How to deal with hard water and iron in water?
In many parts of the world, water quality is a topic of great concern, especially hard water and high iron content in water, which not only affects the quality of life, but may also have adverse effects on health.
This article will explore in detail the sources, effects and treatment methods of hard water and iron in water to help readers better understand and solve these problems.

What is hard water?
Hard water refers to water containing high concentrations of calcium and magnesium ions. According to the different hardness components in water, hard water can be divided into temporary hard water and permanent hard water. Temporary hard water mainly contains calcium bicarbonate and magnesium bicarbonate, which can be removed by boiling, while permanent hard water contains calcium sulfate, magnesium sulfate, etc., which cannot be removed by boiling.
Source of hard water
The formation of hard water is closely related to geological conditions. When water flows through underground rock formations, it dissolves calcium and magnesium ions in the rocks, causing the water quality to become hard. Typical hard water areas include areas rich in limestone, dolomite and gypsum deposits.
Effects of hard water
1. Household appliances
Calcium and magnesium ions in hard water can form scale in heating equipment (such as water heaters and boilers), reducing equipment efficiency, increasing energy consumption, and even causing equipment failure.
2. Laundry effects
Hard water can reduce the cleaning ability of detergents, making clothes hard and gray after washing, and the fibers brittle.
3. Skin and hair
Hard water can make the skin dry and itchy, and the hair loses its luster and becomes dry and brittle.
4. Pipeline system
Hard water accumulates scale in pipes, which can cause pipe blockage, reduce water flow, and increase maintenance costs.
How to deal with hard water?
1. Use a water softener
Water softeners are the most common way to deal with hard water. Water softeners use ion exchange resins to replace calcium and magnesium ions in water with sodium ions, thereby softening the water. Water softeners need to be regenerated regularly with salt to maintain their softening effect.
2. Magnetization treatment
Magnetization treatment is a method of changing the properties of minerals in water through the action of a magnetic field, making it less likely to form scale. Although the effect is limited, it still has certain value for certain application scenarios, such as industrial circulating cooling water systems.
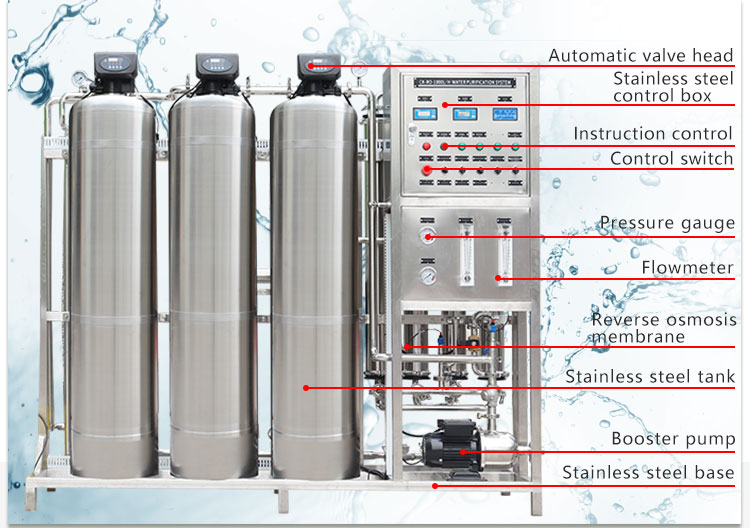
3. Reverse osmosis filtration
The reverse osmosis filtration system removes calcium and magnesium ions from water through a semipermeable membrane, which can effectively soften the water. This method not only removes hardness, but also removes other impurities to provide high-quality drinking water.
4. Adding chemical agents
In equipment such as boilers, chemical agents (such as polyphosphates) can be added to prevent scale formation. These agents react with calcium and magnesium ions to form soluble compounds to prevent their precipitation.
What is iron in water?
Iron in water usually exists in dissolved or suspended states, mainly in the form of divalent iron (Fe²⁺) and trivalent iron (Fe³⁺). High iron content in water will cause the water to turn yellow, have a rusty smell, and easily come into contact with air to form iron oxide precipitation.
Sources of iron in water
Iron in water mainly comes from the following aspects:
Geological conditions: When water flows through iron ore-rich strata, it dissolves iron ions into the water.
Industrial pollution: Industrial wastewater discharge, mining and other activities can also lead to an increase in the iron content in water bodies.
Old pipes: Water transported by iron pipes, especially in old pipes, will also increase the iron content in the water due to rust.
Impact of iron in water
1. Drinking water quality
High iron content in water will cause the water to turn yellow and have an odor, affecting the taste and hygiene of drinking water.
2. Household appliances
Water with high iron content will form iron scale in household appliances, affecting the service life and performance of the equipment.
3. Clothing
Rust will stain clothes with yellow stains, which are difficult to clean.
4. Pipeline system
Rust deposits in pipes will cause pipe blockage and affect the smooth flow of water.
How to deal with iron in water?
1. Oxidation precipitation method
Oxidation precipitation is a common method for treating iron in water. Through aeration or adding oxidants (such as potassium permanganate, chlorine), the dissolved divalent iron is oxidized to trivalent iron to form insoluble iron oxide precipitation, which is then removed by precipitation and filtration.
2. Filtration method
The filtration method removes iron ions and iron oxide particles from water through physical filtration equipment such as sand filters and activated carbon filters. This method is suitable for water treatment with low iron content.
3. Ion exchange method
The ion exchange method removes iron ions from water through ion exchange resins. This method can not only remove iron ions, but also remove other metal ions at the same time to improve water quality.
4. Reverse osmosis method
The reverse osmosis method removes iron ions and other impurities from water through a semipermeable membrane to provide high-quality pure water. This method is suitable for deep treatment of household drinking water and industrial water.

Actual case analysis
Case 1: Household users use water softeners
Ms. Li lives in a hard water area and installed a water softener for 2,000 yuan. Ms. Li said: "Since the installation of the water softener, the failure rate of the water heater and washing machine at home has been significantly reduced, and the condition of the skin and hair has also improved. Although salt needs to be added regularly, the overall maintenance cost is not high."
Case 2: Corporate users use reverse osmosis systems
Mr. Zhang runs a food processing plant and uses a reverse osmosis system to deal with iron and hardness problems in water. Mr. Zhang said: "Although the initial investment of the reverse osmosis system is large, the water quality has been significantly improved, the production process is more stable, the product quality has been improved, and the economic benefits are obvious."
Case 3: The community uses the oxidation precipitation method
The tap water in a community has a high iron content, and the water quality has turned yellow, affecting the lives of residents. The community adopted the oxidation precipitation method to treat the water quality, and successfully removed the iron in the water through aeration and adding oxidants. The community leader said: "The water quality has improved significantly after treatment, and the residents have responded very well."
Conclusion
Hard water and high iron content in water not only affect the quality of life, but may also have adverse effects on health. By understanding the characteristics and applicable scenarios of different treatment methods, users can choose the right solution to improve water quality and improve the quality of life. Whether it is a home user or a corporate user, a reasonable water treatment solution can bring long-term economic and health benefits.