Does India have drinking water treatment plants? How much do they cost?
India, one of the most populous countries in the world, has a particularly prominent drinking water supply problem. To meet this challenge, the Indian government and private enterprises have been investing heavily in the construction of drinking water treatment plants to ensure that the public has access to safe and reliable drinking water.
So, does India currently have drinking water treatment plants? How much do these treatment plants cost to build and operate? This article will take a deep look at the status quo, cost, and social impact of drinking water treatment plants in India.

Current Status of Drinking Water Treatment Plants in India
1.1 Distribution of Drinking Water Treatment Plants:
India has a large number of drinking water treatment plants, which are distributed throughout the country, especially in densely populated and industrially developed areas. Drinking water treatment plants in India are mainly concentrated in large cities and industrial centers, such as Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai, and Kolkata. In addition, drinking water treatment plants also play an important role in arid areas where water resources are relatively scarce, such as Rajasthan and Gujarat.
1.2 Drinking Water Treatment Technology:
Drinking water treatment plants in India use a variety of technologies, including traditional coagulation sedimentation, filtration, disinfection, as well as advanced membrane separation, reverse osmosis, ultraviolet disinfection and ozone disinfection. The combined use of these technologies ensures that drinking water treatment plants can effectively remove pollutants from water and provide safe drinking water that meets national and international standards.
What is the construction cost of a drinking water treatment plant?
2.1 Composition of construction costs:
The construction cost of a drinking water treatment plant mainly includes land acquisition costs, equipment procurement costs, construction engineering costs, pipeline laying costs, technology research and development costs, and management costs. Due to the large differences in land prices, labor costs and technical levels in different regions, the construction costs of drinking water treatment plants in various places are also different.
2.2 Cost estimation:
According to the Indian Water Works Association (IWWA), the cost of building a medium-sized drinking water treatment plant (with a daily processing capacity of 100,000 cubic meters) is approximately between 5 billion and 7 billion Indian rupees (approximately US$67 million to US$94 million). This estimate includes all costs from initial planning and design to construction, installation and commissioning.
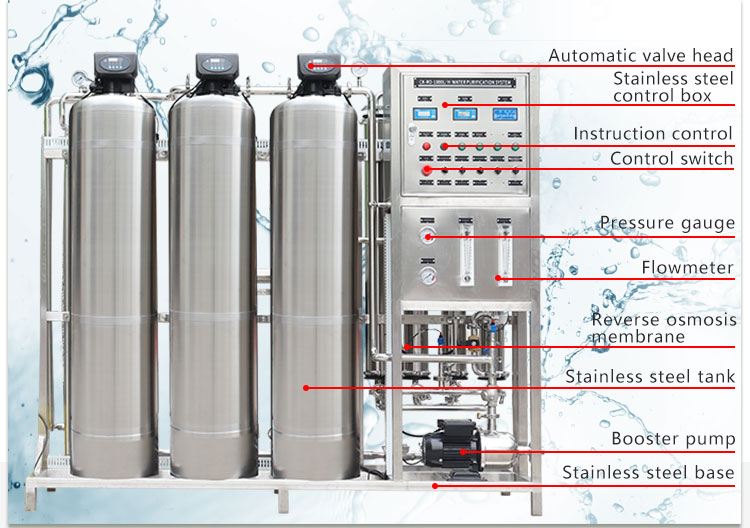
What is the operating cost of a drinking water treatment plant?
3.1 Composition of operating costs:
The operating costs of a drinking water treatment plant mainly include energy costs, chemical costs, maintenance costs, staff wages and management fees. Due to the high energy prices in India, energy costs usually account for the main part of operating costs. In addition, when treating raw water with poor water quality, the use of chemical agents will also increase significantly, thereby pushing up operating costs.
3.2 Cost control measures:
In order to reduce operating costs, drinking water treatment plants in India generally take a series of measures. For example, by optimizing the process flow to improve treatment efficiency; using advanced monitoring systems to monitor and adjust treatment parameters in real time; using renewable energy such as solar and wind energy to reduce dependence on traditional energy. In addition, some treatment plants also achieve efficient use of resources and cost reduction by recycling and reusing by-products in the treatment process.
What impact does a drinking water treatment plant have on society?
4.1 Improving drinking water safety:
The construction and operation of drinking water treatment plants have effectively improved the safety and reliability of drinking water in India. By removing harmful substances in water, such as heavy metals, pesticide residues and pathogenic microorganisms, the quality of treated drinking water has been significantly improved, reducing the threat of water pollution to public health.
4.2 Promoting economic development:
The construction of drinking water treatment plants not only improves the quality of life of residents, but also provides strong support for local economic development. Safe and reliable drinking water supply helps attract foreign investment, promote industrial and commercial development, create employment opportunities, and promote sustainable development of the regional economy.
4.3 Environmental protection:
Drinking water treatment plants use a variety of environmental protection technologies in the treatment process, effectively reducing water pollution and resource waste. For example, through advanced sludge treatment and resource recovery technologies, the discharge of waste is reduced, which plays a positive role in environmental protection.

Future development direction of drinking water treatment plants in India
5.1 Technological innovation:
With the continuous advancement of science and technology, drinking water treatment technology is also developing. In the future, drinking water treatment plants in India will pay more attention to technological innovation and adopt more efficient and low-energy treatment processes, such as nanofiltration, advanced oxidation technology and intelligent monitoring systems, to further improve water treatment effects and reduce operating costs.
5.2 Government support:
In order to accelerate the construction of drinking water treatment plants, the Indian government needs to further increase policy support. For example, introduce preferential policies to encourage social capital to participate in the construction and operation of drinking water treatment plants; provide financial subsidies to reduce the construction and operation costs of enterprises; strengthen supervision to ensure that the effluent quality of treatment plants meets the standards.
5.3 Social participation:
Public participation and support are crucial to the development of drinking water treatment plants. Through strengthening publicity and education, the public's awareness of water conservation and environmental protection can be improved; residents are encouraged to participate in the supervision and management of drinking water treatment plants to jointly maintain drinking water safety.
Conclusion
The construction and operation of drinking water treatment plants in India have played an important role in solving the problem of freshwater shortage, protecting public health, promoting economic development and environmental protection.
Despite the challenges of high construction and operation costs and uneven technical levels, with the advancement of technology and policy support, India's drinking water treatment plants will usher in a broader development prospect.