What are the components of a portable desalination unit?

Portable desalination units have become an essential tool for ocean exploration, rescue missions, and emergency water issues in extreme environments. This device can convert salty seawater into drinkable fresh water, providing users with valuable water resources.
So how do portable desalination units achieve this process? What is its structure and working principle? How large and heavy are these devices, and are they really as easy to carry as their name suggests?

What are the components of a portable desalination unit?
Portable desalination units usually consist of the following key components, each of which performs its own duties and works together to achieve the function of desalination:
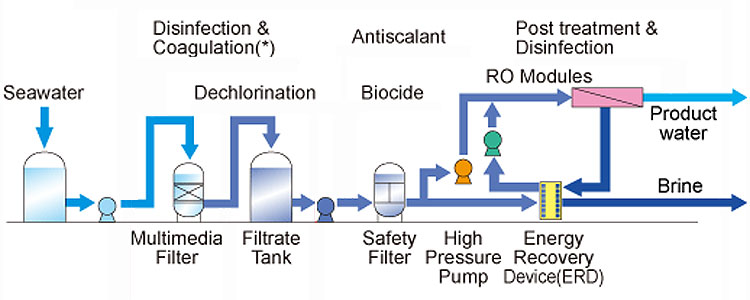
1. Water Intake System
The water intake system is the first step in the desalination process and is responsible for drawing seawater from the ocean. It usually includes a corrosion-resistant pump and filter. The pump delivers seawater to the core processing part of the unit, while the filter is used to remove larger particles and impurities to prevent them from entering the subsequent processing stages of the system.
2. Pre-treatment System
Before the core desalination treatment, seawater needs to be pre-treated. The pre-treatment system usually contains one or more filters to remove impurities such as suspended particles, algae and microorganisms in the seawater. Common pre-treatment methods include sand filtration, ultrafiltration or microfiltration, etc. This step is the key to ensure that the subsequent reverse osmosis membrane is not blocked or damaged.
3. High-pressure Pump
The high-pressure pump is one of the core components of the portable seawater desalination device. It pressurizes the seawater into the reverse osmosis membrane system. Since reverse osmosis desalination needs to overcome the natural osmotic pressure of salt water, water must pass through the membrane under high pressure to separate salt and other impurities. The power and efficiency of the high-pressure pump directly affect the water production and energy consumption level of the desalination device.
4. Reverse Osmosis Membrane
The reverse osmosis membrane is the core technology for achieving seawater desalination. This semi-permeable membrane only allows water molecules to pass through, while blocking most salts and other dissolved substances. The quality and design of the reverse osmosis membrane are the key to determining the purity and efficiency of the produced water. Portable units usually use high-efficiency, low-energy reverse osmosis membranes to ensure that enough fresh water can be produced even with limited volume.
5. Brine Disposal System
During the desalination process, the salt and other impurities retained by the reverse osmosis membrane form concentrated water (brine). The wastewater discharge system is responsible for discharging this high-salinity water back to the ocean. Due to the potential impact of concentrated water on the environment, some portable units are also equipped with environmentally friendly discharge mechanisms to ensure that the impact of the discharge process on the marine ecology is minimized.
6. Freshwater Storage System
The treated fresh water is usually collected and stored in an internal water storage tank, which can be used by users at any time. The water storage system usually has an automatic cut-off function. When the water tank is full, the system automatically stops the desalination process to prevent water overflow.
7. Power Supply System
Portable desalination units are usually designed to be powered by batteries so that they can operate in environments without access to the power grid. Some units may also be equipped with solar panels or manual power devices to increase their adaptability and endurance. The battery life of the power system and the battery capacity directly affect the continuous working time of the device.
8. Control System
Modern portable desalination devices are usually equipped with electronic control systems that users can operate and monitor through a simple interface. These control systems may include functions such as water quality monitoring, fault alarms, and automatic cleaning to ensure the stable operation of the device.

Is the portable desalination device small or light?
Since the portable desalination device has so many components, what is its size and weight? Are such devices really easy to carry?
1. Size
Portable desalination devices are designed with full consideration of volume constraints and are usually kept within the size of a suitcase or backpack. The smallest devices can even be as small as a handbag, suitable for individuals or small teams. These devices are usually modular in design, integrating different components into a compact body, reducing the complexity of external connections and installation.
2. Weight control
The weight of portable devices is another important consideration in design. Due to the portability requirements of the equipment, these devices usually use lightweight materials such as corrosion-resistant plastics and aluminum alloys to reduce weight. Most portable desalination units weigh between 5 and 20 kg, making them easy to carry or transport by vehicle. For applications that require long-term carrying, such as hiking or rescue missions, lighter units are undoubtedly more advantageous.
3. Portability
The portability of portable desalination units is not only reflected in size and weight, but also in the ease of operation. Some advanced units can be set up and started in a few minutes without complicated installation or commissioning processes. This allows them to be put into use quickly in emergency situations and provide fresh water in a timely manner. In addition, some devices are designed with manual operation functions to ensure basic operation even in the absence of power.