What is an Industrial Water Purifier? How does it Work?
Industrial water purifier is one of the indispensable and important equipment in modern industrial production. It is used to purify various industrial water and ensure the safety and stability of water quality in the production process. Industrial water purifiers have a wide range of applications, from electronic manufacturing to food processing, from pharmaceutical industry to power production, all walks of life rely on this equipment to provide high-quality water sources.
So, what is an industrial water purifier? How does it work? This article will explore the definition, working principle, main technology and application scenarios of industrial water purifiers in depth to help readers fully understand this key equipment.
What is an Industrial Water Purifier
Industrial water purifier is a device specially used to purify industrial water. It removes impurities, microorganisms, dissolved solids and organic matter in water through a variety of purification technologies to provide high-quality water sources that meet the requirements of industrial production. Industrial water purifiers are widely used in industrial production processes that require high-purity water or special water quality requirements, such as electronic manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, electricity and chemical industries.
What are the Types of Industrial Water Purifiers?
5 types of industrial water purifiers:
1. Ultrafiltration water purifier,
2. Reverse osmosis water purifier,
3. Ion exchange water purifier,
4. UV disinfection water purifier,
5. Activated carbon water purifier.
1. Ultrafiltration water purifier:
Ultrafiltration water purifier uses ultrafiltration membrane technology to remove impurities such as suspended particles, colloids, bacteria and viruses in water, but retains minerals in water. Ultrafiltration technology has a high filtration accuracy and is suitable for industrial applications with high water quality requirements.
2. Reverse osmosis water purifier:
Reverse osmosis water purifier uses reverse osmosis membrane to almost completely remove dissolved solids, heavy metals, bacteria and viruses in water, providing extremely high purity water quality. Reverse osmosis technology is widely used in industries such as electronics manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverages that require high purity water.
3. Ion exchange water purifier:
Ion exchange water purifier removes hardness ions (such as calcium and magnesium ions) in water through ion exchange resin to prevent scale formation. This technology is mainly used to soften water quality and is suitable for the treatment of boiler water and cooling water.
4. Ultraviolet disinfection water purifier:
Ultraviolet disinfection water purifier uses the strong bactericidal ability of UV-C light (wavelength of 200-280 nanometers) to kill bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms in water. Ultraviolet disinfection is often used to supplement other water purification technologies to ensure the sanitation and safety of water quality.
5. Activated carbon water purifier:
Activated carbon water purifier uses the adsorption capacity of activated carbon to remove organic matter, odor, residual chlorine and some heavy metals in water. Activated carbon is often used for pretreatment and terminal treatment to improve the taste and quality of water.

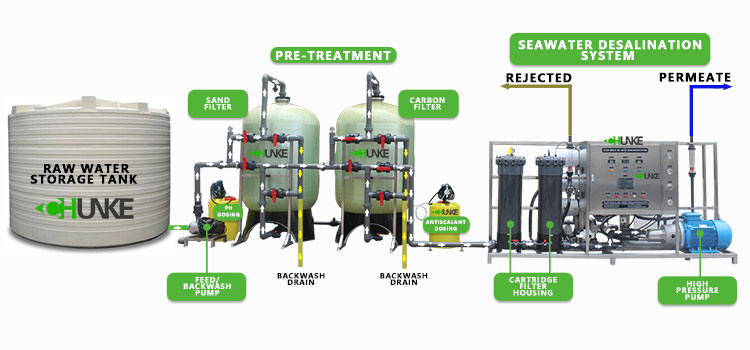
What is the working principle of industrial water purifier?
The working principle of industrial water purifier: pretreatment (mechanical filtration → sand filtration → activated carbon adsorption), main filtration process (ultrafiltration technology → reverse osmosis technology → ion exchange technology), post-treatment (ultraviolet disinfection → ozone disinfection → pH adjustment).
1. Pretreatment:
Pretreatment is the first step in the purification process of industrial water purifiers, aiming to remove large particles of impurities, suspended matter, silt and organic matter in the water and protect the subsequent filtration units. Pretreatment usually includes steps such as mechanical filtration, sand filtration and activated carbon adsorption.
● Mechanical filtration: intercept large particles of impurities in the water, such as silt, rust and suspended matter, through a filter screen or filter element. Commonly used mechanical filtration equipment includes bag filters, precision filters and multi-media filters.
● Sand filtration: use filter materials such as quartz sand to remove suspended matter and colloidal particles in the water. Sand filters are widely used in the pretreatment stage and have the advantages of fast filtration speed and large processing capacity.
● Activated carbon adsorption: adsorb organic matter, residual chlorine and odor in the water through the porous structure of activated carbon. Activated carbon filters are often used as key equipment for pretreatment and terminal treatment to improve water quality and taste.
2. Main filtration process:
After pretreatment, water enters the main filtration process, and suitable filtration technology is selected according to specific needs, such as ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis, ion exchange, etc.
