Are all reverse osmosis water treatment equipment membranes the same?
Reverse osmosis (RO) water treatment technology is widely used in household, commercial and industrial water treatment systems because of its ability to efficiently remove impurities from water. The core component of the reverse osmosis equipment is the reverse osmosis membrane, which determines the effect of water treatment. However, many people are often confused when purchasing reverse osmosis equipment: Are all reverse osmosis water treatment equipment membranes the same? What are the raw materials of these membranes?
This article will explore these issues in depth to help readers better understand the types of reverse osmosis membranes and their production materials.
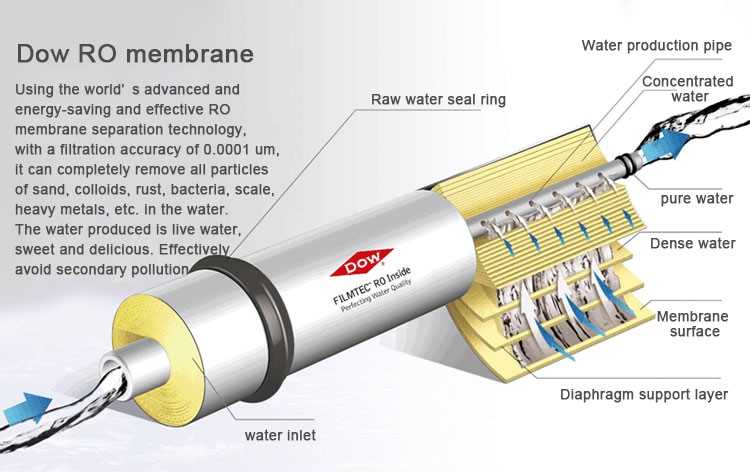
What is the function and principle of reverse osmosis membranes?
The main function of reverse osmosis membranes is to remove impurities such as dissolved solids (such as salts, heavy metals), organic matter, bacteria and viruses in water through physical separation to obtain pure water. The pore size of the reverse osmosis membrane is extremely small, usually 0.0001 microns, which enables it to intercept most impurities and only allow water molecules to pass through.
The working principle of reverse osmosis is based on the phenomenon of osmosis. In nature, water molecules flow from a low-concentration solution to a high-concentration solution through a semipermeable membrane until a concentration equilibrium is reached. In the reverse osmosis process, water molecules are forced to flow from a high-concentration solution to a low-concentration solution by applying external pressure, thereby achieving water purification.

Are all membranes of reverse osmosis water treatment equipment the same?
Although the working principle of reverse osmosis membranes is basically the same, reverse osmosis membranes can be divided into many types according to the usage scenarios, membrane materials and processes. Different types of reverse osmosis membranes differ in performance, durability and scope of application. Therefore, the membranes used in all reverse osmosis equipment are not exactly the same.
Classification by material
The materials of reverse osmosis membranes mainly include the following:
● Polyamide membrane (PA): Polyamide membrane is one of the most commonly used reverse osmosis membrane materials. It has excellent chemical stability and high desalination rate, and can effectively remove salts, heavy metals, bacteria and organic matter in water. Due to its excellent performance, polyamide membranes are widely used in seawater desalination, drinking water purification and industrial water treatment.
● Cellulose Acetate (CA): Cellulose Acetate is an early-applied reverse osmosis membrane material with good chlorine resistance, but relatively low durability and desalination rate. Nevertheless, cellulose acetate membranes still have application value in some specific water treatment scenarios.
● Composite membrane (Thin Film Composite, TFC): Composite membranes are usually composed of multiple layers of different materials and have higher desalination rates and better chemical resistance. Since composite membranes can take into account both high-efficiency filtration and long life, they are widely used in high-end water treatment equipment.
Classification by application scenario
Different application scenarios have different requirements for reverse osmosis membranes, so reverse osmosis membranes can also be classified according to the use scenario:
● Household reverse osmosis membranes: Household reverse osmosis membranes usually require higher water output and good filtration effects, and are often used in household drinking water purification systems. This type of membrane is usually made of composite materials to improve filtration efficiency and extend service life.
● Commercial reverse osmosis membranes: Commercial reverse osmosis membranes are usually used in restaurants, hotels, office buildings and other places, requiring higher filtration capacity and larger water treatment volume. In order to meet higher water quality requirements, commercial membranes often have better durability and anti-pollution ability.
● Industrial reverse osmosis membranes: Industrial reverse osmosis membranes are suitable for large-scale water treatment systems, such as power plants, chemical plants and pharmaceutical plants. Industrial membranes usually have higher anti-pollution ability, high temperature resistance and chemical stability to cope with more stringent water quality and operating conditions.
Classification by performance
According to the specific performance of reverse osmosis membranes, they can also be divided into different types such as high desalination membranes, high flux membranes and anti-pollution membranes:
● High desalination membranes: This type of membrane can remove more than 99% of dissolved solids in water and is suitable for applications with extremely high water quality requirements, such as seawater desalination and ultrapure water preparation.
● High flux membranes: High flux membranes are designed to increase water production and are suitable for occasions that require large amounts of treated water, such as industrial wastewater treatment and municipal water supply systems.
● Anti-pollution membranes: Anti-pollution membranes are designed for treating water sources containing high pollutants. They can effectively resist the erosion of pollutants such as organic matter, bacteria and colloids, and extend the service life of the membrane.

