What is a 2000 LPH Reverse Osmosis System? (Price, Pros and Cons, Energy Consumption)
What is a 2000 LPH reverse osmosis system?
The 2000 LPH reverse osmosis system is a highly efficient water treatment device designed specifically to treat large amounts of water resources every day. The "2000 LPH" here means that the system can treat 2000 liters of water per hour (Liters Per Hour). The reverse osmosis system (RO) applies pressure to force water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane, while most impurities, salts, heavy metals and other pollutants are blocked on the other side of the membrane, thereby obtaining high-purity water.
2000 LPH reverse osmosis systems are commonly used in commercial and industrial fields, such as food and beverage processing plants, pharmaceutical plants, hotels, schools, factories and other places that require large-scale pure water supply. Its design and specifications are also suitable for some larger residential communities, or for centralized treatment of water resources for multiple users.
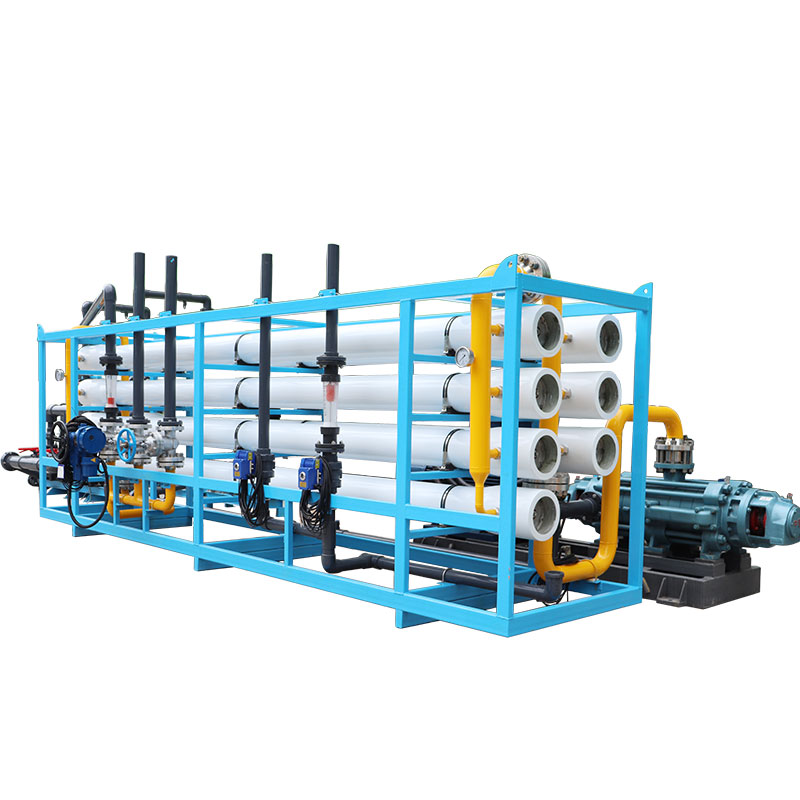

How does a 2000 LPH reverse osmosis system work?
Reverse osmosis technology is based on a basic physical process: when external pressure is applied, water molecules in the solution pass through a semipermeable membrane, while solutes (such as salts, impurities, etc.) are trapped on one side of the membrane. This method is more effective than traditional filtration methods because it can remove molecules smaller than the filter, including bacteria, viruses, and chemical contaminants.
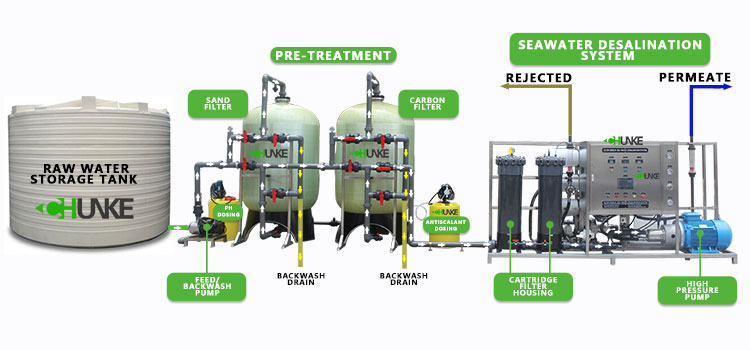
Specifically, a 2000 LPH reverse osmosis system includes the following key components:
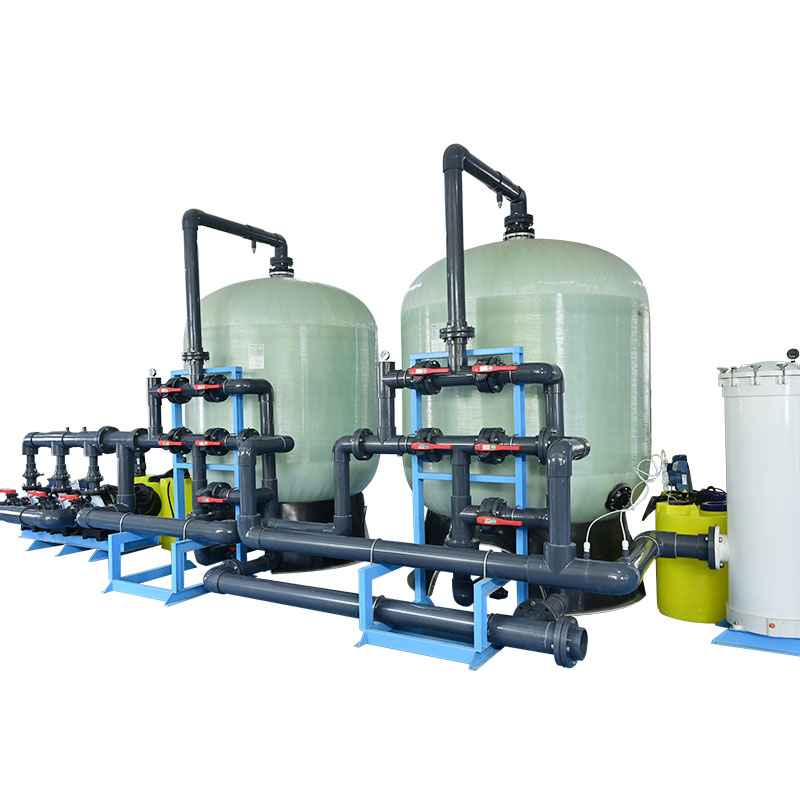
1. Pretreatment system: usually includes multi-stage filters to remove large particles, suspended solids, chlorine and other harmful substances to protect the reverse osmosis membrane from damage.
