How does the filter filter oil from drinking water?
In the field of modern industry and environmental protection, water quality management has become a vital task. In particular, due to the presence of industrial wastewater, oil spills and other pollution sources, drinking water may contain a certain amount of oil substances. These oil pollutants not only affect the taste and smell of water, but may also cause potential harm to human health. Therefore, how to effectively remove oil substances from drinking water has become an important topic in water treatment engineering.
The oil-water filter is a key equipment designed to solve this problem. So, what is an oil-water filter? How does it filter oil from drinking water?

What is an oil-water filter?
The oil-water filter is a device specially designed to separate and remove oil pollutants from water. It is widely used in industrial wastewater treatment, oilfield reinjection water treatment, marine oil pollution treatment, and daily life occasions where oil pollutants need to be removed from drinking water.
The design concept of the oil-water filter is based on the difference in the physical properties of oil and water. Water and oil are two different liquids with different densities and surface tensions. Since water has a greater density than oil, oil usually floats on the surface of water after mixing. In addition, oil and water are immiscible, which makes it possible to effectively separate oil from water through appropriate physical and chemical methods.
How does an oil-water filter work?
The working principle of an oil-water filter can be understood from the following aspects:
Physical separation method
Physical separation is one of the most common oil-water separation technologies, which mainly relies on the density difference between oil and water for separation.
Gravity separation is a common method in physical separation. After the oil-water mixture enters the filter, the flow rate is slowed down by the internal baffles and partitions, allowing the oil-water mixture to be naturally stratified. Due to the low density of oil, it will gradually float to the surface of the water, while the water will settle at the bottom. After a certain residence time, the oil on the upper layer can be collected, and the water at the bottom can be discharged through the outlet.
Centrifugal separation is another effective physical separation method. The centrifugal separator separates oil and water of different densities through the centrifugal force generated by high-speed rotation. The density of oil is low, and under the action of centrifugal force, the oil will be thrown to the periphery of the rotating shaft, while the water will be concentrated on the inner side of the rotating shaft. By adjusting the structure of the outlet, the oil and water can be discharged separately.
Adsorption separation method
The adsorption separation method uses the adsorption properties of specific materials to adsorb oil substances in water on the surface of the material, thereby achieving the purpose of separating oil and water.
Activated carbon filter is one of the common adsorption separation equipment. Activated carbon has a large specific surface area and a highly developed pore structure, which makes it have a strong adsorption capacity for organic matter and oil substances in water. When the oil-water mixture passes through the activated carbon layer, the oil substances are adsorbed by the activated carbon, and the pure water is discharged through the filter layer.
Fiber adsorption filter is also a commonly used adsorption separation equipment. It uses special fiber materials, and the surfaces of these fibers are specially treated to have strong lipophilicity and hydrophobicity. When the oil-water mixture flows through the fiber layer, the oil substances are adsorbed on the fiber surface, while the water passes smoothly. After a period of use, the oil substances in the adsorption layer can be removed by heating or solvent washing, thereby regenerating the filter.
Membrane separation method
Membrane separation is an efficient and precise oil-water separation technology that uses specific membrane materials to separate oil substances from water.
Ultrafiltration membrane and nanofiltration membrane are membrane materials commonly used for oil-water separation. The pore size of ultrafiltration membranes is generally between 0.01 and 0.1 microns, while the pore size of nanofiltration membranes is smaller. Since the diameter of oil molecules is generally large, these membrane materials can effectively block the passage of oil molecules, while water molecules can pass through the membrane layer smoothly. Through membrane separation technology, not only can oil pollutants in water be effectively removed, but also other impurities such as particulate matter and suspended matter can be removed at the same time.
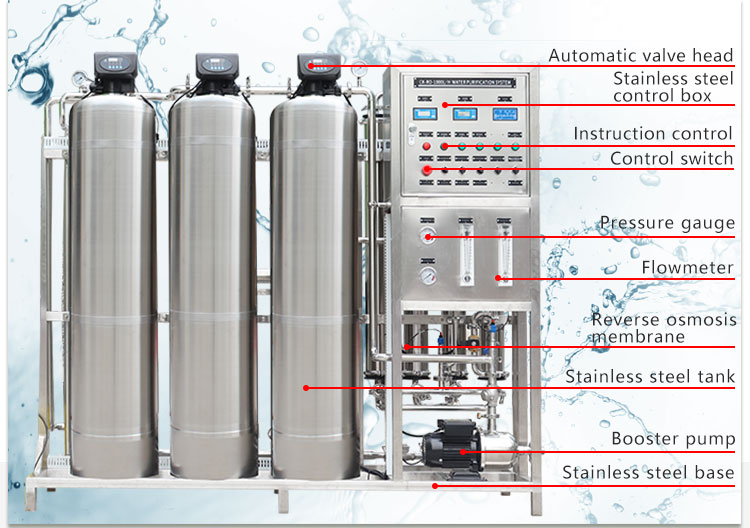
Reverse osmosis membrane technology is also an extremely effective means of oil-water separation. The pore size of reverse osmosis membranes is extremely small, usually around 0.0001 microns, and can remove almost all soluble pollutants, including oil substances. When the oil-water mixture passes through the reverse osmosis membrane under high pressure, pure water molecules are forced to pass through the membrane layer, while oil substances and other impurities are retained on the other side of the membrane, eventually forming concentrated waste liquid.
Chemical treatment method
Chemical treatment method achieves oil-water separation by adding specific chemical reagents to the oil-water mixture to change the interfacial properties of oil and water.
Flocculants and coagulants are commonly used chemical reagents. When these agents are added to an oil-water mixture, they cause the oil molecules to condense into larger particles, which are easily separated from the water due to their high density. The flocculated oil can be further removed by sedimentation, filtration or flotation.
Demulsifiers are a special class of chemical agents specifically used to treat oil-water mixtures in an emulsified state. Demulsifiers aggregate and separate the emulsified oil particles by destroying the emulsified oil-water interface, thereby restoring the oil-water mixture to a state that can be treated by physical or membrane separation methods.

