How often should I flush my industrial reverse osmosis water filtration system?
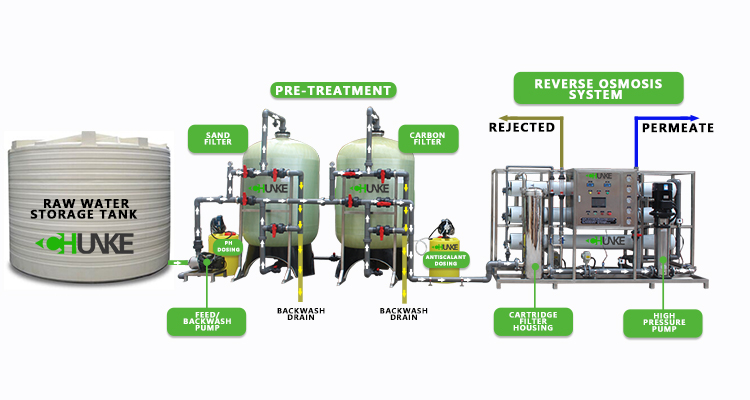
The industrial reverse osmosis (RO) water filtration system is an efficient water treatment technology that is widely used in various industrial fields such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, electricity, and petrochemicals. It removes impurities from water through a semipermeable membrane to provide a pure water source. However, with the long-term use of the system, pollutants will gradually accumulate on the membrane surface, resulting in a decrease in system efficiency. Therefore, regular flushing of the industrial reverse osmosis system is the key to maintaining its normal operation.
So, how should the frequency of flushing be determined? How should the flushing process be carried out? This article will explore these issues in depth to help you maintain the industrial reverse osmosis system scientifically.

What is the importance of flushing the industrial reverse osmosis system?
The membrane in the industrial reverse osmosis system is the core component, which is mainly responsible for removing impurities such as dissolved salts, microorganisms, and organic matter from the water. However, as the water passes through the membrane, these impurities will gradually deposit on the membrane surface to form a "pollution layer". If these pollutants are not removed in time, the following problems will occur:
● Decreased flux: The speed at which water flows through the membrane slows down, resulting in a decrease in water production.
● Deterioration of membrane performance: Pollutants hinder the normal operation of the membrane, making the filtration effect worse and the water quality deteriorate.
● Increased pressure: To maintain the water flow rate, the system may require higher pressure, increasing energy consumption and equipment load.
● Shortened membrane life: Long-term non-cleaning will accelerate the aging of the membrane, resulting in a shortened service life.
Therefore, regular flushing of the system is an important step to maintain the efficient operation of the reverse osmosis device and extend the life of the equipment.
Flushing vs. chemical cleaning, what is the difference?
It should be clear that flushing and chemical cleaning are two different concepts. Flushing usually refers to a simple cleaning of the system with clean water or diluent to remove some surface contaminants; while chemical cleaning uses specific chemical reagents to deeply clean the membrane surface to remove stubborn scaling and organic accumulation. This article mainly discusses the flushing process and its frequency. Chemical cleaning is a more thorough cleaning method that is only required when the pollution is serious.
What are the factors affecting the flushing frequency?
Water quality is the primary factor that determines the flushing frequency of the reverse osmosis system. The higher the content of suspended matter, dissolved organic matter, hardness, rust, microorganisms and other pollutants in the water, the faster the membrane is polluted and more frequent flushing is required. For example, the reverse osmosis system that treats river water or well water often has a higher flushing frequency than the system that treats municipal tap water because the water source may contain more sediment, organic matter, etc.
A series of pretreatment devices are usually installed before the reverse osmosis system, such as sand filters, activated carbon filters, softeners, etc. The main function of these pretreatment equipment is to remove most of the suspended matter and pollutants in the raw water and reduce the burden on the reverse osmosis membrane. If the pretreatment system operates well, it can effectively reduce the content of pollutants entering the reverse osmosis system, and the flushing frequency can be appropriately reduced. On the contrary, poor pretreatment results in faster contamination of the reverse osmosis membrane, which requires more frequent flushing.
Secondly, the operating time of the reverse osmosis system directly affects the degree of membrane contamination. The system that operates around the clock continuously processes a large amount of water, and pollutants accumulate faster, requiring a higher flushing frequency. For the intermittently operating system, the membrane has a certain "rest" time, and the pollutants accumulate more slowly, so the flushing frequency can be relatively reduced. In addition, the water inlet pressure and flow rate of the reverse osmosis system have an important impact on membrane contamination. Higher pressure and flow rate can increase the shear force of water flowing through the membrane, reduce the deposition of pollutants, and slow down the fouling rate of the membrane. However, if the pressure and flow rate are too high, it may cause mechanical damage to the membrane. Therefore, reasonable adjustment of the system's operating parameters can not only optimize the flushing frequency, but also extend the service life of the membrane.
In addition, equipment manufacturers usually provide recommended flushing frequencies based on system design and actual application scenarios. Although these recommendations are based on general experience, in actual applications, the flushing frequency can be better determined by combining the specific circumstances of the above factors.
What are the specific steps for flushing an industrial reverse osmosis system?
Preparations before flushing
Before flushing, the following preparations need to be made:
● Check the system: Make sure that all parts of the system are working properly, especially the water inlet pump and the drain valve.
● Turn off the high-pressure pump: Flushing is usually carried out under low pressure conditions, and the high-pressure pump is turned off to avoid damage to the membrane.
● Adjust the valve: According to the requirements of the flushing operation, adjust the water inlet and drain valves to ensure the correct direction of water flow.
Flushing process
The flushing process mainly includes the following steps:
● Start the low-pressure pump: Start the low-pressure pump and slowly introduce clean water or diluent into the system. The water flow should be evenly distributed on the surface of the membrane to effectively remove pollutants.
● Gradually increase the flow rate: During the flushing process, gradually increase the water flow rate so that the shear force generated by the water flow can better remove pollutants attached to the membrane surface.
● Monitor the water output: Observe the color and turbidity of the water output. When the water output becomes clear, it means that the flushing has achieved the expected effect.
● Complete the flushing: After the flushing is completed, stop the low-pressure pump, readjust the valve settings of the system, and restore normal operation.
Precautions after flushing
After the flushing is completed, pay attention to the following points:
● Check the system parameters: After resuming the operation of the system, check whether the parameters such as water inlet pressure, flow rate, and water output are normal.
● Record the flushing log: Record the flushing time, duration, water consumption and system operation status in detail to facilitate future analysis and adjustment of the flushing frequency.
● Observe the system operation effect: In the next operation, observe the system's water output and water quality to ensure a good flushing effect.