What are the raw materials of reverse osmosis membranes?
The raw materials of reverse osmosis membranes directly affect their performance and service life. Common reverse osmosis membrane raw materials include polyamide, cellulose acetate, polyethylene and polypropylene.
Polyamide
Polyamide is one of the most widely used raw materials for reverse osmosis membranes. Its chemical structure enables it to exhibit excellent chemical resistance and mechanical strength in water treatment. Polyamide membranes are usually composed of a multilayer structure, including a support layer, a semipermeable membrane layer and a protective layer. Among them, the semipermeable membrane layer is the core part, and its extremely small pore size can effectively remove most impurities in water. The advantages of polyamide membranes are high desalination rate, high chemical resistance and long life, but the disadvantage is that they are sensitive to chlorine and easily fail in high chlorine environments.
Cellulose Acetate
Cellulose acetate membranes are one of the main materials for the early application of reverse osmosis technology. Its advantage is that it has good resistance to chlorine, so it has certain advantages in treating chlorinated water sources. However, the desalination rate and mechanical strength of cellulose acetate membranes are relatively low, so they are gradually replaced by polyamide membranes. Despite this, cellulose acetate membranes still have value in some specific applications.
Composite Materials
Composite membranes are usually composed of multiple layers of materials, each of which is optimized to achieve specific functions. For example, the outermost membrane can enhance anti-pollution ability, the middle layer is responsible for high-efficiency filtration, and the innermost layer provides mechanical support. Composite membranes generally have better performance, such as high desalination rate, high flux and long service life, and are therefore widely used in high-end water treatment equipment.

Comparison of different reverse osmosis membranes
Polyamide membranes generally have the highest desalination rate, capable of removing more than 99% of dissolved solids, and are suitable for scenarios requiring ultrapure water. Cellulose acetate membranes have a lower desalination rate, usually between 85%-95%, and are suitable for applications with less demanding water quality.
Secondly, composite membranes have a longer service life and better chemical resistance due to their multi-layer design. Polyamide membranes have better durability in chlorine-free environments, but are prone to failure in chlorine-containing environments. Cellulose acetate membranes have strong tolerance to chlorine, but are prone to aging of the membrane structure during long-term use.
In addition, composite membranes generally have strong anti-pollution ability and are suitable for treating water sources containing high organic matter or high pollutants. Polyamide membranes and cellulose acetate membranes are slightly inferior in anti-pollution ability, especially in highly polluted environments, and may require more frequent cleaning and maintenance.
Through the above analysis, we can conclude that not all membranes of reverse osmosis water treatment equipment are the same. Different types of reverse osmosis membranes have significant differences in materials, performance, and applicable scenarios. Understanding these differences can help users make more informed decisions when purchasing reverse osmosis equipment, thereby ensuring that the selected equipment can meet specific water treatment needs.
The raw materials and manufacturing processes of reverse osmosis membranes directly affect their performance and life. Polyamide, cellulose acetate, and composite materials are the most common raw materials for reverse osmosis membranes, each with different advantages and scopes of application. Users should choose the appropriate reverse osmosis membrane material according to their specific needs to achieve the best water treatment effect.




