Why do saltwater reverse osmosis use polyamide membranes?
In modern water treatment technology, reverse osmosis (RO) is the most widely used method, especially in the fields of seawater desalination and saltwater purification. The core component of reverse osmosis is the membrane, and among the many membrane materials, polyamide membrane has become the preferred material for treating saltwater due to its unique advantages.
This article will discuss in detail why polyamide membranes are commonly used in saltwater reverse osmosis and the specific advantages of this membrane material.
What is the basic principle of reverse osmosis?
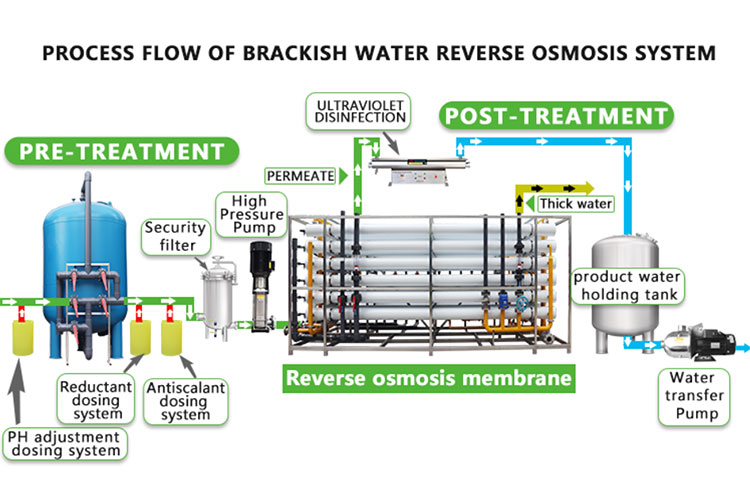
Reverse osmosis is a technology that separates solutes and solvents in water through a semipermeable membrane. By applying pressure, water molecules are forced to pass through the semipermeable membrane, while solutes (such as salts, impurities) are retained on one side of the membrane, thereby achieving the purpose of purification or desalination. Reverse osmosis technology is widely used in seawater desalination, industrial wastewater treatment, drinking water purification and other fields.
The reverse osmosis membrane is the core component of the entire technology, which determines the separation efficiency and effluent quality of the system. The choice of membrane depends on many factors, including membrane material, pore size, chemical stability and durability. For the treatment of salt water and seawater, the choice of membrane material is particularly critical because the salt concentration in these water sources is higher and the requirements for membranes are more stringent.
What is polyamide membrane?
Polyamide membrane is a thin film made of polyamide material, whose chemical structure is mainly composed of repeated amide groups (-CONH-). This material has excellent chemical stability and mechanical strength, which enables it to maintain stable performance under high pressure and complex water quality environments.
The manufacturing process of polyamide membranes usually involves steps such as solution polymerization, coating, drying and cross-linking. The final membrane has a dense surface layer and a porous support layer. This structure enables the membrane to efficiently separate salt from water and has good water permeability.

Why is polyamide membrane commonly used in salt water reverse osmosis?
High salt separation capacity
Salt water and seawater contain a large amount of dissolved salts, which must be effectively removed to obtain fresh water. Polyamide membranes have extremely high salt separation capacity and can intercept most of the dissolved salts. The salt content of the effluent can be as low as 5-10 ppm (parts per million), which is far lower than the requirements of drinking water standards.
This efficient salt separation ability makes polyamide membrane the first choice for treating high-salinity water sources, especially in the field of seawater desalination, where polyamide membrane is almost the only choice.
Excellent water permeability
Although polyamide membrane has high salt separation ability, it does not sacrifice water permeability. By optimizing the pore size and structure of the membrane, polyamide membrane can maintain a high water permeability under high pressure, which means that under the same operating conditions, a higher water yield can be obtained by using polyamide membrane.
This balanced characteristic enables polyamide membrane to efficiently treat high-salinity water sources while maintaining the economy and operating efficiency of the system.
Good anti-fouling performance
Brewery and seawater contain not only salt, but also organic matter, microorganisms and other suspended particles. These pollutants are easy to adhere to the membrane surface, causing membrane pollution and clogging. Polyamide membrane has good anti-fouling performance, especially through surface chemical treatment or adding anti-fouling layer, which further enhances its anti-fouling ability under harsh water conditions.
This characteristic reduces the frequency of membrane cleaning and extends the service life of the membrane, thereby reducing the maintenance cost of the system.

What are the specific advantages of polyamide membrane?
One of the biggest advantages of polyamide membranes is the combination of high selectivity and high flux. Selectivity refers to the ability of the membrane to effectively distinguish and intercept molecules of different sizes or properties, while flux refers to the amount of water passing through the membrane per unit time. In the reverse osmosis process, these two parameters are often difficult to achieve at the same time, but polyamide membranes have successfully achieved a balance between high selectivity and high flux through their unique structural design. This property enables polyamide membranes to effectively remove salt from salt water while maintaining a high water output rate to meet the needs of large-scale industrial and domestic water.
Secondly, salt water may contain a variety of chemical components, such as chloride ions, sulfates, etc., which may corrode or damage certain membrane materials. Polyamide membranes have excellent chemical resistance and can maintain stability for a long time in high-concentration salt solutions, and are not easy to degrade or age.
In addition, the durability of polyamide membranes is also excellent. Under normal operating conditions, they can usually be used for 3-5 years or even longer. This long life reduces the frequency of membrane replacement and further reduces the operating cost of water treatment systems. Polyamide membranes can also maintain stable performance under a wide range of operating conditions, whether under high pressure, low temperature or high salt concentration conditions, and can operate stably. This wide operating range enables polyamide membranes to perform well in a variety of different application scenarios and have high adaptability.
Finally, although the initial cost of polyamide membranes is high, the overall operating cost is relatively low due to their efficient performance and long life. Less frequent replacement, lower cleaning and maintenance requirements make water treatment systems using polyamide membranes have obvious cost advantages in long-term operation.

How do polyamide membranes perform in different application scenarios?
Seawater desalination is one of the most widely used areas for polyamide membranes. In a high-salinity seawater environment, polyamide membranes can efficiently remove salt and produce fresh water that meets drinking water standards. Many large seawater desalination plants around the world use polyamide membranes, such as the Ashkelon Desalination Plant in Israel and the Rabigh Desalination Plant in Saudi Arabia.
In the field of industrial wastewater treatment, polyamide membranes are used to treat wastewater with high salt content and complex chemical composition. Its excellent chemical resistance and anti-fouling properties make it widely used in this field. Polyamide membranes can not only effectively remove salt from wastewater, but also intercept many harmful chemicals to ensure that the effluent meets the standards.
In addition, polyamide membranes are also used for drinking water purification, especially in water sources with high hardness or high salinity. Their high selectivity can effectively remove heavy metals, salts and other pollutants in water, providing safe and reliable drinking water.




