Do cruise ships use seawater desalination?
Cruise travel has always been a popular choice for people to enjoy a vacation and explore the ocean. However, people may be curious, how is water supplied on cruise ships? Is sea water desalination technology used? This article will delve into this topic. First, let’s take a look at the main sources of fresh water on board and the development history of Shipboard Desalination equipment.

Introduction
Ocean-going ships sail in the vast ocean, and it takes anywhere from 5-7 days to 30-40 days to dock. Domestic water for people on board has become a major problem that needs to be solved. The Shipboard Desalination machine (commonly known as fresh water generator) is a seawater desalination equipment designed according to the particular application of ships, yachts, and oil drilling platforms, and has become a solution to this problem.
There are Two Main Sources of Fresh Water on Ships
1. Mainland Shore Supply
2. Seawater Desalination Equipment Provided
Due to differences in personal living habits, if you use the method of carrying it from land, you not only need to invest in the development of hygienic and safe water storage equipment, but also accurately control each person's water consumption to ensure sufficient water sources and hygienic safety. This method is obviously unreliable. Therefore, Shipboard Desalination equipment has become a good choice.
The Development History of Shipboard Desalination Equipment
In the 19th century, that is, after 1800, the emergence of steam engines, as well as the development of navigation and practical needs of ocean colonization, promoted the development of distillation, and the emergence of submersed evaporators, which can be regarded as the beginning of the development of seawater desalination technology. From 1812 to 1840, single-effect and vacuum multiple-effect evaporation were developed, and research and design work on flash evaporation was started. In 1852, the British patented standpipe seawater evaporator was quickly used on ships, and later horizontal tube spray film evaporation was proposed. , vapor compression and other patents. In 1872, the world's first solar desalination device appeared in Chile, with a daily output of 2 tons of desalinated water. In 1884, the United Kingdom built the first ocean desalinator to solve the problem of drinking water for ocean transportation.

Salt Content of Sea Water
● Seawater is an aqueous solution containing more than 80 kinds of salts, of which 11 have concentrations exceeding 1 mg/L. The most abundant ones are NaCI and MgCL2.
● The average salt content of seawater in the ocean is about 35g/L, but the salt content of seawater in different sea areas is different. The salt content of seawater is related to the geology of the sea area, rainfall, river flow into the sea, and seawater evaporation.
● Some inland seas are close to estuaries and have low evaporation. For example, the salt content of the Baltic Sea is only 2~6.7g/L, and the salt content of the Black Sea is 17~18.5g/L. In some inland seas with large evaporation capacity, such as the Red Sea and the Mediterranean Sea, the salt content can be as high as 40g/L or more.
Fresh Water Use and Requirements on Board Ships
Fresh water on board is mainly used for diesel engine cooling water, boiler feed water, washing and drinking water.
● Diesel engine cooling water only needs to be fresh water (310kg/1000kw).
● Wash water generally requires that the chloride ion concentration should not be greater than 200mg/L (Cl⁻) and the hardness should not be greater than 7 milliequivalents/L.
● Drinking water must be free of impurities, germs and odors harmful to health, with a salt content of no more than 500~1000mg/L, a chloride ion concentration of no more than 250~500mg/L (Cl⁻), and a pH value of 6.5~8.5. (The distilled water produced by the water generator contains too few minerals and cannot kill germs, so it should be mineralized and sterilized when used as drinking water.)
● The water quality requirements for boiler feed water are the highest. Generally, the requirements for the salinity content of fresh water produced by marine seawater desalination devices are based on the boiler feed water standards. The Chinese marine boiler feed water standards stipulate that the salt content of the feed distilled water should be less than 10mg/L. (NaCl).
Ship’s Demand for Fresh Water
● Domestic water consumption per person is about 150~250L/day.
● The water used in the power plant is measured by the power of the main engine:
★ Diesel engine ships require about 0.2~0.3L/day per kilowatt.
★ Steam turbine ships require about 0.5~1.4L/day per kilowatt.
● The amount of water supply for auxiliary boilers can be estimated as 1% to 5% of the evaporation capacity, and for medium and high-pressure boilers as 1% to 3% of the evaporation capacity.
Generally, the capacity of diesel engine freighters with a main engine power of about 7500kW does not exceed 20~25m/day.
Cruise Ship Desalination Equipment
After learning about the development history of Shipboard desalination equipment and the demand for fresh water, now we will discuss the application of desalination technology on cruise ships.