What are the applications of oil-water filters in drinking water treatment?
In drinking water treatment, the role of oil-water filters is particularly important. Although the content of oil contaminants in drinking water is usually low, even a small amount of oil can have an adverse effect on water quality, affecting the taste, odor and transparency of the water.
Oil contaminants in drinking water may come from a variety of sources, such as industrial wastewater discharge, accidental leakage of oil substances, and grease residues in domestic sewage. In order to ensure the quality and safety of drinking water, water treatment plants usually use a variety of oil-water separation equipment and technologies to maximize the removal of oil substances in water.

How to properly select and maintain an oil-water filter?
Selecting the right oil-water filter is essential for effectively treating oil pollution. When selecting an oil-water filter, the type and concentration of oil in the water need to be considered. Different types of oil substances may require different filtration technologies. For water sources with higher oil concentrations, multi-stage filters or more efficient separation equipment may be required.
Secondly, the processing capacity of the oil-water filter needs to match the actual water treatment volume. Water sources with larger treatment volumes require the selection of filters with stronger processing capacity. Different types of oil-water filters differ in maintenance and operation. Some filters may require regular replacement of filter elements or membrane elements, while others may require regular cleaning and regeneration.
In addition, when selecting an oil-water filter, local environmental regulations and standards need to be considered to ensure that the filtered water quality meets drinking water safety standards. For the maintenance of the oil-water filter, regular cleaning and replacement of filter elements are key to maintaining its normal operation. Depending on the usage, the filter element, membrane element and other components of the filter may need to be replaced regularly to ensure the filtration effect. In addition, regular inspection of various parameters of the filter, such as inlet and outlet water pressure, flow rate, etc., can timely detect and solve potential problems.