What is the filtration system of a home water filter?
Household water filters have become one of the common appliances in modern households, used to provide clean and safe drinking water. However, water filters are not "one size fits all". There are many types of filtration systems inside them based on different functions and technologies. Different filtration systems not only differ in their ability to remove pollutants, but are also suitable for different water quality conditions and usage needs.
So, what exactly does the filtration system of a household water filter include? What's the difference between them? This article will answer these questions in detail.
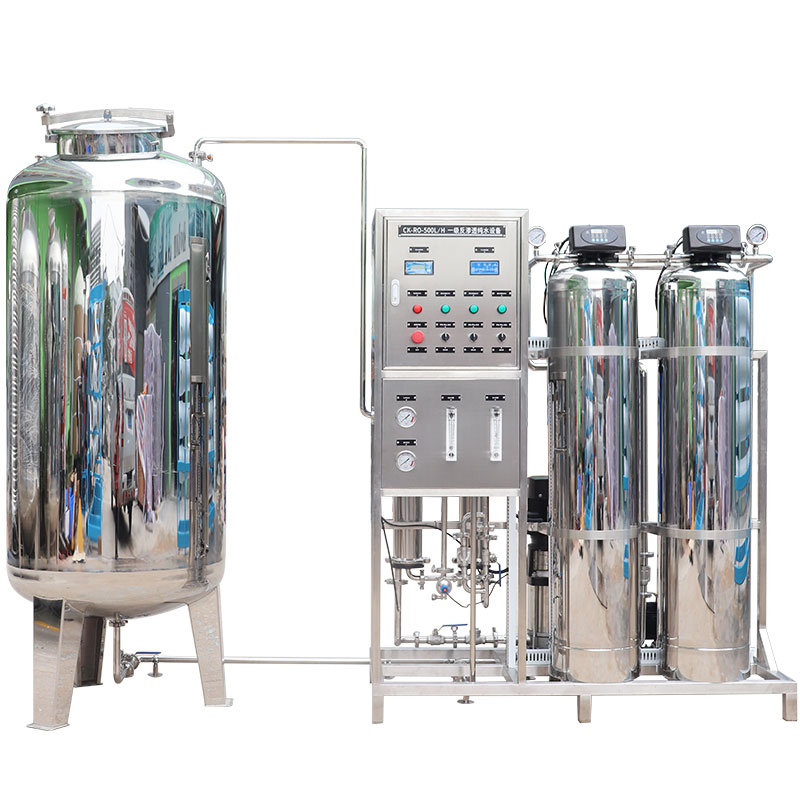

What are the classifications of filtration systems for household water filters?
The filtration system inside a home water filter usually consists of multiple layers of filter material, with each layer responsible for removing specific contaminants. Here are several common filtration systems:
Activated carbon filtration system
● Principle: Utilize the high specific surface area and strong adsorption of activated carbon materials to capture organic compounds, chlorine and odors in water.
● Features: Effective in removing odor and residual chlorine. It has certain adsorption capacity for some organic pollutants such as pesticide residues and benzene series.
● Scope of application: Suitable for treating urban tap water and improving the taste of water.
●Limitations: It has no obvious removal effect on heavy metals, microorganisms, etc., and is usually used as pretreatment or auxiliary filtration.
Ultrafiltration membrane filtration system
● Principle: Through the ultrafiltration membrane with a pore size of about 0.01 micron, particles, bacteria and some viruses in the water are physically trapped.
● Features: Can effectively remove suspended solids, bacteria and colloids. Retain minerals and trace elements in water.
● Scope of application: Suitable for areas with better water quality, such as tap water with lower hardness.
●Limitations: Unable to remove dissolved contaminants such as heavy metals and organic compounds.
Reverse osmosis membrane filtration system (RO membrane)
●Principle: Using a reverse osmosis membrane with a pore size of approximately 0.0001 micron, it is driven by high pressure to separate water molecules from pollutants.
● Features: Can remove almost all dissolved solids, heavy metals, microorganisms and organic pollutants. The effluent is pure, close to the level of distilled water.
● Scope of application: Suitable for areas with poor water quality, especially water sources with high heavy metal content or excessive salt content.
● Limitations: Minerals will be removed from the water, and a mineralizer needs to be added to improve the taste; the proportion of wastewater is high.