1. Water Resources Utilization on Cruise Ships:
Most cruise ships do use desalinated seawater as their primary water source. This process usually occurs via steam evaporation, which means the cruise ship converts seawater into distilled water, removing salt and impurities from it. The cruise ship then mineralizes the distilled water to enhance its taste and chlorines it to ensure the water is safe. At present, cruise ship desalination technology has matured in practice. Cruise ships out to sea have convenient conditions for using seawater desalination. Water intake is convenient and fast, and water sources are sufficient. Only professional technical equipment is needed to provide a stable source of fresh water for people on board. Even on ultra-long voyages across the ocean, drinking water on board is not a problem.
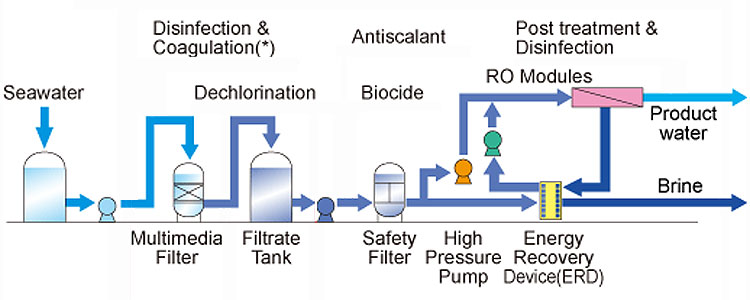
2. The Application of RO Desalination Technology in Cruise Ships:
In addition to steam evaporation, some cruise ships are equipped with reverse osmosis systems to filter and desalinate seawater. These systems create desalinated water by forcing seawater through a semipermeable membrane at high pressure, leaving salts and impurities on one side of the membrane. While ensuring water quality, this technology is also more energy-saving and efficient, making it the choice of some modern cruise ships. Among them, the small cruise ship desalination equipment is small in size, highly integrated, and has stable operating performance, making it very suitable for use on sea cruise ships. Cruise ship desalination equipment mainly consists of water intake system, pretreatment system, seawater desalination system, chemical cleaning system and intelligent control system. Its core technology lies in its internally loaded reverse osmosis membrane technology. The reverse osmosis membrane can realize the separation and filtration of nanoscale substances, and can effectively remove dissolved salts, organic matter, colloids, microorganisms and other substances in seawater. It operates stably and is not affected by the complex and changeable climate at sea. It is a reliable, safe and high-quality freshwater resource development product that can effectively solve the water problem of personnel on cruise ships going out to sea.
3. Cruise Ship Water Management Challenges:
Although cruise ships use sea water desalination technology to obtain fresh water resources, water management still faces some challenges. Cruise ships require a large amount of water during long voyages, so how to effectively manage and save water has become an important task. In addition, the operation and maintenance of sea water desalination technology also requires professional personnel and equipment support, increasing the cost and complexity of water resources management.

Detailed Desalination Steps for Cruise Ship Desalination Equipment
1. Seawater Pretreatment:
In the desalination process of cruise ships, pretreatment is the key to ensuring the long-term stable operation of the reverse osmosis system. When formulating a seawater pretreatment plan, full consideration should be given to the presence of a large number of microorganisms, bacteria and algae in seawater. The reproduction of bacteria, algae and the growth of microorganisms in seawater will not only bring a lot of trouble to water intake facilities, but also directly affect the normal operation of seawater desalination equipment and process pipelines. At the same time, seawater is highly corrosive, so the materials of equipment, valves, and pipe fittings used in the system must be screened to ensure good corrosion resistance.
2. Seawater Sterilization and Algae Removal:
Seawater desalination projects often use chemical reagents such as liquid chlorine, NaClO and CuSO4 to sterilize and kill algae. Taking into account various factors such as transportation, it is difficult to add chemical reagents to sterilize and kill algae. Generally, seawater sodium hypochlorite generator is used. A small stream of pressurized seawater is separated from the seawater pump and enters the sodium hypochlorite generator. NaClO is generated under the action of the DC electric field and is directly injected into the beach caisson based on the position difference to kill bacteria, algae and microorganisms in the seawater.
Due to the high hardness of seawater, direct electrolysis of seawater to produce NaClO must overcome the problem of electrode scaling. During the development process, the electrodialysis frequent pole reversal (EDR) technology was used for reference, that is, the electrode polarity is switched every 5 to 10 minutes, which effectively solved the problem of scaling and precipitation in the sodium hypochlorite generator.
3. Coagulation and Filtration:
Coagulation filtration is designed to remove colloids and suspended impurities in seawater and reduce turbidity. In reverse osmosis membrane separation projects, the pollution index (FI) is usually used to measure, and the FI value of the feed water entering the reverse osmosis equipment is required to be <4. Due to the large specific gravity of seawater, the high pH value, and the large seasonal changes in water temperature, the system uses FeCl3 as the coagulant, which has the advantages of not being affected by temperature, large and strong alum flowers, and fast settling speed.