How often should I flush the industrial reverse osmosis water filtration system?
Under standard operating conditions, that is, when the water quality is good, the pretreatment system is normal, and the equipment runs continuously for 8-12 hours a day, it is generally recommended to flush once a week. This can effectively prevent the accumulation of pollutants on the membrane surface and maintain the efficient operation of the system.
If the raw water treated by the reverse osmosis system is of poor quality, such as water sources with high suspended solids, organic matter or high hardness, it is recommended to increase the flushing frequency, which may require flushing every day or even every shift to prevent serious membrane pollution.
For low-load or intermittent systems, such as when the equipment only runs for a few hours a day, or when the water production demand is low, the flushing interval can be appropriately extended, such as flushing once every two weeks. However, the operating status of the system still needs to be closely monitored to avoid long-term accumulation of pollutants.
Dynamic adjustment of flushing frequency of industrial reverse osmosis water filtration system
The pressure difference of the membrane (the difference between the inlet pressure and the water production pressure) is an important indicator for judging the degree of membrane pollution. As pollutants accumulate, the pressure difference will gradually increase. Therefore, regular monitoring of the pressure difference and adjusting the flushing frequency according to its changes are the key to maintaining efficient operation of the system.
By regularly testing the water quality of the produced water, such as conductivity, turbidity, microbial content, etc., the degree of membrane contamination can be determined. When the water quality indicators begin to decline, it usually means that a certain amount of pollutants have accumulated on the membrane surface and the flushing frequency needs to be increased.
In addition, analyzing the system's operation log, including system performance data after each flushing, can help determine the optimal flushing frequency. If it is found that the system performance recovery time after flushing is long, or the flushing effect is not ideal, it may be necessary to adjust the flushing frequency or improve the flushing method.

What are the effects of too high or too low flushing frequency?
Although flushing can effectively remove pollutants on the membrane surface, too frequent flushing may also have negative effects. Frequent water flow impact may cause wear and tear on the membrane and shorten its service life. In addition, the flushing process requires a certain amount of water resources and energy, and too high a frequency will increase operating costs.
If the flushing frequency is too low, pollutants on the membrane surface will gradually accumulate, resulting in a decrease in water production, deterioration of water quality, and even irreversible damage to the membrane. Severe membrane contamination needs to be solved by chemical cleaning or even replacement of membrane elements, which will increase maintenance costs and downtime.