● Ultrafiltration technology: Ultrafiltration membrane has a high filtration accuracy and can remove impurities such as suspended particles, colloids, bacteria and viruses in water. The ultrafiltration process does not change the mineral content in water and is suitable for industrial applications that need to retain minerals in water.
● Reverse osmosis technology: The pore size of the reverse osmosis membrane is extremely small, allowing only water molecules to pass through, and can effectively remove dissolved solids, heavy metals, bacteria and viruses in water. Reverse osmosis technology provides extremely high purity water quality and is widely used in industries with extremely high water quality requirements.
● Ion exchange technology: Ion exchange resin removes hardness ions (such as calcium and magnesium ions) in water through chemical reactions to soften water. This technology is mainly used for the treatment of boiler water and cooling water to prevent scale formation.
3. Post-treatment:
Post-treatment is an important step to ensure that the purified water quality meets specific requirements, usually including ultraviolet disinfection, ozone disinfection and pH adjustment.
● Ultraviolet disinfection: Use UV-C light to kill bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms in water to ensure the hygienic safety of water quality. Ultraviolet disinfection is often used to supplement other water purification technologies to provide ultimate microbial control.
● Ozone disinfection: Kill pathogenic microorganisms and remove organic pollutants in water through the strong oxidation effect of ozone. Ozone disinfection is highly efficient and environmentally friendly, but the ozone dosage needs to be controlled to avoid the production of by-products.
● pH adjustment: Adjust the pH value of water by adding acid or alkali to ensure that the water quality meets specific process requirements. pH adjustment is particularly important in some special applications, such as electronic manufacturing and chemical production.

What are the application scenarios of industrial water purifiers?
The application scenarios of industrial water purifiers include: electronic manufacturing, pharmaceutical industry, food and beverage, power and energy, chemical industry, etc.
1. Electronic manufacturing:
The electronic manufacturing industry has extremely high requirements for water quality, especially the production process of semiconductors and liquid crystal displays, which requires ultrapure water. Industrial water purifiers use reverse osmosis and ion exchange technology to provide high-purity ultrapure water to ensure the stability of the production process and product quality.
2. Pharmaceutical industry:
The pharmaceutical industry requires purified water and water for injection that meet GMP standards. Industrial water purifiers provide high-quality purified water and water for injection through multi-stage filtration and disinfection to meet the strict requirements of the pharmaceutical process.
3. Food and Beverage:
Food and beverage production has strict requirements on water quality, and water quality directly affects the taste and safety of the product. Industrial water purifiers remove impurities and pollutants in water through technologies such as ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis and activated carbon adsorption, and provide high-quality production water.
4. Power and Energy:
Boiler water and cooling water in the power and energy industry require high-quality softened water to prevent scale formation and ensure the operating efficiency and life of the equipment. Industrial water purifiers use ion exchange technology to provide softened water to ensure the normal operation of boilers and cooling systems.
5. Chemical Industry:
The chemical production process requires water of different quality and purity. Industrial water purifiers use a variety of water purification technologies to provide high-quality water sources that meet process requirements to ensure the smooth progress of chemical production and product quality.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of industrial water purifiers?
1. Advantages of industrial water purifiers: efficient purification (efficient removal of impurities, microorganisms, heavy metals and organic matter in water), flexible configuration (meeting the water requirements of various industrial production), high reliability (advanced design, compact structure, stable operation, and easy maintenance). The details are as follows:
● Efficient purification: Industrial water purifiers use a variety of purification technologies to efficiently remove impurities, microorganisms, heavy metals and organic matter in water, providing high-quality industrial water.
● Flexible configuration: According to different water quality and application requirements, industrial water purifiers can be flexibly configured to meet the water requirements of various industrial production.
● High reliability: Modern industrial water purifiers have advanced design, compact structure, stable operation, simple maintenance, high reliability and service life.
2. Disadvantages of industrial water purifiers: high purchase and installation costs, complex maintenance (regular maintenance and filter element replacement are required), and high energy consumption. The details are as follows:
● High cost: The initial purchase cost and installation cost of high-end industrial water purifiers are high, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises, it may be a large investment.
● Complex maintenance: Industrial water purifiers require regular maintenance and filter element replacement, the maintenance process is complicated, and professional personnel are required to operate.
● High energy consumption: Some water purification technologies such as reverse osmosis and ion exchange consume a lot of energy, which increases operating costs.
Summary of Industrial Water Purifiers
As an indispensable and important equipment in modern industrial production, industrial water purifiers provide high-quality industrial water through a variety of purification technologies to ensure the stability of the production process and product quality. By understanding its definition, working principle, main technology and application scenarios in detail, you can better select and use industrial water purifiers to improve industrial production efficiency and water quality safety. In actual applications, paying attention to equipment maintenance and water quality testing is the key to ensuring the long-term and efficient operation of industrial water purifiers.