Why Shouldn't You Use Reverse Osmosis Water?
Reverse osmosis (RO) water purification systems are widely used in homes and industries due to their ability to efficiently remove contaminants from water. However, there are some situations where using reverse osmosis water may not be the best option, especially for cooking or eating. This article will look at why you shouldn’t use reverse osmosis water and the problems that may arise from using reverse osmosis water in eating and cooking.
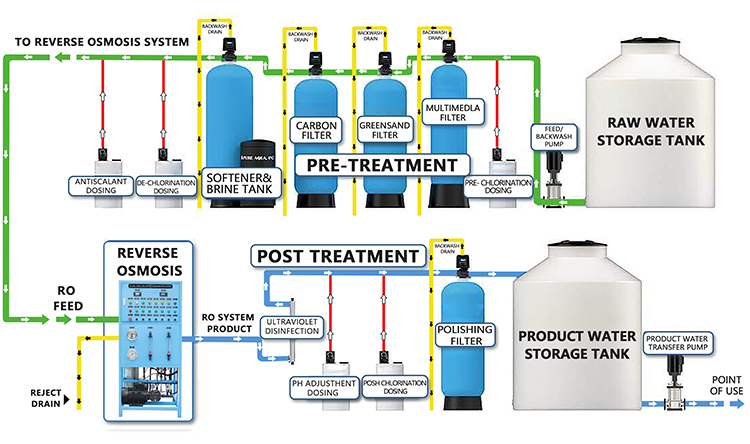
Why shouldn't you use reverse osmosis water?
The purity of reverse osmosis water is indeed one of its main advantages, as it effectively removes impurities, heavy metals, and other harmful substances from the water. However, this purity can become an issue when used in cooking. Reverse osmosis water may cause significant loss of essential elements in food.
When cooking vegetables, meats and grains, reverse osmosis water can cause up to 60% of the calcium and magnesium in the food to be lost. These minerals are essential for bone health and muscle function. Other trace elements, such as copper, manganese and cobalt, may be lost at even higher rates, as high as 66%, 70% and 86% respectively. These minerals and trace elements are essential for human health and nutritional balance, so cooking with reverse osmosis water may result in a decrease in the nutritional value of the food. Additionally, a lack of minerals in reverse osmosis water may have an impact on the taste and quality of your drinking water.
Reasons Not to Use Reverse Osmosis Water:
1. Nutrient loss:
Reverse osmosis water removes dissolved solids and contaminants from the water, but it also removes essential minerals such as calcium and magnesium. The absence of these minerals can result in the loss of nutrients from food during the cooking process.
2. Decrease in food quality:
Reverse osmosis water may cause a decrease in the quality of cooked food, especially when boiling vegetables, grains and meat. Because reverse osmosis water lacks minerals, it will affect the taste and texture of food.
3. Loss of trace elements:
Cooking with reverse osmosis water may result in the loss of trace elements in food. These elements are vital to human health and include trace elements such as copper, manganese, and cobalt.
4. Potential health risks:
Long-term drinking or use of reverse osmosis water may lead to insufficient intake of minerals and trace elements in the human body, leading to potential health problems such as osteoporosis, muscle spasms, etc.
Therefore, the use of reverse osmosis water requires caution when it comes to eating and cooking, especially considering the impact on the nutritional value and quality of food.

What is the difference between reverse osmosis water and other types of drinking water?
Reverse osmosis water differs significantly from other types of drinking water in terms of purity and mineral content. Reverse osmosis water uses a semipermeable membrane to remove impurities, heavy metals, and other harmful substances from the water, making it extremely pure. However, this process also removes minerals from the water, leaving reverse osmosis water with a lower mineral content.
In contrast, other types of drinking water, such as mineral water and spring water, usually retain the natural minerals and trace elements in the water. These water sources come from underground or mountain springs without complex treatment, thus retaining the natural minerals and trace elements in the water.
Tap water is disinfected and filtered, and the mineral content depends on the source and local water treatment standards. In some areas, tap water may have a higher mineral content, while in other areas it may be lower.
How to avoid nutrient loss caused by reverse osmosis water?
Although reverse osmosis water has advantages in purifying water quality, there are some steps we can take to adjust our diet and cooking methods to avoid nutrient loss. The main measures are: remineralizing reverse osmosis water, choosing appropriate cooking methods, combining other water sources and dietary supplements.
1. Remineralize reverse osmosis water: By adding minerals to reverse osmosis water, calcium, magnesium and other trace elements in the water can be restored. This method helps reduce nutrient loss from food.
2. Choose the appropriate cooking method: When cooking with reverse osmosis water, you can choose cooking methods such as steaming and stewing to reduce the loss of nutrients.
3. Combine with other water sources: Mixing reverse osmosis water with other mineral water or water sources containing minerals can balance the mineral content.
4. Supplement nutrition: If there is a lack of minerals and trace elements in the diet, dietary supplements can be used to make up for it to ensure that the body receives adequate nutrition.
By taking these steps, you can continue to enjoy the purification benefits of reverse osmosis water while avoiding excessive loss of nutrients in your food.

What are the alternatives to reverse osmosis water?
Given that reverse osmosis water can cause nutrient loss in food, you may want to consider finding other water purification methods or water sources for your dietary and cooking needs. The main alternatives are: using activated carbon filters, using ion exchange filters, using natural mineral water and using groundwater and well water.
1. Activated carbon filter: Activated carbon filter can effectively remove organic matter, chlorine and other pollutants in water while retaining minerals in the water. They are a better alternative to reverse osmosis systems.
2. Ion exchange filter: Ion exchange filter removes impurities from water by exchanging cations and anions in the water. They maintain the mineral content of the water while purifying it.
3. Mineral water: Buying or using natural mineral water is an easy choice because mineral water is usually rich in minerals and trace elements and can provide high-quality drinking water.
4. Groundwater and Well Water: If you have a reliable source of groundwater or well water, you can use it as a source of drinking water. This water is often rich in minerals, but should be tested before use to ensure the water is safe.
By choosing these alternatives, you can preserve the nutrients in your diet while ensuring water quality.
Summary: While reverse osmosis water purification systems excel in many areas, they may require caution when it comes to eating and cooking. By understanding the possible nutrient losses from reverse osmosis water and taking appropriate measures or choosing alternative water sources, you can ensure the quality and health of your diet. No matter which method you choose, ensuring safe and healthy water quality is always the top priority.