What fields are reverse osmosis water treatment systems suitable for?
Reverse osmosis (RO) water treatment systems are a water purification technology widely used in multiple industries. Through efficient filtration and separation processes, impurities such as dissolved solids, microorganisms and organic matter in water are removed. This article will explore the working principle of the reverse osmosis system and its application in various fields, and deeply analyze how it plays a key role in different industries.

What is the working principle of the reverse osmosis water treatment system?
Reverse osmosis is a water treatment technology based on physical separation. It uses the characteristics of a semipermeable membrane to allow water molecules to pass through the membrane pores under external pressure, while dissolved solids (such as salts, heavy metal ions), organic matter (such as bacteria, viruses) and other pollutants are retained on one side of the membrane, thereby achieving water purification.
What is the role of the reverse osmosis membrane?
The reverse osmosis membrane is the core component of the system. It is made of multi-layer polymer materials with extremely small pore sizes (usually around 0.0001 microns) and can effectively block most pollutants. The selective permeability of the membrane allows only water molecules and a very small number of tiny molecules to pass through, while most other solutes are blocked.
The reverse osmosis process relies on an applied pressure, which is usually greater than the osmotic pressure of water, to force water molecules to flow back through the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a natural pressure caused by the difference in solution concentration. The reverse osmosis process is carried out by overcoming the applied pressure. The reverse osmosis system can remove more than 90%-99% of pollutants such as dissolved solids, microorganisms, viruses, organic matter and heavy metals. The final water purity depends on the quality of the membrane, the quality of the influent water and the specific parameters of the system design.
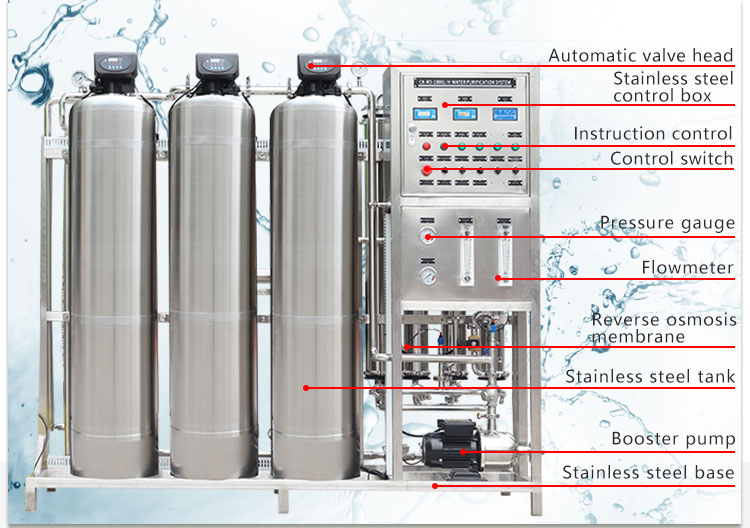
What fields are reverse osmosis water treatment systems suitable for?
Drinking water treatment is one of the most common applications of reverse osmosis systems. Whether it is urban water supply or bottled drinking water production, reverse osmosis systems can effectively remove dissolved salts, heavy metals, pesticide residues and other harmful substances in water to provide safe and pure drinking water.
● Urban water supply: In urban water supply systems, reverse osmosis systems are usually used as a deep purification step to remove pollutants that are difficult to remove by conventional treatment methods to ensure that the water quality meets national and international drinking water standards.
● Bottled drinking water: Reverse osmosis technology plays a key role in the production of bottled drinking water, and can produce extremely high-purity water to meet consumers' needs for health and safety.
Secondly, seawater desalination is also one of the important application areas of reverse osmosis technology, especially in areas with scarce water resources and coastal cities. Through the reverse osmosis system, salt and other impurities in seawater are effectively removed and converted into drinkable fresh water.
● Coastal city water supply: Many coastal cities solve the problem of drinking water shortage through seawater desalination. The high efficiency of the reverse osmosis system makes it the mainstream choice in seawater desalination technology.
● Industrial water: In some industrial applications that require high-purity water, fresh water from desalinated seawater can be used as production water to ensure the stability of the production process and product quality.
Reverse osmosis technology also occupies an important position in industrial water treatment and is widely used in industries such as electronics manufacturing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals and chemicals.
● Electronic manufacturing: Ultrapure water is essential in the manufacture of semiconductors and electronic components. The reverse osmosis system can remove almost all impurities in the water and provide high-quality process water for the production process.
● Food and beverage production: The food and beverage industry has strict requirements on water quality. The reverse osmosis system can ensure the purity of production water, avoid possible contamination in the product, and ensure food safety and taste.
● Pharmaceutical industry: The purity of water used in the pharmaceutical industry directly affects the quality of medicines. The reverse osmosis system can provide pure water that meets the pharmacopoeia standards and is widely used in pharmaceutical processes, the preparation of water for injection, etc.
● Chemical industry: The reaction, cooling and solvent preparation in the chemical production process have high requirements for water quality. Reverse osmosis technology provides high-purity water sources to ensure the quality of chemical products and the safety of the production process.
In addition, in power and industrial boilers, the purity of water has a direct impact on the operating efficiency and safety of the boiler. Minerals and impurities in water can cause problems such as boiler scaling and corrosion, affecting the life and operating efficiency of the equipment. The reverse osmosis system can effectively remove most of the soluble solids in the water, reduce the risk of scaling and corrosion, and ensure the long-term stable operation of the boiler.
Finally, reverse osmosis technology is also widely used in wastewater treatment, especially in the recycling and treatment of industrial wastewater to meet emission standards.
● Industrial wastewater reuse: Through the reverse osmosis system, most of the dissolved pollutants in industrial wastewater can be removed, and the treated water can be reused in the production process, reducing the consumption of fresh water and reducing production costs.
● Wastewater discharge compliance treatment: In some areas with strict environmental protection standards, reverse osmosis systems are used to treat wastewater so that it meets the prescribed standards before discharge and reduces pollution to the environment.

Maintenance and cost of reverse osmosis water treatment system
Although reverse osmosis systems are widely used in the field of water treatment, their operation and maintenance costs are also important factors to consider. The reverse osmosis membrane is the core component of the system, but its service life is limited. Since pollutants in the water may cause clogging or damage to the membrane, regular cleaning and replacement are necessary. Properly used reverse osmosis membranes can be used for several years, but frequent use and treatment of highly polluted water sources may accelerate their aging.
In order to extend the service life of the reverse osmosis membrane, the inlet water usually needs to be pretreated, including sand filtration, carbon filtration, softening and other steps to remove large particulate matter, residual chlorine and hardness ions. These pretreatment steps can effectively reduce membrane fouling and scaling, and reduce maintenance frequency and cost. The operating costs of the reverse osmosis system mainly include energy consumption, chemical agent consumption and equipment maintenance costs. Since the reverse osmosis process relies on the pressure provided by the high-pressure pump, the system has a high energy consumption. In addition, in order to prevent scaling and biological fouling of the membrane, chemical agents are usually added, which also increases the operating cost.
In addition, after the reverse osmosis system has been running for a long time, impurities may accumulate on the membrane surface, resulting in a decrease in water permeability. Regular cleaning can restore the performance of the membrane, but it will also increase the downtime and maintenance costs of the system. Therefore, optimizing operating conditions and reasonably arranging cleaning cycles are crucial to reducing the operating costs of the system.




