Can water filters remove phosphates?
In daily life and industrial production, water quality issues have attracted much attention. Phosphates are a common pollutant that is widely present in agricultural runoff, industrial wastewater, and domestic sewage. With the improvement of environmental protection awareness, people have begun to pay attention to how to effectively remove phosphates from water to ensure the safety and ecological balance of water sources.
Among the many water treatment methods, whether water filters can remove phosphates has become a key issue. This article will explore the effectiveness of water filters in removing phosphates, analyze their working principles and applicability in different environments.

What are the sources and hazards of phosphates?
Before discussing the phosphate removal capacity of water filters, we need to understand the sources of phosphates and their potential hazards to the environment and human health.
Sources of phosphates
Phosphates are widely present in nature, and their sources mainly include:
● Agricultural runoff: Fertilizers often contain phosphates, and agricultural irrigation and rainfall will bring these phosphates into surface water and groundwater.
● Industrial wastewater: Certain industrial processes, such as detergent production, metal surface treatment, etc., will produce a large amount of phosphorus-containing wastewater.
● Domestic sewage: Detergents, soaps, washing powder and other products used in daily life also contain phosphates, which enter the sewage system after discharge.
Hazards of phosphates
Phosphates themselves are not toxic substances, but their excessive presence will cause a series of environmental problems:
● Eutrophication of water bodies: Phosphates are one of the main nutrient sources for algae growth. Excessive phosphates entering the water body will cause algae to multiply in large numbers, forming a "water bloom" phenomenon, destroying the aquatic ecosystem, reducing the dissolved oxygen content of the water body, and causing the death of fish and other aquatic organisms.
● Drinking water safety: In eutrophic water bodies, algae will produce toxic metabolites when they decompose, affecting the safety of drinking water.
● Pipeline corrosion: Water containing phosphates will settle in water pipes, forming phosphate precipitation, causing pipe blockage or accelerating pipe corrosion.

How does a water filter work?
To understand whether a water filter can remove phosphates, you first need to understand how a water filter works. Common water filters are mainly of the following types:
Mechanical filtration
Mechanical filters remove suspended particles, sediments and some microorganisms in water through physical barriers (such as sand filters, activated carbon filters, microporous filter membranes, etc.). When water passes through the filter material, larger particles are intercepted by the filter material to form clean water. Mechanical filters usually cannot effectively remove soluble substances such as phosphates.
Activated carbon filtration
Activated carbon filters use the adsorption capacity of activated carbon to remove organic matter, chlorine, odors and some heavy metals in water. The porous structure of activated carbon provides a large amount of surface area, which can adsorb soluble organic matter and some heavy metal ions in water, but has limited removal capacity for inorganic salts (such as phosphates).
Ion exchange filtration
Ion exchange filters remove specific ions, such as calcium and magnesium ions in hard water, by exchanging cations or anions in water. Resins are used to exchange calcium, magnesium and other ions in water to form softened water. Phosphate ions may also be partially removed under specific ion exchange resins, but the effect is limited and depends on the selection of resins and the processing volume.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Filtration
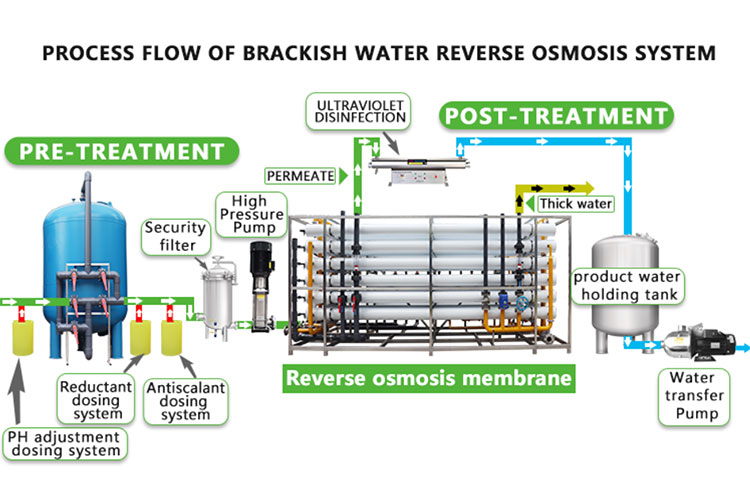
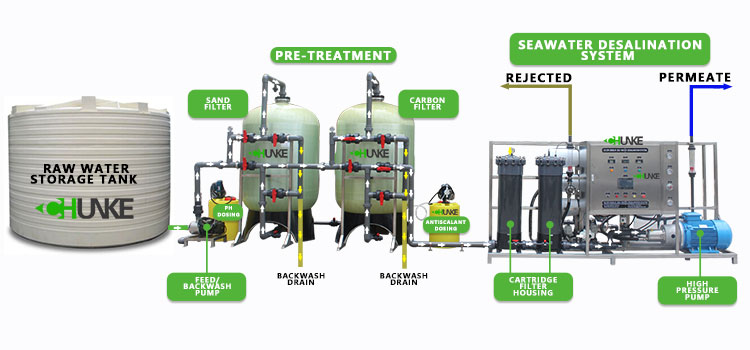
Reverse osmosis filters remove dissolved salts, metal ions, organic matter and microorganisms from water through the selective permeability of semipermeable membranes. Water passes through the semipermeable membrane under pressure, and dissolved substances (including phosphates) are retained by the membrane, leaving only water molecules and a very small number of small molecules. Therefore, reverse osmosis systems can effectively remove phosphates from water.