Ion exchange resin system
● Principle: Remove specific pollutants such as calcium, magnesium ions (softened water) and nitrates from water through cation or anion exchange resin.
● Features: Effectively reduce water hardness and reduce scale formation. Can remove specific ionized contaminants.
● Scope of application: Commonly used in hard water areas or used in combination with other filtration systems.
Limitations: It cannot be used as the main filtration system alone, and its ability to remove other pollutants is limited.
UV disinfection system
● Principle: Use ultraviolet (UV) to destroy the DNA structure of microorganisms to achieve sterilization and disinfection effects.
● Features: High sterilization efficiency, can effectively inactivate pathogens such as E. coli and viruses. No chemical additions, no secondary pollution to water quality.
● Scope of application: used to supplement the sterilization function, suitable for water sources with high microbial content.
● Limitations: Cannot remove other types of contaminants.
mineralization filtration system
● Principle: By adding mineralized balls or other mineral materials, mineral elements are added to the water during the filtration process.
● Features: Improve the taste of purified water. Provides calcium, magnesium and other minerals that are beneficial to the human body.
● Scope of application: Usually used in conjunction with reverse osmosis systems to balance water quality.
●Limitations: It cannot directly remove pollutants, but only improves water quality components.

Different Water Filtration Systems: What Are the Differences?
In order to more intuitively understand the advantages and disadvantages of various filtration systems, the following will compare three aspects: pollutant removal capacity, scope of application and maintenance requirements.
Pollutant removal capacity
● Activated carbon: mainly targets organic pollutants and odors, but cannot remove dissolved pollutants.
● Ultrafiltration membrane: It can intercept particulate matter and microorganisms, but cannot remove dissolved heavy metals and chemical pollutants.
● Reverse osmosis membrane: Can remove almost all kinds of contaminants, including dissolved salts and microorganisms.
● Ion exchange resin: focuses on the removal of ionic pollutants.
● Ultraviolet light: It can only kill microorganisms and cannot remove other pollutants.
Scope of application
● Activated carbon and ultrafiltration membrane: suitable for tap water with better water quality.
● Reverse osmosis membrane: suitable for areas with poor water quality.
● Ion exchange resin: for hard water treatment needs.
● UV disinfection: suitable for supplementing microbial control.
Maintenance requirements
● Activated carbon and ultrafiltration membrane: The filter element needs to be replaced regularly, and the maintenance cost is low.
● Reverse osmosis membrane: The maintenance cycle is long, but the replacement cost is high, and it needs to be cleaned to avoid membrane clogging.
● Ion exchange resin: The resin needs to be regenerated or replaced regularly.
● Ultraviolet disinfection: Make sure the lamp is clean and the light intensity is stable.
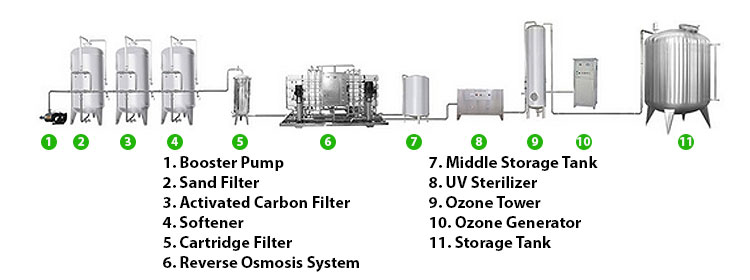
How to choose the right filtration system?
Depending on the water quality conditions and actual needs of your home location, different types of filtration systems can be selected or combined:
● For areas with good water quality: If the water source is drinking water treated by water plants, but there are problems with odor or residual chlorine, you can choose a combined system of activated carbon and ultrafiltration membrane. This configuration can not only retain minerals but also improve the taste. .
● For areas with poor water quality: If the water contains high dissolved salts, heavy metals or other chemical pollutants, it is recommended to use a reverse osmosis system and cooperate with a mineralization filter to improve the quality of the effluent.
● For areas with hard water: Hard water can easily lead to scale problems, so you can choose an ion exchange resin system for softening, and if necessary, install a reverse osmosis system to deal with other pollutants.
● Users who are sensitive to microbial contamination: In rural areas or special areas, where water sources may be contaminated by bacteria and viruses, you can choose an ultrafiltration membrane system combined with ultraviolet disinfection.




