How to purify water without using reverse osmosis filters?
Water is an essential resource for human survival, but with the intensification of environmental pollution, the types and concentrations of pollutants in water sources are also increasing. Reverse osmosis (RO) technology, as an efficient means of water purification, has been widely used in drinking water and industrial water treatment. However, reverse osmosis is not the only way to purify water.
In many cases, based on different needs, the use of other types of filters can also achieve effective water purification. This article will explore the feasible solutions for water purification without reverse osmosis technology and the various filtration technologies it relies on.

What are the common non-reverse osmosis water filtration technologies?
1. Activated carbon filtration:
Activated carbon filtration is one of the most widely used non-reverse osmosis water treatment technologies, especially in household water dispensers and filter jugs. Activated carbon has a strong adsorption capacity and can remove organic matter, residual chlorine, odor and some heavy metals in water. The core of the activated carbon filter lies in the microporous structure of the activated carbon, which provides a large surface area, so that dissolved chemicals and particulate matter in the water can be effectively captured.
The purification process of activated carbon filtration includes two stages: adsorption and catalytic reduction. First, when water flows through the activated carbon filter, organic matter, residual chlorine and other pollutants are adsorbed on the surface of the activated carbon. Subsequently, the activated carbon can also convert some harmful substances (such as chlorine) into harmless substances through a catalytic reduction process. Although activated carbon filtration cannot completely remove all dissolved solids or bacteria in water, it performs well in improving the taste of water, removing odors and reducing organic pollutants.
2. Mechanical filtration:
Mechanical filtration is the most basic water purification method, which is usually used to remove large particles such as suspended particles, silt, rust and other impurities in water. Mechanical filters generally use filter screens or filter elements of different precisions to physically intercept impurities in the water. The filtration accuracy of this type of filter can be adjusted according to needs, and the common filtration accuracy ranges from 1 micron to tens of microns.
Mechanical filters are usually divided into many types, including sand filters, fiber filter elements, ceramic filter elements, etc. Sand filters are usually used to treat large water sources, such as swimming pool water or large industrial water. Ceramic filter elements are mostly used for household drinking water filtration. It can not only remove particulate impurities, but also effectively block some bacteria.
3. UV disinfection:
UV disinfection technology does not rely on physical filtration, but uses the high energy of ultraviolet rays to destroy the DNA structure of microorganisms in the water to achieve the effect of sterilization and disinfection. UV filters are usually used to remove bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms in water without affecting the mineral content in the water.
UV disinfection systems are usually installed in the final stage of water treatment because they have high requirements for turbidity and transparency of water quality. Particles in the water may shield ultraviolet rays, thereby affecting the disinfection effect. Therefore, water usually needs to undergo mechanical filtration and other pretreatment steps before using UV disinfection.
4. Ion exchange:
Ion exchange technology is often used to soften hard water. It reduces the hardness of water by exchanging calcium and magnesium ions in water, thereby preventing scaling of pipes and equipment. Ion exchange resin is a material that can undergo ion exchange reactions. It adsorbs calcium and magnesium ions in water and releases an equal amount of sodium ions.
Although ion exchange technology is very effective in reducing water hardness, it cannot remove organic pollutants, bacteria or dissolved solids in water. Therefore, ion exchange is usually used as a link in the water treatment system in combination with other filtration technologies.
5. Ultrafiltration technology:
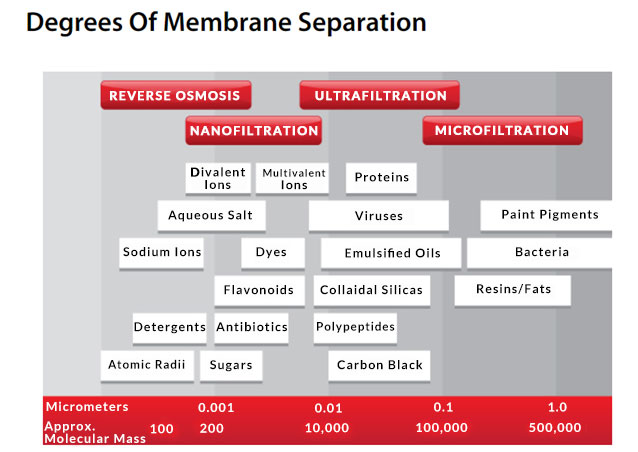
Ultrafiltration is a pressure-driven membrane separation technology that lies between reverse osmosis and microfiltration. The pore size of the ultrafiltration membrane is usually 0.01 to 0.1 microns, which can remove suspended particles, bacteria, viruses and some organic matter in water. Unlike reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration does not remove dissolved minerals in water, so the treated water usually has a better taste.
