What types of water treatment machines are there? Do they work in the same way?
In today's society, water quality issues have become a global focus. Whether in the home, industry or agriculture, the application of water treatment machines has become more and more common. However, facing the wide variety of water treatment machines on the market, many consumers may be confused: What types of water treatment machines are there? Do they work in the same way?
This article will explore these issues in detail to help readers better understand the different types of water treatment machines and their working principles.

What is a water treatment machine?
A water treatment machine is a device specifically used to improve water quality. It removes harmful substances from water through physical, chemical or biological means to make the water quality meet the requirements for use. Water treatment machines are widely used in the fields of household drinking water, industrial water, agricultural irrigation water, etc., and can effectively improve the safety and availability of water.
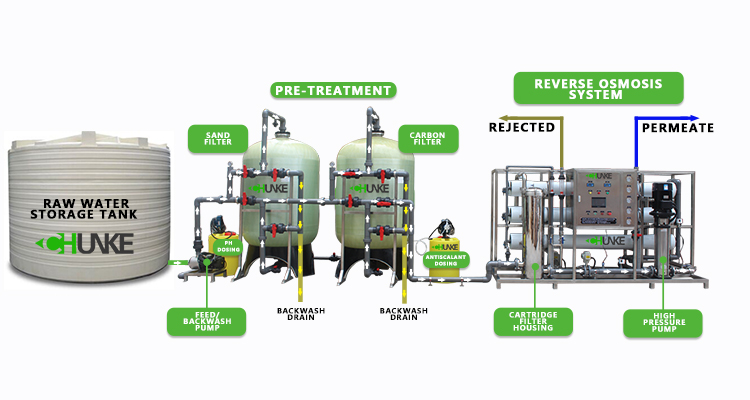
What are the main types of water treatment machines?
According to different uses and working principles, water treatment machines can be divided into many types. Here are some common types of water treatment machines:
Reverse Osmosis Water Treatment Machine
Reverse Osmosis water treatment machines use the high-precision filtration technology of reverse osmosis membranes to remove pollutants such as dissolved solids, bacteria, viruses and heavy metals from water. When water passes through the reverse osmosis membrane, only water molecules are allowed to pass through, while other larger molecules and ions are intercepted to obtain pure water.
RO water treatment machines are widely used in household drinking water, laboratory pure water preparation and industrial production water. Due to its efficient filtration capacity, RO water treatment machines are particularly suitable for occasions that require extremely high water quality.
RO water treatment machines can provide high-purity water, but its filtration process will produce a large amount of wastewater and require high water pressure to push water through the reverse osmosis membrane. In addition, RO water treatment machines also require regular replacement of filter cartridges and reverse osmosis membranes, and the maintenance cost is high.
Ultraviolet (UV) disinfection water treatment machine
Ultraviolet disinfection water treatment machines achieve the purpose of disinfection by emitting ultraviolet rays of a specific wavelength (usually 254 nanometers) to destroy the DNA or RNA structure of microorganisms in the water, causing them to lose their reproductive ability. This treatment method does not add chemical agents and can effectively kill bacteria, viruses and other pathogens in the water.
UV disinfection water treatment machine is widely used in places that require efficient disinfection, such as household drinking water, swimming pools, and the pharmaceutical industry. It is usually used as an auxiliary disinfection method in conjunction with other water treatment equipment.
The advantages of ultraviolet disinfection are easy operation and no harmful byproducts, but its effect depends on the transparency of the water. Excessive suspended matter in the water may affect the penetration of ultraviolet rays. In addition, UV lamps need to be replaced regularly and the equipment needs to be kept clean to ensure the disinfection effect.
Activated carbon water treatment machine
Activated carbon water treatment machine uses the powerful adsorption capacity of activated carbon to remove organic pollutants, odors, chlorine and some heavy metals in water. Activated carbon captures and adsorbs pollutants through the microporous structure on its surface to improve the taste and smell of water.
Activated carbon water treatment machines are usually used in household water purifiers, and can also be used as pretreatment equipment for industrial water treatment systems to remove residual chlorine and organic matter in water.
