How many kWh does a 20m³/hr seawater RO unit consume per day?
As the global water shortage problem becomes increasingly serious, desalination technology has gradually become an important means to solve the shortage of fresh water resources. Recently, a study on a 20 cubic meter per hour (20m³/hr) seawater reverse osmosis device has attracted widespread attention.
This device can not only efficiently convert seawater into drinkable fresh water, but also has a relatively low energy consumption level, providing the possibility for large-scale promotion and application in the future.
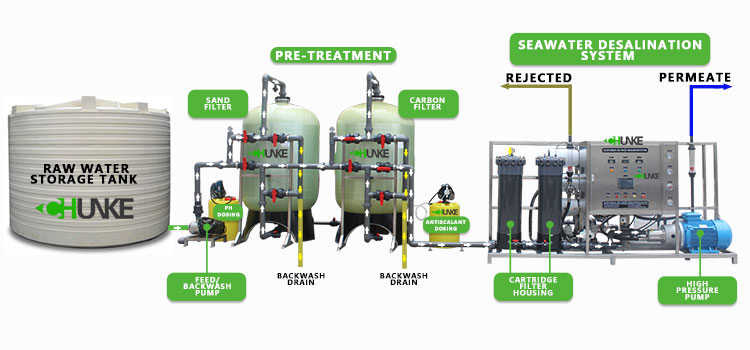
Background and development of seawater desalination technology
The history of desalination technology can be traced back hundreds of years, but it was not until the mid-20th century, with the rise of reverse osmosis technology, that desalination truly became a reality. Reverse osmosis technology applies pressure to pass seawater through a semi-permeable membrane, filtering out salt and impurities, thereby obtaining pure fresh water. The core of this technology lies in the selection of membrane materials and the energy efficiency of the system.
In recent years, with the advancement of materials science and engineering technology, the performance of reverse osmosis membranes has been continuously improved and energy consumption has been reduced. However, despite significant technological progress, the high energy consumption of desalination remains a challenge. Traditional reverse osmosis devices usually consume about 3-6 kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity for each cubic meter of fresh water produced, which poses certain limitations to large-scale promotion and application.
Technical highlights of 20m³/hr reverse osmosis device
The 20m³/hr seawater reverse osmosis device reported this time has achieved significant breakthroughs in energy consumption. According to the research team, the total power consumption required to operate the device for one day (24 hours) is significantly lower than traditional technology, thanks to the following key technological innovations:
1. High-efficiency reverse osmosis membrane: The device adopts the latest generation of high-efficiency reverse osmosis membrane, which has higher water flow rate and lower salt rejection rate. This membrane material not only improves desalination efficiency, but also significantly reduces energy consumption.
2. Advanced energy recovery device: The system is equipped with an advanced energy recovery device, which greatly reduces the total energy consumption of the system by recovering and reusing the energy in high-pressure concentrated brine.
3. Intelligent control system: Through the intelligent control system, operating parameters are monitored and adjusted in real time to ensure that the device operates at optimal energy efficiency. This not only reduces power consumption, but also extends the service life of the equipment.
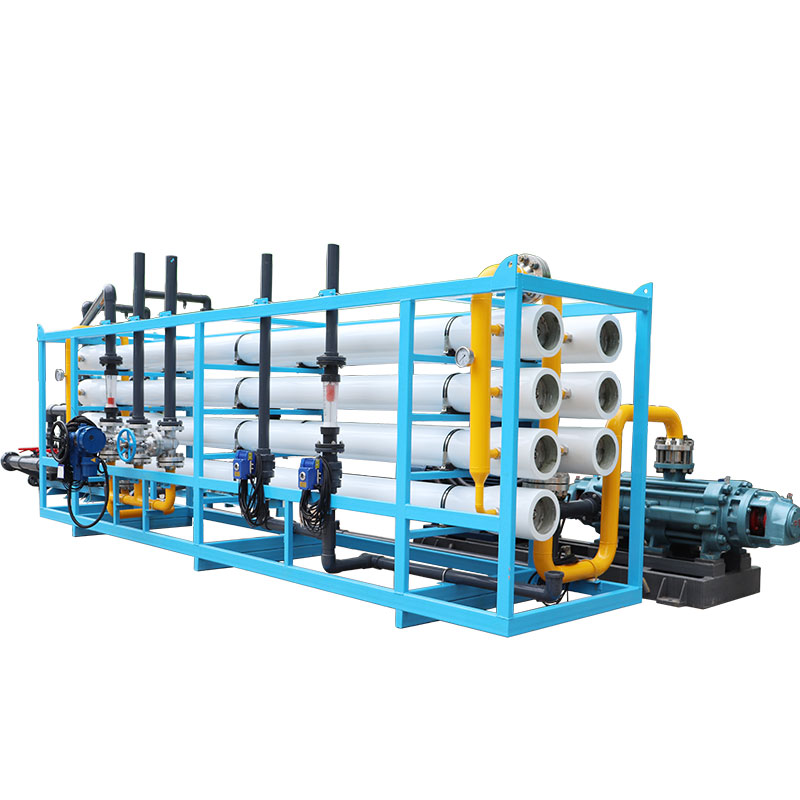

Energy consumption analysis for one day's operation
According to experimental data, the power consumption required for a 20m³/hr reverse osmosis device to operate for one day (24 hours) under ideal conditions is approximately 240 kilowatt hours (kWh). This data shows that the electricity consumption per cubic meter of fresh water is about 0.5kWh, which is far lower than the energy consumption level of traditional devices. This means that the device can produce 480 cubic meters of fresh water a day, while consuming only as much electricity as an average household uses for a month.
