the environment, the location and depth of the intake must also be scientifically planned.
Pretreatment
The pretreatment step is to remove suspended solids, organic matter and other substances in the seawater that may damage subsequent desalination equipment. Pretreatment usually uses methods such as physical filtration, chemical flocculation and sedimentation. Physical filtration uses sand filters or microfilters to remove larger suspended particles, while chemical flocculation uses chemicals to aggregate small particles into larger flocs, which facilitates subsequent sedimentation and filtration.
Another important step in the pretreatment process is to prevent the growth of microorganisms and algae in the seawater, which will affect the desalination effect and may clog the equipment. Common prevention methods are to add biocides or use ultraviolet disinfection devices.
Core desalination process
The core process of seawater desalination can be achieved by different technologies, mainly including the following two: reverse osmosis (RO) vs. multi-stage flash evaporation (MSF).
Reverse osmosis (RO): Reverse osmosis is currently the most common seawater desalination technology. This technology uses the characteristics of semi-permeable membranes to separate water molecules from salt in seawater through high pressure. The specific process is as follows:
● Under the action of a high-pressure pump, the pre-treated seawater is pressurized through the reverse osmosis membrane.
● The reverse osmosis membrane only allows water molecules to pass through, while most of the salt and other impurities are trapped on one side of the membrane, forming a highly concentrated brine (concentrated water).
● The water that passes through the membrane is fresh water and can be further treated to meet drinking water standards.

Multi-stage flash evaporation (MSF): Multi-stage flash evaporation is a thermodynamic process that rapidly evaporates seawater in multiple stages by reducing pressure. The specific process is as follows:
● The seawater is first heated and then enters the first flash chamber. Due to the reduced pressure, part of the seawater evaporates rapidly to produce fresh water vapor.
● The steam condenses into fresh water in the condenser, while the unevaporated salt water continues to enter the next flash chamber to repeat the evaporation and condensation process.
● After being treated in multiple flash chambers, pure fresh water is obtained.
Post-treatment
Fresh water after the core desalination process usually needs further treatment to ensure that it meets drinking water standards. Post-treatment includes adjusting the pH value of the fresh water, removing any remaining trace pollutants, and adding necessary minerals (such as calcium and magnesium) to enhance the taste and nutritional value of the water.
Brine discharge
During the desalination process, undesalinated brine contains high concentrations of salt and other impurities and needs to be safely discharged back to the ocean. Brine discharge usually discharges brine evenly into the ocean through a diffusion device to reduce the impact on the marine ecosystem. At the same time, some seawater desalination plants are also exploring the reuse of brine resources, such as salt extraction or further desalination of brine.

What technical equipment does a desalination plant include?
The core equipment of a desalination plant includes water intake pumps, pretreatment equipment, core desalination devices (such as reverse osmosis membranes or flash towers), high-pressure pumps, post-treatment systems, and concentrate discharge devices. These devices work together to ensure the smooth progress of the desalination process.
Reverse osmosis membrane
The reverse osmosis membrane is the core component of reverse osmosis desalination technology, and its quality and performance directly affect the output and quality of fresh water. Reverse osmosis membranes are usually made of composite materials with high selectivity and high anti-fouling ability. Since reverse osmosis membranes are easily contaminated, they need to be cleaned and replaced regularly.
High-pressure pumps
High-pressure pumps are used to pressurize seawater to push seawater through reverse osmosis membranes or support multi-stage flash evaporation processes. High-pressure pumps have high energy consumption, so energy efficiency is an important consideration when designing and selecting high-pressure pumps. In order to improve overall efficiency, many desalination plants are also equipped with energy recovery devices to use the energy of concentrate water to reduce energy consumption.
Pretreatment equipment
Pretreatment equipment includes sand filters, microfilters, ultrafilters, chemical dosing systems, etc. These devices are responsible for removing suspended particles, colloids, organic matter and microorganisms from seawater to ensure the stable operation of subsequent desalination equipment.
Post-treatment system
The post-treatment system includes pH adjustment devices, activated carbon filters, ultraviolet disinfectors, etc. They ensure that the final quality of fresh water meets drinking water standards while improving the taste and safety of water.
Concentrate discharge device
The concentrate discharge device is responsible for safely discharging highly concentrated salt water back to the ocean. In order to reduce the impact on the marine environment, concentrate water is usually diluted before discharge, and the discharge port is designed as a diffusion structure to promote the rapid diffusion of concentrate water.

What is the energy consumption of seawater desalination plants?
Desalination is an energy-intensive process, especially reverse osmosis technology, which requires a lot of electricity to maintain the operation of high-pressure pumps. Depending on the process and scale, the energy consumption of seawater desalination ranges from 2 to 6 kWh/m3 of fresh water. The level of energy consumption directly affects the cost of desalinated water, so improving energy efficiency and reducing energy consumption are key directions for the development of seawater desalination technology.




