Can the water treated by a water softener be drunk directly?
In daily life, we often hear the terms "hard water" and "soft water". Hard water refers to water with a high concentration of calcium and magnesium ions. Although these minerals are beneficial to the human body, they are easy to form scale in water pipes, water heaters, boilers and household appliances, resulting in reduced equipment efficiency and shortened service life. On the contrary, soft water refers to water with a low content of calcium and magnesium ions, which is not easy to form scale and is more friendly to household equipment.
Therefore, water softeners have become one of the preferred devices for many families to improve water quality. So, what is a water softener machine? Can the water treated by a water softener be drunk directly? This article will discuss these issues in detail.

What is a water softener machine?
A water softener machine is a device that reduces the content of calcium and magnesium ions in water through ion exchange technology. Its working principle mainly relies on ion exchange resins, which are usually negatively charged polymer matrices with sodium ions (Na⁺) or potassium ions (K⁺) attached to them. When hard water passes through a water softener, the calcium and magnesium ions in the water will be replaced by the sodium or potassium ions on the resin, thereby reducing the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions in the water and achieving the effect of softening the water quality.
The basic components of a water softener include:
1. Resin tank: This is the core part of the water softener machine, which is filled with ion exchange resin. When hard water flows through the resin tank, the ion exchange reaction occurs here and the hardness ions in the water are replaced.
2. Brine tank: Used to store regeneration salt (usually sodium chloride or potassium chloride). During the regeneration process of the water softener machine, the brine solution will flow through the resin tank, replacing the calcium and magnesium ions adsorbed on the resin and restoring the softening ability of the resin.
3. Control valve: Controls the working process of the water softener, including water softening, resin regeneration, flushing and other processes. Modern water softeners are usually equipped with automatic control systems that can automatically adjust the working mode according to household water consumption and water quality.
4. Regeneration system: When the exchange capacity of the resin is close to saturation, the water softener will automatically start the regeneration system, introduce salt water into the resin tank, wash away the calcium and magnesium ions, and restore the resin to its original state so that it can continue to work.
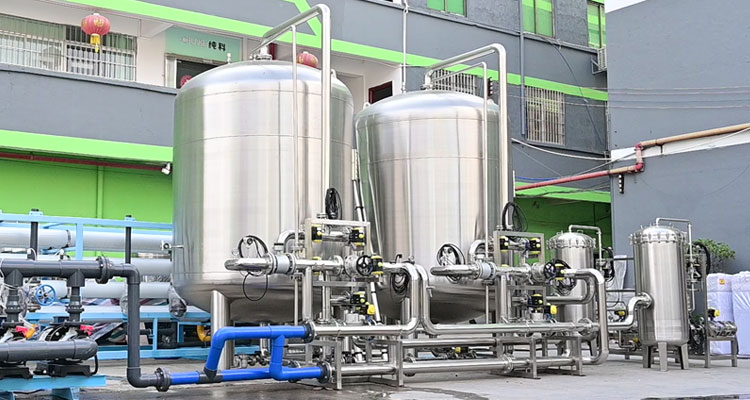

