Can desalination make seawater drinkable?
In some arid and semi-arid areas, the shortage of freshwater resources has had a serious impact on social and economic development and people's daily lives. As one of the effective means to solve the shortage of freshwater resources, desalination has received more and more attention in recent years.
So, can desalination really make seawater drinkable? This article will discuss in detail the principles, technologies, application status of desalination, and its feasibility and challenges in drinking water supply.
What are the principles and technologies of desalination?
The basic principles of desalination:
Desalination is the process of converting seawater into fresh water by removing salt and other impurities in seawater through physical or chemical methods. The basic principle is to use the difference in salt concentration between seawater and freshwater, and separate the salt and impurities in seawater through specific treatment methods to obtain drinkable fresh water.
Common desalination technologies:
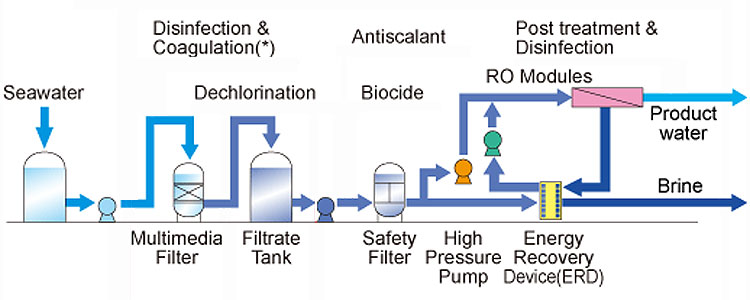
At present, there are two main technologies for desalination: reverse osmosis (RO) and multi-stage flash evaporation (MSF).
1. Reverse osmosis technology
Reverse osmosis technology uses a semipermeable membrane to intercept salt and impurities in seawater under high pressure, allowing only water molecules to pass through. The pore size of the reverse osmosis membrane is extremely small, which can effectively remove dissolved salts, bacteria, viruses and organic matter in the water. This technology has the advantages of low energy consumption, high water quality and simple operation. It is currently the most widely used seawater desalination technology.
2. Multi-stage flash evaporation technology
Multi-stage flash evaporation technology is to evaporate seawater step by step under different pressures through multi-stage heating and evaporation, and then condense into fresh water. This technology is suitable for large-scale seawater desalination projects, but it has high energy consumption and relatively high operating costs. It is mainly used in areas with rich energy resources.

Current application status of seawater desalination
1. Development of global seawater desalination
Currently, there are hundreds of seawater desalination plants in operation around the world, and the production capacity is increasing year by year. According to statistics from the International Desalination Association (IDA), as of 2023, the total global seawater desalination capacity has exceeded 95 million cubic meters/day. Seawater desalination has become an important water source guarantee for areas with scarce freshwater resources such as the Middle East, North Africa and Australia.
2. Typical Cases
2.1 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is one of the countries with the largest scale of seawater desalination in the world, and its fresh water supply mainly depends on seawater desalination. The country has one of the world's largest seawater desalination plants, the Rabigh Seawater Desalination Plant, with a daily production capacity of more than 1 million cubic meters, which meets the drinking water needs of a large population in the country.
2.2 Israel
Due to its geographical location and climatic conditions, fresh water resources in Israel are extremely scarce. The country has effectively solved the problem of domestic fresh water shortage by building a series of seawater desalination plants. For example, Israel's Sorek Seawater Desalination Plant is one of the world's largest reverse osmosis seawater desalination plants, with a daily production capacity of 625,000 cubic meters.
Safety of drinking desalinated water
1. Effluent water quality standards
Before drinking, desalinated water must undergo strict water quality testing to ensure that it meets drinking water standards. The World Health Organization (WHO) and national drinking water standards of various countries are generally adopted internationally to monitor and evaluate the water quality of desalinated water. Desalination technologies such as reverse osmosis and multi-stage flash evaporation can effectively remove salt, heavy metals, organic matter and microorganisms from seawater, so that the effluent water quality meets or even exceeds the drinking water standard.
2. Risk of secondary pollution
Although desalination technology can provide high-quality fresh water, secondary pollution still needs to be prevented during storage and transportation. For example, the pipelines and water storage facilities of the desalination plant need to be cleaned and maintained regularly to prevent bacterial growth and the invasion of harmful substances. In addition, in order to ensure the safety of drinking water, it is often necessary to install equipment such as ultraviolet disinfectors or ozone generators at the end.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of desalination?
Advantages of desalination:
1.1 Abundant resources
Seawater, as an abundant resource, accounts for more than 70% of the earth's surface area. Through desalination, almost unlimited fresh water supply can be obtained, which is an effective way to solve the shortage of fresh water resources.
1.2 High reliability
After years of development and application, desalination technology has become increasingly mature, and the effluent water quality is stable and reliable, which can meet the high standards of drinking water and industrial water.
1.3 Strong adaptability
Desalination technology is suitable for various coastline terrains and climatic conditions, especially in arid and semi-arid areas, and can effectively alleviate the shortage of fresh water resources.
Disadvantages of desalination:
2.1 High energy consumption
The desalination process consumes a lot of energy, especially the multi-stage flash evaporation technology has high energy consumption, resulting in high operating costs and strong dependence on energy.
2.2 Environmental impact
The discharge of concentrated brine produced during the desalination process will have a certain impact on the marine ecological environment. In addition, the use of chemical agents and energy consumption in the desalination process may also cause environmental problems.
2.3 Large initial investment
The construction and equipment investment of desalination plants is large, especially large-scale desalination projects, which require a lot of capital investment, which may pose economic pressure on some developing countries and regions.
Conclusion
As an effective means to solve the shortage of fresh water resources, desalination has broad application prospects and huge potential. Although there are currently challenges such as high energy consumption, environmental impact and large initial investment, these problems are expected to be gradually solved with the continuous advancement and innovation of technology.




