How big a water treatment plant can be called a large water treatment plant?
Water treatment plants play a vital role in modern society, responsible for treating polluted water sources into safe water bodies to meet the needs of human daily life, industrial production and agricultural irrigation. Water treatment plants vary in size, from small community treatment plants to large urban water treatment facilities, covering a wide range of treatment capabilities and technical means.
So, how big a water treatment plant can be called a large water treatment plant? This question involves multiple factors such as treatment capacity, service population, technical configuration and infrastructure. This article will explore these perspectives in depth to reveal the specific connotation of the concept of "large water treatment plant".

What is a large water treatment plant?
Treatment capacity is the primary indicator to measure the size of a water treatment plant. Usually, the treatment capacity of a water treatment plant is expressed in cubic meters per day (m³/d) or million gallons per day (MGD). Generally speaking, a water treatment plant with a treatment capacity of more than 100,000 cubic meters/day is usually considered a large water treatment plant. This standard varies depending on the region and water treatment needs. In some densely populated cities, this number may be higher, while in some areas with low water demand, a plant with a treatment capacity of 50,000 cubic meters per day may also be considered a large water treatment plant.
Secondly, the size of a water treatment plant depends not only on its treatment capacity, but also on the number of people it serves. Large water treatment plants usually serve millions or even tens of millions of residents. For example, a water treatment plant serving New York City must be large enough to meet the water needs of nearly 9 million people in the city, which obviously requires a larger treatment capacity and a more complex treatment process. In contrast, a water treatment plant serving a small city or rural area may not be considered a large plant even if its treatment capacity is relatively large.
In addition to treatment capacity and service population, the complexity of technical configuration is also one of the important criteria for measuring the size of a water treatment plant. Large water treatment plants usually adopt a multi-stage treatment process, including pretreatment, coagulation sedimentation, filtration, disinfection and post-treatment steps. In addition, they are often equipped with advanced treatment technologies such as reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration, ozone oxidation and activated carbon adsorption to ensure that the treated water quality meets strict hygiene and environmental standards. The complexity and diversity of these technical configurations enable large water treatment plants to treat larger volumes of water and deal with more diverse pollutants.
In addition, large water treatment plants usually cover a large area and have a large infrastructure, covering a series of facilities from water inlet pumping stations to treatment workshops to water outlet pipe networks. The extensiveness of these infrastructures enables large water treatment plants to efficiently treat and transport large amounts of water, and to achieve automation and remote monitoring during the treatment process, thereby improving treatment efficiency and safety. In addition, large water treatment plants usually also include auxiliary facilities such as wastewater treatment, sludge treatment, and waste gas treatment to ensure the environmental protection and sustainability of the entire treatment process.
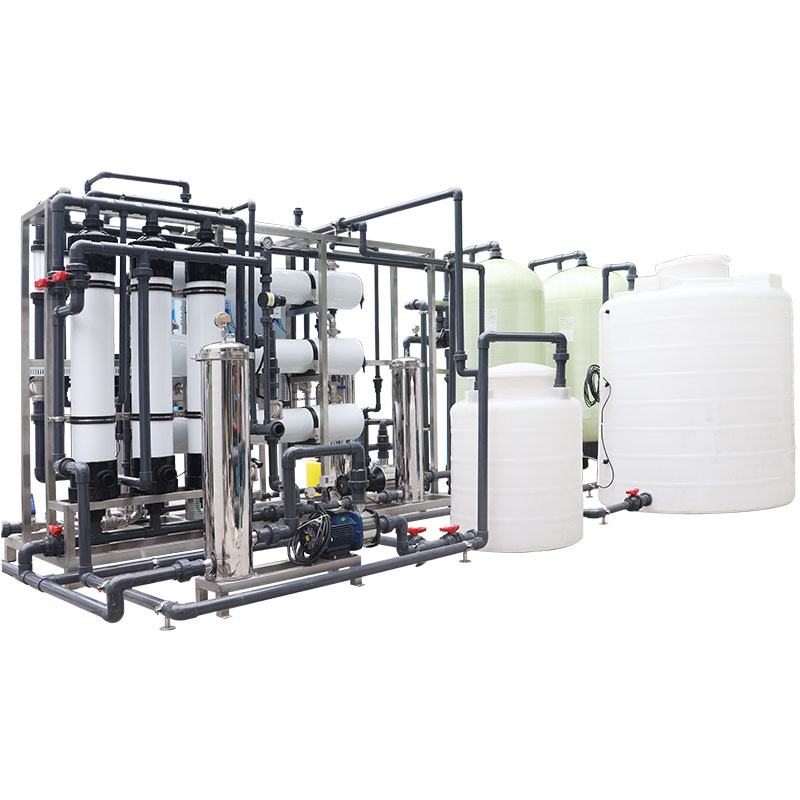

What are some typical examples of large water treatment plants?
