What types of ultrafiltration devices are there?
As an important water treatment equipment, ultrafiltration devices are widely used in various fields, including industrial production, pharmaceutical manufacturing, food and beverage processing, and municipal water supply.
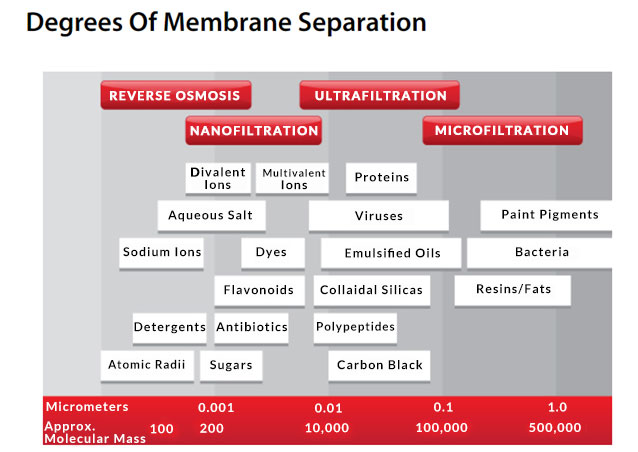
Ultrafiltration technology has become an indispensable part of modern water treatment processes because it can effectively remove impurities such as suspended particles, bacteria and viruses in water. However, there are many types of ultrafiltration devices, each with its own unique characteristics and application scenarios.
This article will introduce the main types of ultrafiltration devices in detail, and analyze their respective advantages and disadvantages and applicable fields.
What types of ultrafiltration devices are there?
The types of ultrafiltration devices are:
1. Organic membrane ultrafiltration device,
2. Inorganic membrane ultrafiltration device,
3. Hollow fiber membrane ultrafiltration device,
4. Flat membrane ultrafiltration device,
5. Roll membrane ultrafiltration device,
6. Intermittent ultrafiltration device,
7. Continuous ultrafiltration device,
8. Industrial ultrafiltration device,
9. Municipal ultrafiltration device,
10. Food and beverage ultrafiltration device,
11. Pharmaceutical ultrafiltration device.
Classification by membrane material
1. Organic membrane ultrafiltration device:
Organic membrane ultrafiltration devices are usually made of polymer materials such as polysulfone, polyethersulfone, and polyvinylidene fluoride. This type of membrane has good mechanical strength, chemical corrosion resistance, and heat resistance, and is suitable for most industrial water treatment applications. The advantages of organic membranes include mature membrane manufacturing technology, uniform membrane pore size, and stable filtration effect. However, organic membranes may be affected by organic pollutants during long-term use, resulting in membrane contamination and performance degradation, and require regular cleaning and maintenance.
2. Inorganic membrane ultrafiltration device:
Inorganic membranes are usually made of inorganic materials such as alumina, titanium dioxide, and silicon dioxide. Inorganic membranes have excellent high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and high mechanical strength, and are suitable for water treatment applications in extreme environments such as high temperature, high pressure, and strong acid and alkali. The disadvantages of inorganic membranes are high manufacturing costs and brittle membrane materials that are easy to break.

Classification by membrane component structure
3. Hollow fiber membrane ultrafiltration device:
Hollow fiber membrane is one of the most widely used ultrafiltration membrane components. The structure of the hollow fiber membrane is similar to that of a tiny tubular fiber. Water is filtered through the membrane wall and impurities are trapped outside the membrane. Hollow fiber membranes have the advantages of high flux, low energy consumption and easy cleaning, and are widely used in municipal water supply, industrial wastewater treatment and food and beverage industries. However, when hollow fiber membranes are used to treat water containing large particle impurities, membrane clogging is prone to occur, and a pretreatment process is required to protect the membrane assembly.
4. Flat membrane ultrafiltration device:
The flat membrane is composed of flat membrane sheets with a certain gap between the membrane sheets. Water flows between the membrane sheets and impurities are trapped on the membrane surface. The advantages of the flat membrane ultrafiltration device are simple structure, easy cleaning and strong adaptability. It is suitable for water treatment containing high suspended solids. However, the installation of the flat membrane occupies a large area and the initial investment cost is high.
5. Rolled membrane ultrafiltration device:
The rolled membrane is a membrane assembly formed by winding a flat membrane on a central tube. Water enters from one end of the membrane assembly and is filtered through the channel where the membrane is wound, and impurities are trapped on the membrane surface. The roll membrane ultrafiltration device has a compact structural design and a small footprint, which is suitable for water treatment systems with limited space. However, when the roll membrane is used to treat water with high concentrations of suspended solids, the membrane is prone to clogging and needs to be backwashed and chemically cleaned regularly.

Classification by operation mode
6. Intermittent ultrafiltration device:
Intermittent ultrafiltration device refers to the device running for a period of time, and then stopping for backwashing or chemical cleaning to remove impurities on the membrane surface. The advantages of intermittent ultrafiltration devices are simple equipment structure and convenient operation and maintenance. They are suitable for application scenarios with small processing volume or large changes in water quality. However, the treatment efficiency of intermittent ultrafiltration devices is low, and they cannot operate continuously, affecting the overall production efficiency.
7. Continuous ultrafiltration device:
The continuous ultrafiltration device adopts a continuous operation mode, and the water flow is continuously filtered through the ultrafiltration membrane, while the membrane is kept clean by online backwashing or chemical cleaning. The advantages of continuous ultrafiltration devices are high processing efficiency and suitable for large-scale continuous production application scenarios. They are widely used in municipal water supply, industrial wastewater treatment, food and beverage production and other fields. However, the design and operation of continuous ultrafiltration devices are relatively complex, and they need to be equipped with automatic control systems and complete cleaning procedures.

Classification by application field
8. Industrial ultrafiltration device:
Industrial ultrafiltration devices are mainly used for water treatment in industrial production processes, such as boiler feed water in power plants, water for chemical production, and textile printing and dyeing wastewater treatment. Industrial ultrafiltration devices require equipment with high corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, and high flux to meet the high requirements of industrial production.
9. Municipal ultrafiltration device:
Municipal ultrafiltration devices are mainly used for urban water supply and sewage treatment, such as water purification in water plants and reuse of reclaimed water in sewage treatment plants. Municipal ultrafiltration devices require equipment with stable filtering effects and long life to ensure the safety and stability of urban water supply.
10. Food and beverage ultrafiltration devices:
Food and beverage ultrafiltration devices are mainly used for water treatment in food and beverage production processes, such as dairy production, juice processing, drinking water purification, etc. Food and beverage ultrafiltration devices require equipment to meet food-grade hygiene standards, have good anti-pollution capabilities, and be easy to clean.
11. Pharmaceutical ultrafiltration device:
Pharmaceutical ultrafiltration device is mainly used for water treatment in the pharmaceutical production process, such as water for injection, pharmaceutical water, water for biological product production, etc. Pharmaceutical ultrafiltration device requires the equipment to have high-purity filtration effect and good biocompatibility to ensure the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products.

Conclusion
Ultrafiltration device, as a highly efficient water treatment equipment, has been widely used in various fields. Different types of ultrafiltration devices have their own characteristics in materials, structures, operation modes and application fields. Users should choose appropriate ultrafiltration devices according to specific application requirements to achieve the best water treatment effect.