4. Osmotic Seawater Desalination:
Seawater has high salt content and hardness, which is highly corrosive to equipment, and the seasonal changes in water temperature make the reverse osmosis seawater desalination system much more complex than the conventional brackish water desalination system, and the engineering investment and energy consumption are also much higher. . Therefore, it is particularly important to reduce engineering investment and energy consumption through careful process design and reasonable equipment configuration, thereby reducing unit water production costs and ensuring stable operation of the system.
5. Chemical Conditioning Treatment:
In order to prevent insoluble inorganic salts, such as CaCO3 and CaSO4, from being produced due to the concentration of seawater during the desalination process, and scaling and precipitation on the surface of the reverse osmosis membrane and system pipe fittings, an anti-scaling agent must be added before seawater enters the reverse osmosis desalination system.
Adding H2SO4 to adjust the pH value of seawater to decompose HCO-3 in seawater to prevent the precipitation of CaCO3 is the most commonly used and economical method in seawater desalination. Adding (NaPO3) 6 (SHMP) is an effective method to prevent CaSO4 precipitation, but the by-product phosphate produced by (NaPO3) 6 while inhibiting scale will encourage the growth of microorganisms, bacteria and algae, and its use has certain limitations.
6. Remove Organic Matter and Odors From Seawater:
The seawater around the island is greatly affected by the surrounding environment. The chemical oxygen demand (COD) of seawater is 1.7-2.5m g/L. Especially in summer and autumn, seawater sometimes has a strong odor. Therefore, in addition to adding NaClO for oxidation, an activated carbon filter is added. Fruit-shaped granular activated carbon with high mechanical strength can effectively absorb organic matter and odors, improve the quality of reverse osmosis water, and at the same time reduce pollution to the reverse osmosis membrane surface. , extend the service life of the membrane.
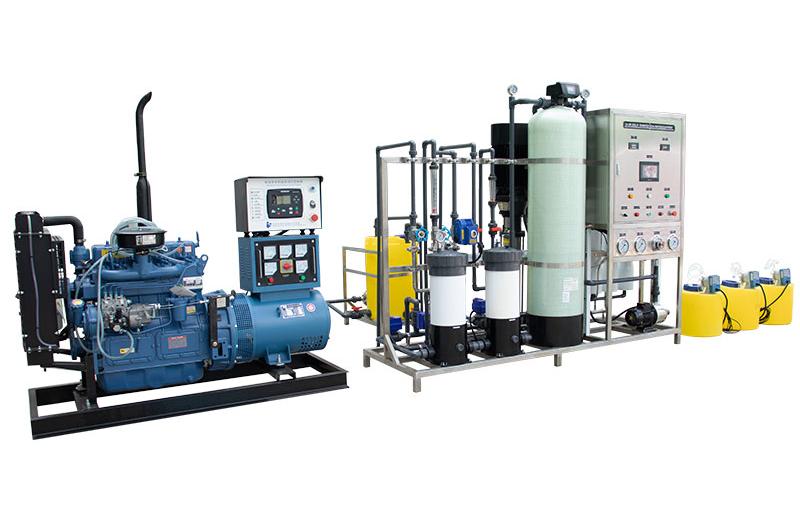

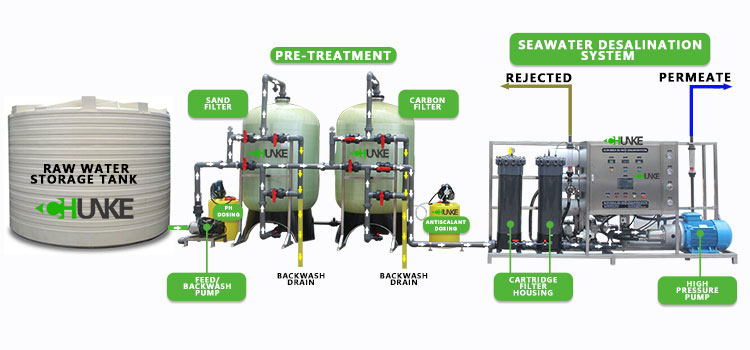
Introduction to the Process Flow of Cruise Ship Desalination Equipment
Cruise ship engine room seawater pump → sterilization system → pipeline pressure pump → bag filter → precision filter → ultrafiltration system → high pressure pump reverse osmosis system → UV sterilizer → intermediate pressure pump → primary filtration → secondary filtration → high Low pressure switch → high pressure pump → small reverse osmosis system → activated carbon filter → UV sterilizer → direct drinking water.
● The Above Process Is Divided into Three Parts:
1. Pre-Treatment Part: the seawater pump, sterilization system, pipeline pressure pump and bag filter in the engine room can be arranged reasonably according to the space position on the ship.
