What is the best way to filter well water?
Well water often contains various impurities and contaminants, such as bacteria, viruses, rust, silt, organic matter and heavy metals. Drinking unfiltered well water directly may have adverse effects on health. Therefore, how to effectively filter well water to ensure its safety and hygiene has become the focus of many families and communities.
This article will explore in detail the best way to filter well water and the scientific principles behind it.
What are the common contaminants in well water and their hazards?
Before choosing a suitable filtration method, it is crucial to understand the possible contaminants in well water and their hazards. The main sources of well water pollution include the following:
1. Microbial contamination
Common microbial contamination in well water includes bacteria, viruses and parasites. These microorganisms may cause diseases such as gastroenteritis, cholera, dysentery, etc.
2. Inorganic pollution
Inorganic pollution mainly includes iron, manganese, nitrates and heavy metals (such as lead, arsenic, mercury, etc.). These substances may cause long-term harm to human health, such as heavy metal poisoning, cancer, etc.
3. Organic pollution
Organic pollution includes pesticides, herbicides, industrial chemicals, etc. These chemicals may cause health problems such as endocrine disorders and nervous system damage.
4. Suspended matter and sediment
Suspended matter and sediment can make water turbid, affect the taste and appearance of water, and may also carry other pollutants.
Basic principles of well water filtration
The basic principle of filtering well water is to remove pollutants in water through physical, chemical and biological means to make it meet the standards of drinking water. Common filtration methods include physical filtration, chemical filtration and biological filtration.
1. Physical filtration
Physical filtration mainly intercepts suspended matter, sediment and some microorganisms in water through filter media. Common physical filtration equipment includes sand filters, activated carbon filters and ultrafiltration membranes.
2. Chemical filtration
Chemical filtration removes soluble pollutants in water by adding chemical agents or using chemical reactions. Common methods include redox reactions, ion exchange and adsorption.
3. Biological filtration
Biological filtration uses microbial metabolism to degrade organic pollutants in water. Common biological filtration systems include biological sand filters and artificial wetlands.

What is the best way to filter well water?
According to the characteristics of different pollutants in well water, the following methods are considered to be the best methods for filtering well water in terms of filtration effect, cost and maintenance convenience.
1. Multi-stage filtration system
The multi-stage filtration system combines a variety of filtration technologies to gradually remove various pollutants in the water through multiple filtration stages to ensure the safety and cleanliness of the effluent water quality. A typical multi-stage filtration system includes the following stages:
1.1 Mechanical pre-filtration
Mechanical pre-filtration mainly removes large particles and suspended matter in the water. Commonly used equipment includes coarse filters, mesh filters and sedimentation tanks.
1.2 Activated carbon filtration
Activated carbon filtration uses the adsorption properties of activated carbon to remove organic pollutants, odors and some heavy metals in water. Activated carbon filters are usually used as the second stage in a multi-stage filtration system to further purify the water quality.
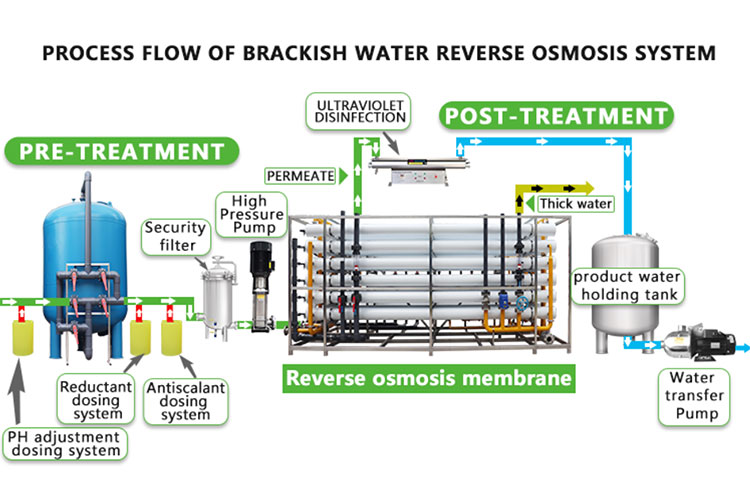
1.3 Reverse osmosis (RO) system
The reverse osmosis system is one of the most effective water treatment technologies currently available, capable of removing dissolved salts, heavy metals, organic matter and microorganisms from water. The pore size of the reverse osmosis membrane is extremely small, allowing only water molecules to pass through, and most pollutants are trapped on the other side of the membrane.
1.4 Ultraviolet disinfection
Ultraviolet disinfection destroys the DNA of microorganisms through high-energy ultraviolet rays emitted by ultraviolet lamps, achieving the effect of sterilization and disinfection. Ultraviolet disinfection is usually installed in the last stage of the filtration system to ensure that the microbial indicators of the effluent meet the drinking water standards.
2. Biosand filter
The biosand filter is a low-cost and efficient water treatment technology, especially suitable for rural and remote areas. Its working principle is to degrade organic pollutants in the water through the biofilm on the surface of the sand layer, and the sand layer itself can also filter out suspended matter and some microorganisms.
3. Ion exchange filter
Ion exchange filters remove hardness ions (calcium, magnesium) and certain toxic heavy metals (such as lead, chromium, etc.) from water through ion exchange resins. Ion exchange filters are often used for softening treatment and heavy metal removal in well water treatment.

Specific case analysis
Case 1: Rural household well water filtration
A rural household mainly relies on well water as a source of drinking water, but tests have found that the water contains high levels of rust and bacteria. To solve this problem, the family installed a multi-stage filtration system, including mechanical pre-filtration, activated carbon filtration, reverse osmosis system and ultraviolet disinfection. The quality of the well water after treatment has improved significantly and reached the drinking water standard.
Case 2: Small community well water treatment station
A small community has established a well water treatment station to provide safe drinking water for the entire community. The treatment station uses a biological sand filter combined with an ion exchange filter, and through multi-stage filtration and disinfection, ensures that the effluent quality meets the national drinking water standards.