Activated carbon water treatment machines are low-cost and do not require electricity to drive, but their main function is to adsorb pollutants, and the removal effect of microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses is limited. In addition, activated carbon needs to be replaced after adsorption saturation, otherwise it may become a source of pollution.
Water softener
The water softener replaces calcium and magnesium ions in water with sodium ions through ion exchange resin, thereby reducing the hardness of water. Calcium and magnesium ions in hard water are easy to form scale. The use of water softeners can effectively prevent the formation of scale and protect pipes and equipment.
Water softeners are widely used in household water heaters, boilers, dishwashers and other equipment that need to prevent scale, and can also be used for softening industrial water.
Water softeners can effectively extend the service life of equipment, but the softened water has a high sodium content, and long-term drinking may be harmful to health. In addition, the water softener needs to be regularly replenished with salt to maintain the regeneration ability of the resin.
Ultrafiltration (UF) water treatment machine
Ultrafiltration water treatment machine uses ultrafiltration membrane as the filtration medium, and uses pressure to trap suspended matter, bacteria, viruses, colloids, etc. in water on the membrane surface to achieve the purpose of purifying water quality. The pore size of ultrafiltration membrane is generally between 0.01 microns and 0.1 microns, which can effectively filter most microorganisms and impurities.
Ultrafiltration water treatment machines are mostly used for household water purifiers and drinking water purification, and can also be used in the pretreatment of industrial water and wastewater treatment.
Ultrafiltration water treatment machines can effectively retain minerals in water, but the removal effect of dissolved pollutants (such as salts and chemical pollutants) is limited. Compared with RO systems, the ultrafiltration process produces less wastewater, but the ultrafiltration membrane still needs to be cleaned and maintained regularly.
Electrolysis water treatment machine
The electrolysis water treatment machine separates the ions in water into acidic water and alkaline water through the electrolysis process. Alkaline water is considered to have better drinking value, while acidic water can be used for disinfection, cleaning and other purposes. This equipment is usually used in conjunction with other filtration systems to ensure that the water quality before electrolysis is pure enough.
Electrolysis water treatment machines are mainly used for household drinking water preparation, especially being promoted by some people as a healthy drinking water choice. In addition, electrolyzed water can also be used in certain specific medical and cosmetic applications.
Electrolysis water treatment machines can provide water with different pH values and adapt to a variety of uses, but their effectiveness is controversial in the scientific community and the equipment cost is relatively high. In addition, the effect of electrolyzed water depends on the quality of the raw water. If the water contains too many impurities, the electrolysis effect may be affected.

Are the working modes of water treatment machines consistent?
As can be seen from the previous introduction, different types of water treatment machines have significant differences in working modes. The following is a summary of the working modes of various water treatment machines:
Physical filtration mode
● Representative equipment: reverse osmosis water treatment machine, ultrafiltration water treatment machine
● Working mode: Impurities in water are intercepted through physical barriers (such as membrane filtration) to achieve purification purposes. This type of equipment mainly relies on water pressure to push water through the filter medium to remove particulate matter, bacteria, viruses, etc. in the water.
Chemical adsorption mode
● Representative equipment: activated carbon water treatment machine
● Working mode: Using the principle of chemical adsorption, organic pollutants and odor molecules in water are captured through adsorbents (such as activated carbon). This mode does not rely on water pressure, but the adsorbent needs to be replaced after a period of use.
Ion exchange mode
● Representative equipment: water softener
● Working mode: Calcium and magnesium ions in water are replaced with sodium ions through ion exchange resins to soften the water. This mode relies on chemical reactions and requires regular regeneration of the resin to maintain the effectiveness of the equipment.
Electrolysis mode
● Representative equipment: electrolysis water treatment machine
● Working mode: Using the principle of electrolysis, the ions in the water are separated by electric current to generate water with different pH values. This mode relies on electric drive and requires pretreatment of the water before electrolysis.
Photochemical mode
● Representative equipment: UV disinfection water treatment machine
● Working mode: The purpose of disinfection is achieved by emitting ultraviolet rays to destroy the DNA or RNA structure of microorganisms in the water. This mode does not rely on water pressure, but on light intensity and water transparency.