2. Main Part: precision filter, ultrafiltration, high-pressure pump, reverse osmosis system, ultraviolet sterilizer. This part is temporarily considered as an integrated structure. If the space on the ship is limited, it can also be installed as a separate structure.
3. Direct Drinking Water Part: primary filtration, secondary filtration, high and low pressure switches, high pressure pump, small reverse osmosis system, activated carbon filter, UV sterilizer. The direct drinking water part can be hung on the wall, occupying approximately 600mm×500mm×400mm.
How efficient is cruise ship seawater desalination technology?
Now that we understand the use of sea water desalination technology on cruise ships, let’s dive into the efficiency of these technologies.
1. Advantages of steam evaporation technology:
Steam evaporation is one of the commonly used technologies for sea water desalination on cruise ships. Although this method is relatively traditional, it is simple, reliable, and can convert seawater into distilled water in a relatively short period of time. The advantages of this technology are simple operation and low cost, and it is suitable for some small and medium-sized cruise ships.
2. The efficiency of reverse osmosis technology:
In comparison, reverse osmosis technology is more advanced and efficient. This technology more completely removes salt and impurities from seawater, producing higher-quality desalinated water. Although equipment investment and operating costs are high, its desalination efficiency and water quality reliability are higher, so it is favored by more and more cruise ships.
3. Technical updates and improvements:
With the continuous advancement of science and technology and the continuous innovation of seawater desalination technology, the seawater desalination technology of cruise ships is also constantly updated and improved. In the future, with the application of new materials and technologies, the seawater desalination efficiency and energy saving of cruise ships will be further improved, providing tourists with a better water experience.

Factors Affecting Fresh Water Output of Cruise Ship Desalination Equipment
The amount of water produced (evaporation) of the cruise ship desalination equipment mainly depends on the amount of heat transferred from the heated water to the seawater.
● The heat exchange surface is dirty and scaled, which reduces the heat transfer coefficient of the evaporator.
● A "gas lock" occurs on the heating side, and the gas inside will affect the flow of the heating medium and hinder heat exchange. The air can be released through the deflation cock.
● The water level in the evaporator is too low, which reduces the actual heat exchange area between the heating water and the heated seawater. The most appropriate water level in the evaporator is to just reach the position of the upper tube plate.
● Insufficient vacuum will cause the boiling point of seawater to increase.
● The flow rate of the heated water is insufficient or the temperature is too low, causing the average temperature of the heated water to drop.
● As the water supply volume increases (the water supply rate increases) or the water supply temperature decreases, more heat is consumed in preheating or taken away by salt water.
● The condensate return solenoid valve is not closed tightly, causing part of the produced fresh water to leak back into the distiller.
In daily management, whether the cruise ship desalination equipment produces fresh water and the amount of water produced have the greatest impact on whether the appropriate vacuum can be established and maintained. However, the water production of cruise ship desalination equipment will gradually decrease after being used for a long time, which is often caused by dirt and scaling on the heating surface.
Is sea water desalination technology on cruise ships environmentally friendly?
Environmental impact of cruise ship sea water desalination technology
The application of sea water desalination technology on cruise ships ensures the safety and sufficiency of water for tourists, but it also raises concerns about environmental impact. The sea water desalination process consumes a lot of energy, especially the steam evaporation method, which will increase the carbon emissions of cruise ships. In addition, the wastewater discharged from sea water desalination plants may also have certain impacts on the marine ecosystem.
Reduce the environmental impact of seawater desalination
In order to reduce the negative impact of seawater desalination technology on the environment, some cruise lines are researching and adopting more environmentally friendly seawater desalination technologies, such as solar seawater desalination systems and more efficient reverse osmosis technology. In addition, cruise lines are also strengthening the treatment and recycling of wastewater to reduce the impact on the marine ecosystem and promote sustainable development.
What are the future trends in cruise ship water management?
Now that we understand the efficiency of cruise ship seawater desalination technology, let’s explore the future development trends of cruise ship water management.
1. Application of intelligent water resources management system:
In the future, with the development of intelligent technology, cruise ship water management systems will become more intelligent. By introducing advanced sensors and data analysis technology, cruise ships can achieve real-time monitoring and precise control of water resources, thereby managing and utilizing water resources more efficiently.
2. Introduction of the concept of sustainable development:
Cruise ship water management will gradually develop towards sustainable development. In the future, cruise ships will pay more attention to water conservation and reuse of water resources, adopt more environmentally friendly seawater desalination technology, reduce dependence on natural water sources, and achieve sustainable utilization and recycling of water resources.
3. International cooperation and experience exchange:
Finally, the cruise industry will strengthen international cooperation and experience exchange to jointly address the challenges facing water resources management. Through cooperation with other countries and regions, the cruise industry can learn from advanced water resources management experiences and technologies in other regions and promote the common development of global water resources management.