Ultrafiltration systems are commonly used for the treatment of household drinking water, beverage production and pharmaceutical water. Its advantages are low energy consumption, high treatment efficiency and long membrane life. Although ultrafiltration cannot remove all pollutants like reverse osmosis, in most cases, it is sufficient to meet daily water needs.
6. Distillation:
Distillation is an ancient and effective water purification method that uses the evaporation and condensation process of water to separate impurities from water. During the distillation process, water is heated to boiling, the water vapor rises and condenses into pure water, and the salts, minerals and most organic matter in the raw water remain in the heater.
Distillation can effectively remove most pollutants in water, including bacteria, viruses, heavy metals and dissolved solids. However, due to the time-consuming and high energy consumption of the distillation process, it is more suitable for use in laboratories, medical institutions or emergency situations, rather than large-scale daily water treatment.

How to choose a non-reverse osmosis filter?
Although reverse osmosis systems are highly regarded for their high-efficiency filtration capabilities, not all water treatment needs must rely on reverse osmosis technology. According to the water quality characteristics of the water source, treatment requirements, and economic considerations, choosing a suitable non-reverse osmosis filter is also an effective water treatment solution.
In terms of household drinking water treatment, if the hardness of tap water is moderate and there is no excessive dissolved solids or heavy metal pollution, activated carbon filters and ultrafiltration equipment are sufficient to meet daily needs. Such filters can not only improve the taste of water, but also remove residual chlorine, odor, and most harmful substances. If the household water contains a high hardness, you can also consider adding an ion exchange device to reduce the formation of scale.
For industrial water, especially water that needs to be softened, ion exchangers are indispensable equipment. If there are many impurities in the water, mechanical filtration and ultrafiltration devices are also essential. In addition, in order to prevent the influence of microorganisms on products or production equipment, ultraviolet disinfection systems are also commonly used in industrial water treatment.
Portable activated carbon filters and ultraviolet sterilizers are commonly used equipment in outdoor expeditions or emergencies. Portable activated carbon filters are small and lightweight, suitable for outdoor use, while ultraviolet sterilizers can quickly and efficiently treat microorganisms in water to make the water reach drinking standards.
What are the advantages and limitations of non-reverse osmosis filters?
Although non-reverse osmosis filters perform well in water treatment, they are not superior to reverse osmosis systems in all cases. Therefore, understanding the advantages and limitations of these filtration technologies is crucial to the correct selection and use of water treatment equipment.
1. Advantages:
● Low energy consumption: Most non-reverse osmosis filters (such as activated carbon filters and mechanical filters) have low energy consumption and relatively small operating costs, making them suitable for long-term use.
● Fast processing speed: Non-reverse osmosis filters usually have a fast processing speed, especially when high-precision filtration is not required, and can quickly meet large water needs.
● Simple maintenance: Most non-reverse osmosis filters have a simple structure and are relatively easy to maintain. Users only need to replace the filter element or clean the equipment regularly.
2. Limitations:
● Unable to remove dissolved solids: Non-reverse osmosis filters have difficulty removing dissolved salts, heavy metals and certain organic pollutants in water, and the treatment effect is limited.
● High water quality requirements: Some technologies (such as ultraviolet disinfection and ultrafiltration) have high requirements for influent water quality. If the water quality is too poor, the filtration effect may be affected.
● Multi-stage treatment requirements: In order to achieve the ideal water quality standards, non-reverse osmosis filters usually require multi-stage combined action, which increases the complexity and cost of the system.