In order to better understand this level of energy consumption, we can compare the following aspects:
1. Compared with traditional devices: Traditional reverse osmosis devices consume about 3-6kWh of electricity per cubic meter of fresh water, while this device only requires 0.5kWh, which means that its energy consumption is reduced by about 80% to 90%.
2. Comparison with other water treatment technologies: Other common water treatment technologies, such as distillation and electrodialysis, usually have higher energy consumption and are difficult to compare with this device.
3. Comparison with daily electricity consumption: An average household consumes about 300-400kWh of electricity per month, while the device consumes 240kWh of electricity per day, which is equivalent to a household's electricity consumption for two to three weeks. This shows that while the device produces water efficiently, energy consumption is also significantly controlled.
Commercialization prospects and applications
Not only has this technological breakthrough been successful in a laboratory setting, the research team also plans to conduct large-scale testing in practical applications. If the test results are as expected, this technology is expected to be widely used in the following fields:
1. Coastal water-scarce areas: For coastal areas where seawater resources are abundant but freshwater resources are scarce, this technology can provide local residents with a reliable source of drinking water and improve the quality of life.
2. Offshore platforms and ships: Offshore oil platforms, fishery bases, and ocean-going ships that require a large supply of fresh water will also benefit from this and reduce their dependence on land fresh water resources.
3. Emergency rescue and post-disaster reconstruction: In areas where natural disasters occur frequently, this portable, high-efficiency desalination device can be quickly deployed to provide emergency drinking water supply to the affected people.
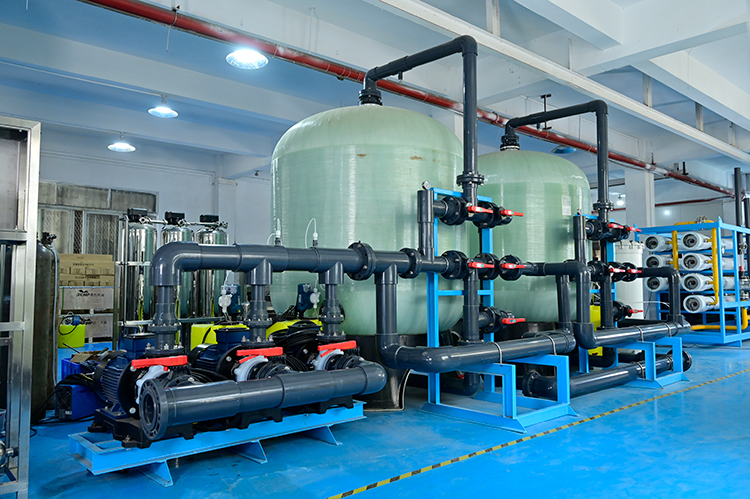

Future prospects and challenges
Although the 20m³/hr seawater reverse osmosis device has demonstrated significant technical advantages, it still faces some challenges in the process of achieving large-scale commercial application. The first is the cost issue. Although energy consumption is reduced, initial investment and equipment maintenance costs still need to be considered. Secondly, there is the environmental impact. The disposal of concentrated brine needs to be properly solved to avoid secondary pollution to the marine ecosystem.
In addition, continuous improvement and innovation of technology remain key. The research team stated that it will continue to work on the optimization of membrane materials and energy recovery systems to continuously improve the overall performance and economy of the device. At the same time, strengthening international cooperation and technical exchanges is also an important way to promote the development of seawater desalination technology.
In short, the breakthrough in energy consumption control of the 20m³/hr seawater reverse osmosis device has injected new hope into the application prospects of seawater desalination technology. With the continuous advancement of technology and the gradual reduction of costs, this device is expected to be widely used in water-scarce areas around the world in the future, contributing to the sustainable development of human society.