What is the difference between modern water filters and traditional water filters?
In the context of the increasingly serious water pollution problem and people's growing demand for healthy drinking water, water filtration technology has developed rapidly. There are significant differences between modern water filters and traditional water filters in terms of technical principles, performance effects, and ease of use.
This article will compare the two in detail to help readers better understand the advantages and advancements of modern water filtration technology.
What is a traditional water filter?
Traditional water filters generally refer to simple filtration devices that have been widely used over the past few decades. Common traditional filtering methods include:
1. Sand filter and gravel filter
Sand filtration and gravel filtration are one of the earliest water filtration methods. They remove suspended solids and particulate matter from the water through one or more layers of sand and gravel. This method is widely used in large-scale water treatment and preliminary purification of drinking water.
2. Activated carbon filter
Activated carbon filter removes organic matter, chlorine, odor and some heavy metals from water through the adsorption of activated carbon. Traditional activated carbon filters are mostly used for secondary purification of household water dispensers and municipal water supply systems.
3. Ceramic filter element
Ceramic filter elements filter bacteria and suspended solids in water through micron-sized pores and are commonly used in household drinking water filtration equipment. The advantage of this filter is that it can be washed and reused.
Advances in Modern Water Filtration Machines
Modern water filters combine a variety of advanced filtration technologies to provide a more efficient and comprehensive water purification solution. Here are some of the technologies commonly used in modern water filtration machines:
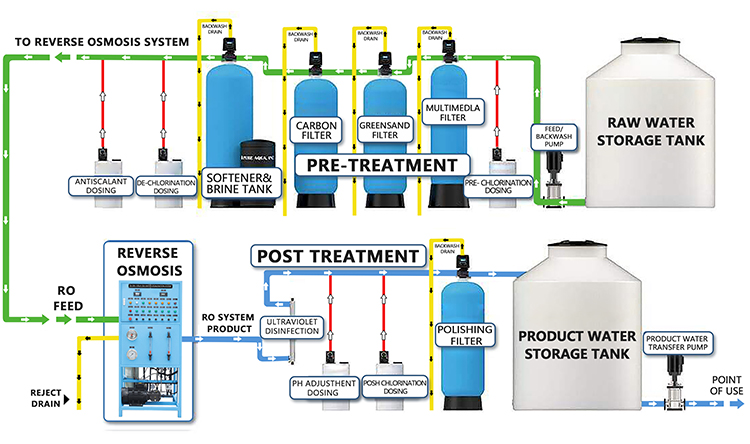
1. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Technology
Reverse osmosis technology removes dissolved solids, heavy metals, bacteria and viruses from water through a semi-permeable membrane, providing drinking water of the highest purity. The pore size of the RO membrane is only 0.0001 micron, which can effectively filter most pollutants.
2. Ultrafiltration (UF) technology
Ultrafiltration membranes have pore sizes between 0.01 and 0.1 microns and can remove bacteria, viruses, colloids and suspended solids. Ultrafiltration technology is commonly used for domestic drinking water purification and industrial water treatment.
3. Ultraviolet (UV) sterilization
Ultraviolet sterilization technology uses short-wave ultraviolet rays to kill bacteria and viruses in water. It is an efficient and environmentally friendly disinfection method. UV sterilizers are often used in combination with other filtration technologies to provide double protection.
4. Nanofiltration (NF) technology
The pore size of the nanofiltration membrane is between that of the ultrafiltration membrane and the reverse osmosis membrane. It can remove most organic matter, some inorganic matter and hardness ions, and is suitable for application scenarios in which specific pollutants are removed.

Comparison of traditional and modern water filters
1. Filtering effect
The filtration effect of traditional water filters is limited and mainly targets suspended solids, particulate matter and some organic matter. Modern water filters combine advanced technologies to remove a wider range of contaminants, including dissolved solids, heavy metals, bacteria, viruses and organic compounds.
2. Ease of use
Traditional water filters usually have a simple structure and are easy to operate and maintain, but they require frequent replacement of filter materials and cleaning. Although modern water filters are technologically complex, many devices have intelligent functions such as automatic flushing and filter element replacement reminders, which greatly improve the convenience of use and user experience.
3. Economic cost
The initial purchase cost of a traditional water filter is low, but due to the limited filtration effect, the filter material and filter element may need to be replaced frequently, and the long-term use cost is high. The initial investment of a modern water filter is relatively large, but its efficient filtration effect and intelligent management system can reduce maintenance costs and replacement frequency in long-term use.
4. Applicable scenarios
Traditional water filters are suitable for areas with relatively good water quality and are mainly used to remove large particles and some organic matter. Modern water filters are suitable for various complex water quality environments, especially in serious situations such as heavy metal pollution and excessive microorganisms, and can provide safer drinking water.
5. Environmental performance
Modern water filters have also improved in terms of environmental performance. For example, some reverse osmosis systems are equipped with wastewater recovery devices to reduce wastewater discharge. At the same time, modern filtration equipment consumes less energy and is more environmentally friendly and energy-saving when running for a long time.

Comparison of specific cases
In order to more intuitively demonstrate the difference between traditional and modern water filters, two specific cases are compared below:
Case 1: Household drinking water purification
1. Traditional water filter: A family uses a traditional activated carbon water filter to mainly filter chlorine and odor in tap water. Although water quality has improved, heavy metals and bacteria cannot be removed.
2. Modern water filter: The same household switched to a reverse osmosis water purifier, which combines activated carbon pre-filtration and RO membrane filtration to remove almost all contaminants in the water. The purified water tastes better and is safer. It is also equipped with filter element replacement reminder and automatic flushing function, making it more convenient to use.
Case 2: Industrial water treatment
1. Traditional water filter: A factory uses sand filters and gravel filters for preliminary filtration to remove large suspended particles and sediment in the water. Although the equipment is simple to maintain, its filtration effect is limited and cannot meet high-standard industrial water needs.
2. Modern water filtration machine: The factory has been upgraded to ultrafiltration membrane and ultraviolet sterilization system, which can effectively remove bacteria, viruses and colloidal particles in water, significantly improving water quality. At the same time, the high flux and long life of the ultrafiltration membrane reduce the frequency of equipment maintenance and replacement, reducing long-term operating costs.
Conclusion
Modern water filters have significant advantages over traditional water filters in terms of filtration effect, ease of use, economic cost and environmental performance. With the continuous advancement of technology, future water filters will be more intelligent, efficient, and environmentally friendly, providing safer and purer water solutions for households and industries.