Which desalination device is suitable for agricultural water?
As global climate change and population growth intensify, water shortages are becoming increasingly serious, especially in arid and semi-arid regions, where agricultural water use has become a key issue. Desalinated water has received increasing attention as a potential solution. So, is desalinated water good for agriculture? Which desalinators are suitable for agricultural use? This article will explore these questions in depth.

What is desalinated water?
Desalinated water is fresh water obtained by removing salt and other impurities from seawater or brackish water. There are two main methods for the desalination process: thermal and membrane. The thermal method uses heating evaporation and condensation to separate water from salt, while the membrane method relies on a semipermeable membrane to separate water molecules from salt under pressure, of which the most common membrane method is reverse osmosis (RO).
Desalinated water is commonly used for drinking water supply, industrial water, and agricultural irrigation. In agriculture, desalinated water is seen as an alternative to traditional freshwater resources, especially in areas where water resources are scarce.
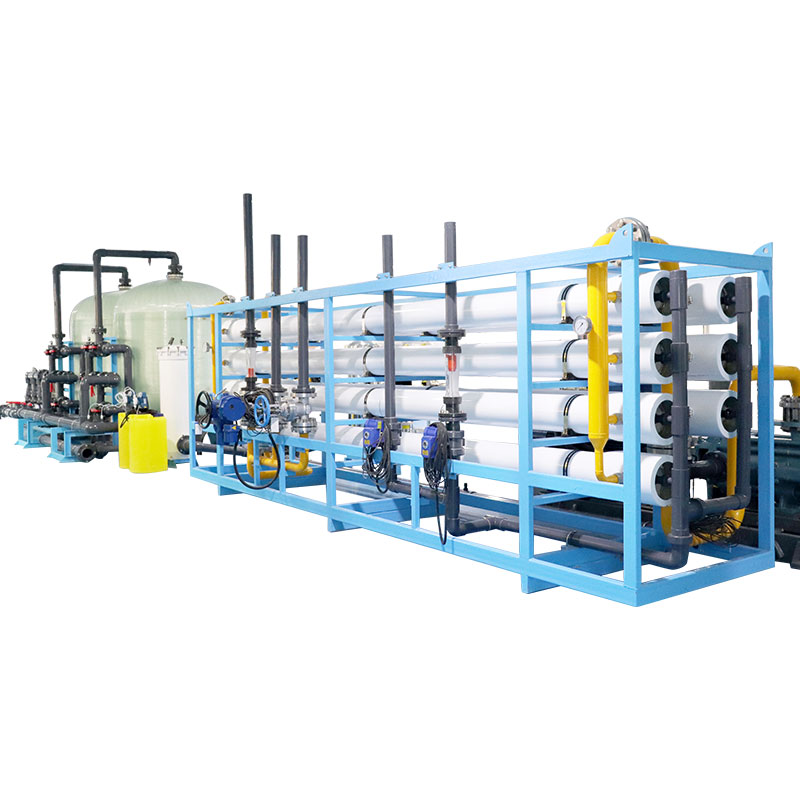

Is desalinated water good for agriculture?
The impact of desalinated water on agriculture can be analyzed from the following aspects:
The impact of water quality on crops
The quality of desalinated water is generally better than that of ordinary surface water and groundwater, especially in terms of salt content and mineral content. The low salinity and low hardness of desalinated water make it suitable for irrigating salt-sensitive crops, such as fruits, vegetables and flowers. However, the low mineral content in desalinated water may cause crops to lack necessary trace elements, such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, etc. This means that when using desalinated water for irrigation, these elements may need to be supplemented to ensure the healthy growth of crops.
Soil salinization problem
Although the salt content in desalinated water is low, long-term use of desalinated water for irrigation may lead to soil salinization. The reason is that the low conductivity and low mineral content of desalinated water may make it difficult for the residual salt in the soil to be fully flushed, thereby accumulating in the soil and gradually forming salinization. This may have an adverse effect on the growth of crops, so when using desalinated water, the salt content of the soil needs to be regularly tested and managed.
Sustainable use of water resources
The use of desalinated water can alleviate the shortage of fresh water resources, especially in areas with scarce water resources. For agriculture, this means that farmland can get sufficient irrigation water even in dry seasons or when groundwater resources are exhausted, thus ensuring the yield and quality of crops. However, the high energy consumption and high cost in the production process of desalinated water also need to be considered, especially for large-scale agriculture, the economic feasibility of desalinated water remains a challenge.
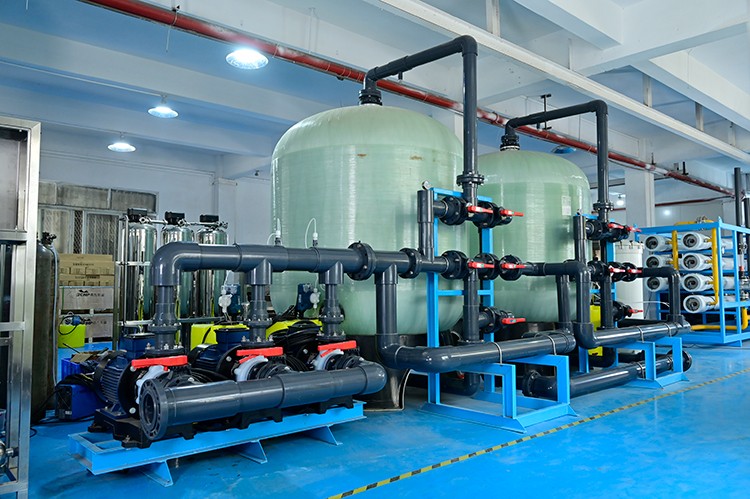