Can water filters remove phosphates?
From the principles of the above filters, it can be seen that different types of water filters have different abilities to remove phosphates. The following is a detailed analysis of the phosphate removal abilities of several common water filtration systems:
Mechanical filters
Mechanical filters are mainly used to remove suspended particles and sediments from water, and have little effect on soluble phosphates. Since phosphates are in an ionic state dissolved in water, mechanical filters cannot retain these small molecules. Therefore, mechanical filters are not suitable as the main tool for removing phosphates.
Activated carbon filters
Activated carbon filters are effective in removing organic pollutants, but have limited adsorption capacity for inorganic salts, such as phosphates. Although the surface area of activated carbon is large, its adsorption capacity for phosphates is not strong, and it cannot effectively remove large amounts of phosphates. Therefore, activated carbon filters are usually used only as pretreatment or auxiliary removal of some phosphates, rather than as the main means.
Ion exchange filter
Ion exchange filters can remove phosphates from water under certain circumstances. Phosphates are anions. If specially designed anion exchange resins are used, phosphate ions in water can be replaced through the ion exchange process. However, the removal efficiency of ion exchange depends on the type of resin, the amount of water treated, and the concentration of phosphates. If the phosphate content in the water is high, the exchange capacity of the resin may quickly reach saturation, affecting the removal effect.
Reverse osmosis filter
Reverse osmosis system is one of the most effective water filtration methods for removing phosphates. The pore size of the RO membrane is extremely small (usually around 0.0001 microns), which can prevent most soluble substances from passing through, including most ions including phosphates. The reverse osmosis system can not only effectively remove phosphates from water, but also remove other soluble salts, organic matter and pathogenic microorganisms to produce pure water.
The removal efficiency of the reverse osmosis system is usually as high as 90% or more, which is suitable for occasions with extremely high water quality requirements, such as drinking water purification, laboratory water, etc. However, the operating cost of reverse osmosis systems is high, and regular replacement of the filter membrane and maintenance of the equipment are required.
What are other methods for removing phosphates?
Although water filters can remove phosphates to a certain extent, other treatment methods may be more effective in some cases, especially in water bodies with high phosphate concentrations.
Chemical precipitation method
Chemical precipitation method is one of the traditional methods for removing phosphates. Phosphates are removed from water by adding chemical agents (such as ferric chloride, aluminum sulfate, etc.) to the water to form insoluble phosphate precipitates. The agent reacts chemically with the phosphates in the water to form a precipitate, which is removed by sedimentation or filtration. This method can effectively remove a large amount of phosphate in a short period of time and is suitable for treating wastewater with high phosphate concentrations.
Chemical precipitation method is often used in sewage treatment plants and industrial wastewater treatment to control the phosphate concentration in the discharged water.
Biological treatment method
Biological treatment method removes phosphates from water through microbial metabolic processes. This method is often used in sewage treatment processes and is an important means to control eutrophication of water bodies. By controlling the ratio of nutrients in water, the growth of specific microorganisms is promoted, which can absorb and accumulate phosphates in water to form phosphate precipitates.
Biological treatment is mainly used in sewage treatment and natural water restoration, and is usually combined with chemical precipitation to achieve higher removal efficiency.
Conclusion
The effectiveness of water filters in removing phosphates depends on the specific filter type and treatment process. Mechanical filtration and activated carbon filtration have limited phosphate removal capacity, while ion exchange filters can remove some phosphates under certain conditions. Reverse osmosis systems are one of the most effective phosphate removal tools, which can purify water while removing phosphates efficiently.
However, in water bodies with high phosphate concentrations, chemical precipitation and biological treatment may be more applicable. The comprehensive application of multiple treatment methods can effectively control the phosphate content in water and protect the environment and water resources.




