What filters can make river water drinkable?
As an important source of freshwater resources, how to treat river water into safe drinking water has become a matter of great concern. Filters play a key role in the purification process of river water.
This article will explore in detail which filters can make river water drinkable, as well as the working principles, advantages and disadvantages of these filters and practical application cases.
What are the main pollutants in river water?
Before discussing filters, it is necessary to first understand the common pollutants in river water. There are many types of pollutants in river water, including:
1. Suspended matter and sediment: solid particles brought into rivers by natural erosion and human activities.
2. Organic matter: including organic pollutants in animal and plant debris, industrial wastewater and agricultural runoff.
3. Microorganisms: including bacteria, viruses and parasites, which may cause a variety of waterborne diseases.
4. Chemical pollutants: including pesticides, heavy metals and industrial chemicals.
5. Nutrients: such as nitrogen and phosphorus, which can cause eutrophication of water bodies when excessive.

What filters can make river water drinkable?
Types of filters that make river water drinkable:
1. Coarse filter:
Coarse filter is the first line of defense in water treatment, mainly used to remove large particles and suspended matter.
● Working principle: Through physical screening, large particles, silt and suspended matter in the water are filtered out.
● Application: Usually used as a pretreatment step to lay the foundation for subsequent fine filtration and disinfection steps.
● Advantages: simple structure, easy maintenance and low cost.
● Disadvantages: cannot remove tiny particles, microorganisms and soluble pollutants.
2. Activated carbon filter:
Activated carbon filters are widely used in water treatment processes, mainly for removing organic pollutants, odors and some chemical pollutants.
● Working principle: Activated carbon has a high specific surface area and strong adsorption capacity, and removes organic matter, chlorine and odors from water through physical adsorption and chemical adsorption.
● Application: Commonly used in household water purifiers and municipal water treatment plants to improve water quality and taste.
● Advantages: can effectively remove organic matter and odors, and improve the taste of water; moderate price.
● Disadvantages: Limited removal effect on heavy metals and microorganisms, need to be replaced regularly.
3. Ceramic filter element:
Ceramic filter element is a microporous filter medium, widely used to remove bacteria and suspended matter in water.
● Working principle: Ceramic filter element physically filters water through its microporous structure, intercepts bacteria and tiny suspended matter.
● Application: Suitable for household drinking water purification equipment, especially in areas lacking electricity and complex equipment.
● Advantages: High filtration accuracy, can effectively remove bacteria and suspended matter; can be repeatedly cleaned and used, long service life.
● Disadvantages: Cannot remove soluble chemical pollutants and viruses, small flow rate.
4. Reverse osmosis (RO) filter:
Reverse osmosis filter is one of the most efficient water purification technologies currently, capable of removing most pollutants.
● Working principle: Water is separated under high pressure through a semipermeable membrane, water molecules pass through the membrane, and most soluble substances, heavy metals, microorganisms and organic pollutants are intercepted.
● Application: Widely used in household, commercial and industrial water treatment systems, especially in places where high-purity water is required.
● Advantages: It can remove almost all pollutants, including bacteria, viruses, heavy metals and chemicals; it provides high-purity water.
● Disadvantages: The equipment is complex and the cost is high; it requires electricity support and the proportion of wastewater is high.
5. Ultraviolet (UV) sterilizer:
Ultraviolet sterilizer is mainly used to inactivate microorganisms in water and is a representative of physical disinfection technology.
● Working principle: Through ultraviolet irradiation, the DNA structure of microorganisms is destroyed to achieve the inactivation effect.
● Application: It is used in the last disinfection process of household and municipal water treatment systems to ensure that pathogens in water are inactivated.
● Advantages: It can effectively inactivate bacteria and viruses without adding chemicals and changing the taste of water.
● Disadvantages: It cannot remove chemical pollutants and suspended solids and needs to be used in conjunction with other filtration technologies.

Practical application case analysis
Case 1: Simple water purification system in rural areas
In some rural areas that lack complete water treatment facilities, simple water purification systems are widely used. A rural area successfully treated river water into drinkable water by using a coarse filter, a ceramic filter element and an ultraviolet sterilizer. The coarse filter removes large particles and suspended solids, the ceramic filter further removes bacteria and tiny particles, and finally the ultraviolet disinfector is used to inactivate microorganisms. This system has a simple structure and low cost, which solves the drinking water problem of local residents.
Case 2: Application of household water purifiers
In urban households, water purifiers using reverse osmosis filters are becoming more and more common. A family installed a multi-stage water purifier, including a pre-filter, an activated carbon filter, a reverse osmosis membrane, and a UV disinfector. The pre-filter removes large particles, the activated carbon filter adsorbs organic matter and odors, the reverse osmosis membrane removes most pollutants, and finally ultraviolet disinfection ensures microbial safety. The system provides high-quality drinking water and meets the health needs of family members.
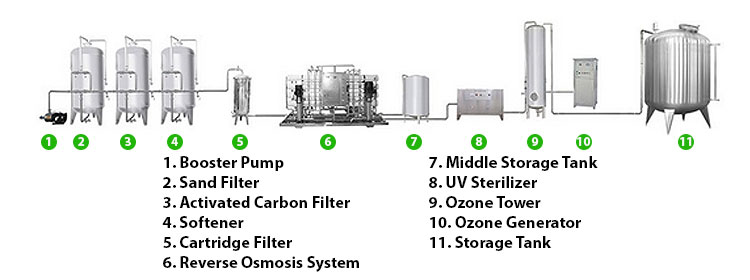
Case 3: Comprehensive application of municipal water treatment plants
In a municipal water treatment plant, a combination of multiple filtration technologies is used to ensure that river water is treated into tap water that meets national drinking water standards. The treatment process includes pretreatment (sand filtration and activated carbon filtration), reverse osmosis membrane filtration, and ultraviolet disinfection. The pretreatment stage removes most suspended solids and organic matter, the reverse osmosis membrane filtration stage removes dissolved pollutants and microorganisms, and the ultraviolet disinfection stage ensures that pathogens in the water are completely inactivated. The integrated treatment system operates stably and has excellent water quality, ensuring the safety of drinking water for urban residents.

Conclusion
There are many types of filters that make river water drinkable, each with its own advantages and disadvantages and applicable scenarios. Coarse filters, activated carbon filters, ceramic filter elements, reverse osmosis filters and ultraviolet disinfectors play an important role in different application scenarios
Actual application cases show that these filtration technologies are widely used in household, rural and municipal water treatment systems, providing reliable technical support for solving drinking water problems.