Which desalinator is suitable for agricultural water use?
When considering the use of desalinated water for agricultural irrigation, it is crucial to choose a suitable desalinator. Different desalination technologies and equipment have their own unique advantages and disadvantages. The following desalinators are suitable for agricultural water use.
Reverse osmosis desalinator
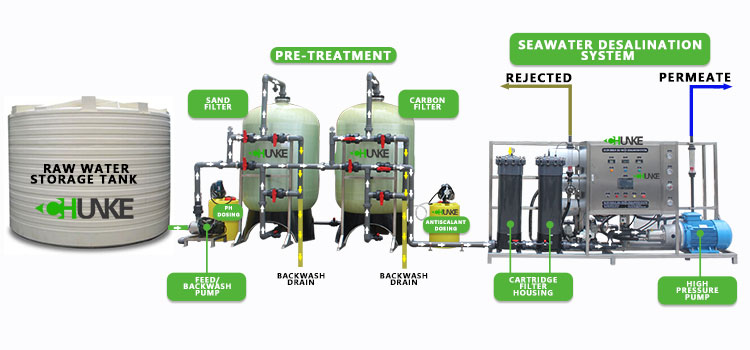
Reverse osmosis (RO) technology is one of the most commonly used desalination methods. RO desalinators separate water molecules and dissolved salts under pressure through semi-permeable membranes to produce high-purity fresh water. For agriculture, the advantage of reverse osmosis desalinators is that they can effectively remove salts and other dissolved substances in water and provide high-quality irrigation water.
Advantages of RO desalination:
● Efficient removal of salt and impurities
● Excellent water quality, suitable for irrigation of salt-sensitive crops
● Relatively mature system, relatively stable technology
Disadvantages of RO desalination:
● High energy consumption
● Requires regular replacement of membrane elements, high maintenance costs
● Produced brine needs to be properly handled
For large-scale agricultural irrigation, RO desalination may be more suitable for supplementing groundwater or surface water rather than as the only water source.
Electrodialysis desalination
Electrodialysis (ED) technology uses an electric field to drive ions through a selective ion exchange membrane to remove salt from water. Compared with RO, ED desalination has advantages in energy consumption and is particularly suitable for treating water sources with moderate salt content, such as brackish water.
Advantages of electrodialysis desalination:
● Relatively low energy consumption, suitable for large-scale use
● The degree of desalination can be precisely controlled to retain some beneficial minerals
● The system can be adjusted according to water quality, with high flexibility
Disadvantages of electrodialysis desalination:
● Limited processing capacity for high-salinity water sources
● High system complexity, requiring professional knowledge for operation and maintenance
● Large initial equipment investment
Electrodialysis desalination is suitable for small and medium-sized agricultural projects, especially in areas with relatively good water quality, which can reduce energy consumption and reduce the impact on soil salinization.
Low-temperature multi-effect distillation (LT-MED) desalination
Low-temperature multi-effect distillation (LT-MED) is a device that uses multi-stage evaporation and condensation technology to desalinate seawater or brackish water. This desalination device usually operates at low temperatures and is suitable for agricultural water with high water quality requirements.
Advantages of Low Temperature Multi-Effect Distillation (LT-MED) Desalination:
● Stable water quality, suitable for irrigation of high-value crops
● Reliable operation, long system life
● Low energy consumption, suitable for long-term operation
Disadvantages of Low Temperature Multi-Effect Distillation (LT-MED) Desalination:
● Complex system, high installation and maintenance costs
● Large equipment footprint, not suitable for small farms
● High initial investment, long payback period
LT-MED desalination is more suitable for high value-added agriculture, such as flower planting, orchards, etc., because of its excellent water quality and stable system operation, but the high initial cost and long-term investment return need to be considered.
Evaporation Crystallization Desalination
Evaporation crystallization is a method of separating salts by evaporating water and crystallizing it. Although this method consumes a lot of energy, it is the only effective desalination method for extremely high-salinity water sources (such as groundwater or industrial wastewater in some mining areas).
Advantages of evaporation crystallization desalination:
● Able to treat water sources with extremely high salt content
● Pure water quality, almost no salt
● Recyclable salt for industrial or agricultural purposes
Disadvantages of evaporation crystallization desalination:
● Extremely high energy consumption and expensive operating costs
● Complex system, professional maintenance required
● Only suitable for water source treatment under specific conditions
The application of evaporation crystallization desalination in agriculture is relatively limited, but in some special cases (such as the cultivation of specific crops in high-salinity areas) it may be the only viable option.
Agricultural application examples and challenges of desalinated water
Although the application of desalinated water in agriculture has potential, there are still some challenges in actual operation. First, the cost of desalinated water is high, which may be a reasonable choice for cash crops (such as fruits and flowers), but it is not economical for large-scale food crops. In addition, the long-term use of desalinated water may lead to soil salinization, so it is necessary to combine other water sources and irrigation technologies (such as drip irrigation and micro-sprinkler irrigation) to reduce this risk.
Secondly, the production and distribution of desalinated water requires a sound infrastructure. For remote farms, transporting and storing desalinated water can add additional costs and complexity.