New York City Water Treatment Plant
New York City is one of the most densely populated cities in the United States, and its water supply needs are large and complex. To meet the city's daily water needs, New York City has several large water treatment plants with a total treatment capacity of more than 4 billion gallons per day (approximately 15,000,000 cubic meters/day). These water treatment plants use advanced treatment technologies such as ozone disinfection, activated carbon filtration, and ultraviolet disinfection to ensure the safety and quality of water supply. In addition, these water treatment plants also transport treated water to every corner of the city through a complex pipe network system, ensuring the supply of water for residents and industries throughout the city.
Beijing Water Group
The large water treatment plants under the Beijing Water Group are also typical cases. Beijing's water treatment plants are responsible for supplying water to more than 20 million residents. The total treatment capacity of the group's water treatment plants exceeds 4 million cubic meters per day, and a number of advanced technologies including membrane treatment technology, activated carbon adsorption, reverse osmosis, and ozone disinfection are used to cope with complex water quality challenges. At the same time, Beijing's water treatment plants are also equipped with advanced automated control systems to achieve real-time monitoring and management of the water treatment process, ensuring the stability and reliability of water quality.
London Thames Water
London Thames Water operates one of the largest water treatment plants in Europe, with a treatment capacity of more than 2.7 billion liters (about 2,700,000 cubic meters) per day. These water treatment plants provide clean drinking water to about 15 million residents in London and surrounding areas. Thames Water uses a variety of advanced treatment technologies, such as reverse osmosis, ozone disinfection and biological treatment, to ensure that the treated water quality meets the strict standards of the UK and the EU. In addition, these water treatment plants also safely transport the treated water to thousands of households through an extensive pipe network system.
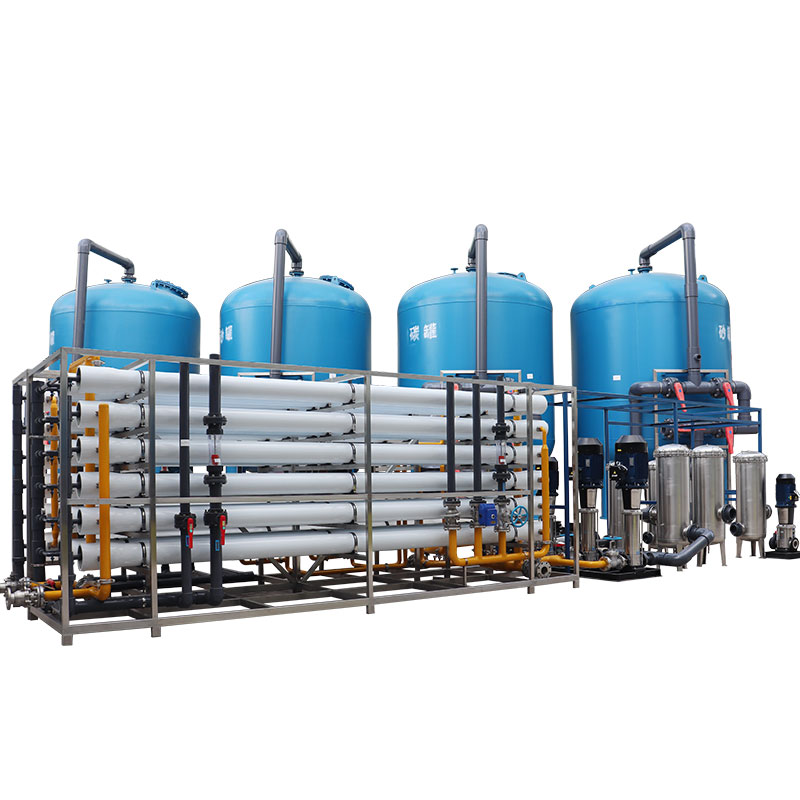

What are the key technologies and processes of large water treatment plants?
Multi-stage treatment process
Large water treatment plants usually use multi-stage treatment processes to deal with complex water quality problems. These processes usually include:
● Pretreatment: Remove large suspended particles and floating objects in the water through screens, grit chambers, etc.
● Coagulation and sedimentation: Add coagulants to make tiny particles in the water aggregate into flocs and remove them through sedimentation.
● Filtration: Use filter media such as sand filtration and activated carbon filtration to further remove suspended matter and organic matter in the water.