How does a water softener machine work?
A water softener softens water through an ion exchange process. When hard water passes through a water softener, the calcium and magnesium ions in the water are replaced by the sodium or potassium ions on the resin. The chemical equation for this process is:
Ca²⁺+2Na⁺+→Ca²⁺[resin]+2Na⁺
This reaction indicates that the calcium ions (Ca²⁺) in the water will exchange with the sodium ions (Na⁺) on the resin, so that the calcium ions are fixed on the resin and the sodium ions are released into the water. Similarly, magnesium ions (Mg²⁺) will also undergo a similar exchange reaction.
Over time, the sodium or potassium ions on the resin will be replaced by a large amount of calcium and magnesium ions, causing the softening ability of the resin to gradually decrease. When the resin is saturated, the water softener machine will regenerate by introducing a brine solution to restore the resin's softening capacity.
Can the water treated by the water softener be drunk directly?
This is a widely concerned issue. Is the water treated by the water softener machine suitable for direct drinking? The answer is not a simple "yes" or "no", but needs to be judged according to the specific situation.
The impact of increased sodium content:
In the process of softening water, the water softener will replace the calcium and magnesium ions in the water with sodium ions. Therefore, the sodium content in the treated water will increase. For healthy adults, moderate sodium intake will not have a significant effect on the body. However, for patients with high blood pressure, heart disease or kidney disease, excessive sodium intake may aggravate the condition. Therefore, softened water is not recommended as a long-term drinking water source for these people.
Potassium ion selection:
Some water softeners use potassium chloride (KCl) as the regeneration salt instead of sodium chloride (NaCl). In this case, the sodium content in the water will not increase, but potassium ions will replace it. For most people, potassium intake is safe and even good for the heart. But similarly, people with kidney disease may need to control their potassium intake, so this group of people should also be cautious about drinking softened water regenerated with potassium chloride.
Complete removal of hardness:
The purpose of a water softener machine is to reduce the hardness of water, not to remove all impurities. Therefore, the water treated by the water softener may still contain other impurities, such as microorganisms, heavy metals, organic matter, etc. If the water quality of the household water source is not good, the water softener alone cannot completely purify the water quality. Other water purification equipment, such as activated carbon filters, ultraviolet sterilizers or reverse osmosis systems, may be needed to ensure the safety of the water quality.
Taste and lack of minerals:
The taste of soft water is different from that of hard water. Because calcium and magnesium ions are replaced by sodium or potassium ions, softened water may appear "slippery" and not as "refreshing" as hard water. In addition, calcium and magnesium ions are beneficial to human health to a certain extent, and long-term drinking of softened water may lead to a decrease in the intake of these minerals. Therefore, some families choose to install mineral filters on drinking water pipes to replenish the removed calcium and magnesium ions.
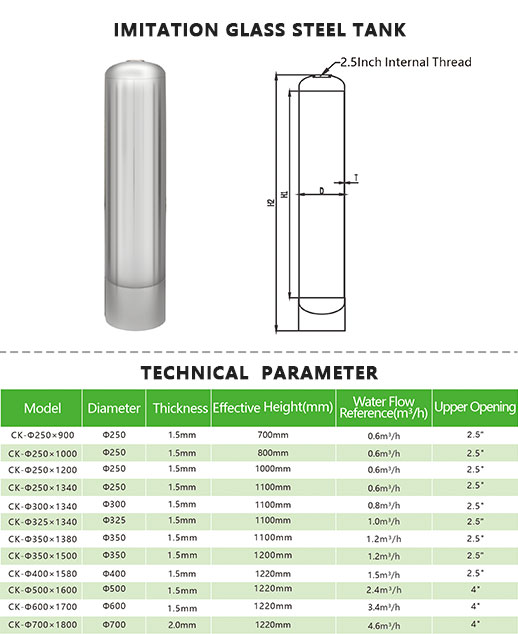
How to choose a suitable water softener machine?
Before purchasing a water softener machiner, it is recommended to conduct a water quality test to understand the hardness of household water and whether it contains other contaminants. This can help determine whether a water softener is needed and whether additional water purification equipment is needed. The capacity and flow rate of the water softener machine should be selected according to the household water consumption. A water softener with a larger capacity is suitable for large households or users with large water consumption, while a water softener with a smaller capacity is suitable for small households or single users.
Secondly, the size and design of the brine tank have a direct impact on the regeneration frequency and operating convenience of the water softener. Automatic brine tanks can reduce the frequency of manual operation and improve user convenience.
In addition, the operating cost of the water softener machine should also be considered. The operating cost of the water softener mainly includes the cost of regeneration salt and maintenance costs. Choosing a water softener machine with low salt consumption and easy maintenance can reduce the long-term use cost. In addition, regular maintenance and replacement of resins are also the key to ensure the long-term and stable operation of the water softener. For people who need to control sodium or potassium intake, they should consult a doctor or nutritionist for advice when purchasing a water softener to choose a suitable water treatment method.
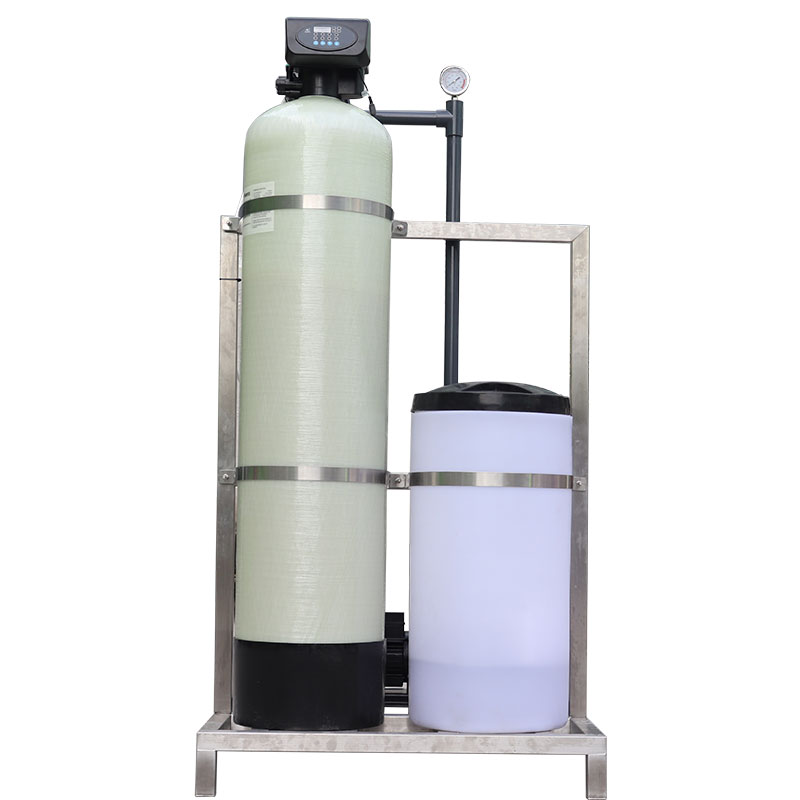

How to maintain a water softener on a daily basis?
Depending on the amount of water used and the quality of the water, check the regeneration salt content in the brine tank regularly to ensure that it is sufficient. It is usually recommended to check once a month and add regeneration salt as needed. The resin is the core part of the water softener, and regular regeneration can maintain the softening ability of the resin. If the resin's effect decreases after multiple regenerations, you should consider replacing the resin. Generally speaking, the service life of the resin is 5-10 years, depending on the water quality and frequency of use.
In addition, after long-term use, sediment or impurities may accumulate in the brine tank, affecting the regeneration effect. It is recommended to perform a thorough cleaning once a year to ensure the smooth progress of the regeneration process. Finally, even if a water softener machine is used, it is recommended to test the water quality regularly to ensure that the treated water meets the household water needs, especially the safety of drinking water.




