Which water filtration equipment is best for drinking water?
In modern society, the safety and quality of drinking water have attracted more and more attention. With the intensification of water pollution problems, choosing a suitable water filtration equipment has become an important means to ensure the safety of household drinking water.
So, facing the dazzling array of water filtration products on the market, which equipment is best for drinking water filtration? This article will explore the principles, advantages, disadvantages and applicability of several common water filtration equipment in depth to help readers make wise choices.
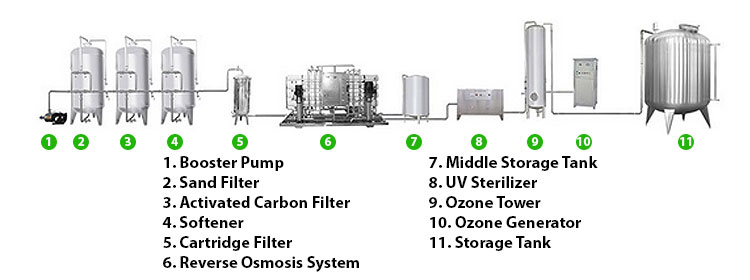
Common types of water filtration equipment
1. Activated carbon filter
● Working principle: Activated carbon filters use the adsorption properties of activated carbon to purify water by adsorbing organic matter, residual chlorine, odor and some heavy metals in water. The porous structure of activated carbon gives it a large surface area, thereby improving the adsorption capacity.
Advantages:
● Remove odor and residual chlorine: Activated carbon filters can effectively remove odor and residual chlorine in water and improve the taste of water.
● Low cost: Activated carbon filters are relatively cheap and have a long service life, making them an economical choice.
Disadvantages:
● Unable to remove all pollutants: Activated carbon filters have limited removal effects on bacteria, viruses and dissolved inorganic substances (such as nitrates and heavy metals).
● Filter cartridges need to be replaced regularly: The adsorption capacity of activated carbon is limited, and the filter cartridge needs to be replaced after a period of use to maintain the filtering effect.
● Applicability: Suitable for families with low requirements for water quality, mainly used to improve the taste of water and remove residual chlorine.
2. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Filter
● Working Principle: The reverse osmosis filter passes water molecules through the membrane pores under high pressure through a semipermeable membrane, while pollutants such as dissolved salts, heavy metals, bacteria and viruses are retained on the other side of the membrane to achieve the purpose of water purification.
Advantages:
● High efficiency filtration: The pore size of the reverse osmosis membrane is very small, which can remove almost all pollutants in the water, including dissolved salts, heavy metals, bacteria and viruses.
● Wide application: Due to its high efficiency, the reverse osmosis system is widely used in household drinking water purification and industrial water treatment.
Disadvantages:
● High cost: The initial investment and maintenance costs of the reverse osmosis system are high.
● Wastewater problem: The reverse osmosis system will produce a certain proportion of wastewater, which is generally 2-3 times the amount of water produced, and this wastewater needs to be properly treated.
● Demineralization: The reverse osmosis filter not only removes harmful substances, but also removes beneficial minerals in the water, so some systems are equipped with a mineral refill device.
● Applicability: Suitable for families with high water quality requirements, especially in areas with serious water pollution or poor water quality.

3. Ultrafiltration (UF) filter
● Working principle: The ultrafiltration filter uses ultrafiltration membrane to remove suspended matter, colloids, bacteria and some organic matter in the water through microfiltration, ultrafiltration and other technologies.
Advantages:
● No electricity required: The ultrafiltration system usually does not require electricity support and is easy to use.
● Retain minerals: The pore size of the ultrafiltration membrane is large, which can retain beneficial minerals in the water.
Disadvantages:
● Limited filtration accuracy: The pore size of the ultrafiltration membrane is relatively large, and it cannot remove dissolved salts and some small molecular organic matter.
● Limited scope of application: For areas with serious water pollution, the water purification effect of the ultrafiltration system may not be ideal.
● Applicability: Suitable for areas with less water pollution, mainly used to remove suspended matter and bacteria, and retain beneficial minerals in the water.
4. Ultraviolet (UV) sterilizer
● Working principle: The UV sterilizer irradiates the water flow with an ultraviolet light source, destroys the DNA structure of microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses, and makes them lose their reproductive ability, thereby achieving the effect of disinfection.
Advantages:
● High efficiency sterilization: The UV sterilizer has a high efficiency in killing bacteria and viruses in the water.
● No change in water quality: The UV sterilizer will not change the chemical composition of water and maintain the original properties of water.
Disadvantages:
● No filtering function: The UV sterilizer can only kill microorganisms, but cannot remove dissolved salts, organic matter and heavy metals in the water.
● Power required: The UV sterilizer requires power support, and the power supply needs to be stable during use.
● Applicability: Suitable for use in combination with other water filtration systems as a secondary disinfection method to ensure the microbial safety of drinking water.

Comprehensive comparison and selection suggestions
When choosing drinking water filtration equipment, the following factors need to be considered comprehensively:
● Water source quality: Choose appropriate filtration equipment according to the water source quality in the area where the family is located. If the water source is seriously polluted, it is recommended to choose a reverse osmosis filter; if the water source quality is good, you can choose an activated carbon filter or an ultrafiltration filter.
● Cost budget: Choose the appropriate equipment according to the family budget. Although the reverse osmosis system has a good filtration effect, it is more expensive; activated carbon filters and ultrafiltration filters are economical and suitable for families with limited budgets.
● Usage habits: Consider the family's usage habits and maintenance capabilities. The reverse osmosis system requires regular replacement of filter elements and wastewater treatment, which is more complicated to use; activated carbon filters and ultrafiltration filters are simple to use and easy to maintain.
● Water quality requirements: Choose the appropriate equipment according to the family's requirements for water quality. If the water quality requirements are high, it is recommended to choose a reverse osmosis system; if the main focus is on removing odors and residual chlorine, you can choose an activated carbon filter.
Conclusion
Choosing appropriate drinking water filtration equipment is an important means to ensure the safety of family drinking water. Different types of water filtration equipment have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the applicable environment and needs are also different.
When choosing, you should comprehensively consider the water source quality, cost budget, usage habits and water quality requirements to make the most appropriate choice.