● Disinfection: Kill pathogenic microorganisms in the water through chlorination, ozone or ultraviolet rays to ensure the safety of water.
● Advanced treatment: Use reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration and other technologies to remove dissolved salts and trace organic pollutants in the water.
Automation and Intelligent Control
Large-scale water treatment plants are usually equipped with advanced automation and intelligent control systems to improve treatment efficiency and operational reliability. The automation system monitors key parameters in the treatment process, such as water flow, pressure, turbidity, and residual chlorine, in real time through sensors and controllers, and automatically adjusts the treatment process according to the set control logic. In addition, the intelligent control system can also optimize the treatment process, reduce energy consumption, and improve water quality stability through big data analysis and machine learning algorithms.
Sludge treatment and waste recycling
Large-scale water treatment plants will produce a large amount of sludge during the treatment process, which needs to be properly treated and disposed of. Common sludge treatment methods include concentration, dehydration, drying, and incineration. In addition, some large-scale water treatment plants are also equipped with waste recovery systems, which convert sludge into energy or useful by-products through biological treatment, incineration power generation, etc., reduce the impact on the environment, and realize the recycling of resources.
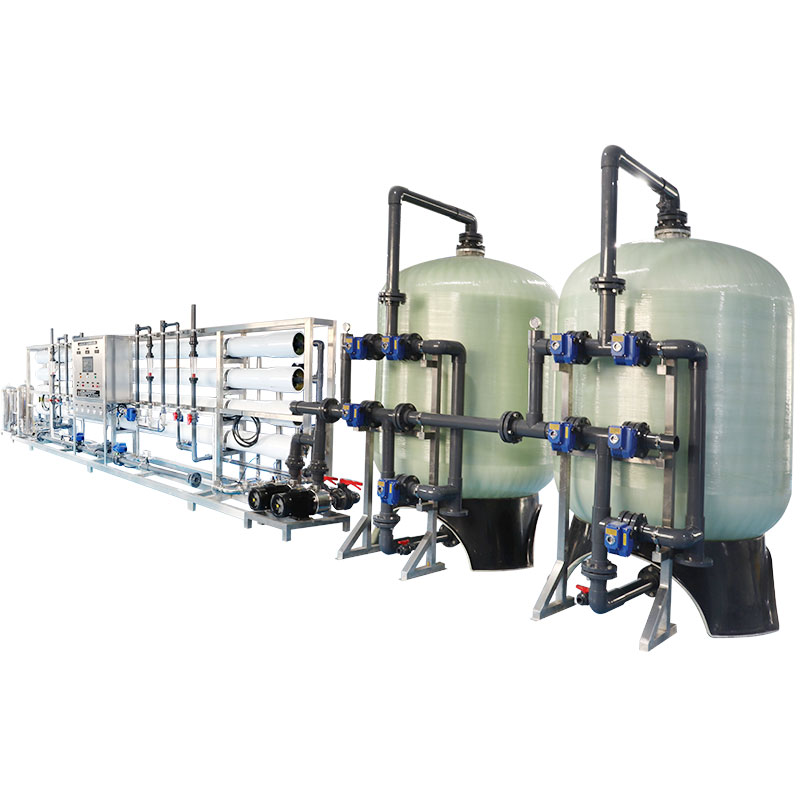

Operation and management of large-scale water treatment plants
The operating costs of large-scale water treatment plants mainly include energy consumption, chemical use, staff wages, and equipment maintenance. Due to their large processing capacity and complex processes, large water treatment plants usually have high energy consumption, mainly reflected in the operation of water pumps, mixers, blowers and heating equipment. In addition, to ensure that the water quality meets the standards, large water treatment plants need to use a large amount of chemical agents, such as coagulants, disinfectants and deodorants, which also increases operating costs.
Large water treatment plants need to strictly comply with national and local water quality standards to ensure safe and reliable water supply. To this end, these water treatment plants usually have established a complete quality control system to monitor key indicators in the treatment process, such as turbidity, pH value, residual chlorine and microbial content, through regular sampling and testing. At the same time, large water treatment plants also need to be regularly supervised and inspected by government departments to ensure that their operations comply with the requirements of relevant laws and regulations.
Large water treatment plants need to pay special attention to environmental protection issues during operation. In addition to strictly controlling wastewater discharge and preventing secondary pollution, these water treatment plants also need to take measures to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions to achieve sustainable development goals. For example, by adopting energy-saving equipment, optimizing process flow, and using renewable energy, the environmental impact during operation can be reduced and the overall environmental benefits can be improved.