2. High-pressure pump: By increasing the pressure of the water, it pushes water molecules through the reverse osmosis membrane. This is the core part of the system and determines the efficiency of the entire system.
3. Reverse osmosis membrane assembly: It consists of multiple membrane elements and is responsible for the actual separation process. Water molecules are squeezed through the membrane, leaving behind contaminants.
4. Post-treatment system: usually includes sterilization devices, mineralizers, etc., to further improve water quality and make it more suitable for drinking or other uses.
5. Storage tank: The purified water is stored in the storage tank and is ready to be supplied to the end user.
6. Control system: Integrated monitoring and automated control ensures stable operation of the system and promptly warns of any faults or abnormalities.
How much does a 2000 LPH reverse osmosis system cost?
The price of a 2000 LPH reverse osmosis system varies depending on the brand, configuration, material quality, and additional features. Generally speaking, the price of such systems can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands of dollars. Specific factors include:
1. Brand: Well-known brands are usually more expensive, but they also tend to have better durability, after-sales service, and technical support.
2. Material quality: Systems that use high-quality materials (such as stainless steel instead of plastic) are usually more expensive, but they are also more durable and can better resist corrosion and high pressure.
3. Configuration and additional features: Systems with additional features such as automated control systems, remote monitoring, and energy consumption optimization modules are usually more expensive.
4. Regional differences: Logistics, taxes, and installation costs in different regions will also affect the total price.
Generally speaking, a standard 2000 LPH RO system usually costs between $5,000 and $20,000. Some high-end systems, especially in demanding industrial applications, can cost more.

How much energy does a 2000 LPH RO system consume?
The energy consumption of a RO system is mainly concentrated in the high-pressure pump, because the device needs enough pressure to push water molecules through the semipermeable membrane. The specific energy consumption depends on the following factors:
1. System efficiency: Efficient systems are usually more compact, with optimized pipes and less pressure loss, which reduces energy consumption.
2. Type of water source: Treating water with higher salinity (such as seawater) requires higher pressure and therefore higher energy consumption; treating fresh water or slightly polluted water consumes less energy.
3. Working hours: If the system needs to run 24/7, the energy consumption will increase significantly. In contrast, systems used intermittently consume less energy.
Typically, the energy consumption of a 2000 LPH RO system is between 2 and 5 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per cubic meter of water (1000 liters). Depending on the daily usage time and the amount of water treated, energy costs may range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars per month.
In order to optimize energy consumption, many modern reverse osmosis systems are also equipped with energy recovery devices to recover part of the energy on the high-pressure side and reuse it in the system, reducing overall energy consumption.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of a 2000 LPH reverse osmosis system?
Advantages of a 2000 LPH reverse osmosis system:
1. Efficient removal of pollutants: Reverse osmosis technology is one of the most effective water purification methods currently available, capable of removing almost all dissolved solids, heavy metals, bacteria and viruses from water, ensuring that the effluent water quality is highly pure.
2. Wide range of applications: The processing capacity of 2000 LPH makes it suitable for a variety of application scenarios, whether it is industrial production, commercial use, or centralized water supply in large residential communities.
3. Relatively mature technology: After years of development, reverse osmosis technology has become very mature, with high equipment reliability, relatively simple maintenance, and easy operation.
4. High degree of automation: Modern reverse osmosis systems are usually equipped with automated control systems that can monitor water quality and equipment status in real time, reduce human intervention, and improve system stability.
5. Environmentally friendly: Although reverse osmosis technology produces a certain amount of concentrated water waste, with proper treatment and recycling methods, this technology has a relatively small impact on the environment.
Disadvantages of 2000 LPH reverse osmosis system:
1. High initial cost: Although the long-term economic benefits of reverse osmosis systems are obvious, their initial purchase and installation costs are high, which may be a barrier for users with limited budgets.
2. High energy consumption: Compared with some other water treatment methods, reverse osmosis technology has a high energy consumption, especially large-scale treatment systems, which may result in high operating costs.
3. Low water resource utilization: Reverse osmosis systems produce a certain proportion of concentrated water (usually 20-50% of the total treated water), which still contains a lot of salt and other pollutants and must be properly treated, otherwise it will cause a waste of water resources.
4. High maintenance requirements: Although the service life of reverse osmosis membranes is long, the membranes, filter elements and other components in the system need to be replaced and cleaned regularly to keep the system running efficiently.
5. Sensitive to influent water quality: The reverse osmosis system has high requirements on the quality of influent water. Large particles, grease, rust, chlorine and other substances in the influent water may damage the membrane, so a pre-filtration system is usually required to protect the reverse osmosis membrane.




